| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-05 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-05 |
|
|
View PDF |
A function is a subprogram that returns a single value. You must declare and define a function before invoking it. You can either declare and define it at the same time, or you can declare it first and then define it later in the same block, subprogram, or package. A function invocation, or function call, is an expression.
A function declaration is also called a function specification, or function spec.
Note:
This topic applies to functions that you declare and define inside a PL/SQL block, subprogram, or package. These functions differ from standalone stored functions that you create with the "CREATE FUNCTION Statement", as explained in "Overview of PL/SQL Subprograms".
A function declared and defined in a package is affected by the AUTHID clause of the package. For more information, see "CREATE PACKAGE Statement".
Topics:
Syntax
function_declaration ::=
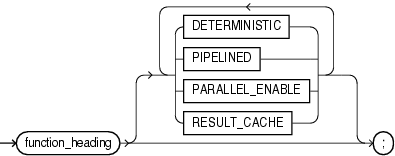
function_heading ::=
See:
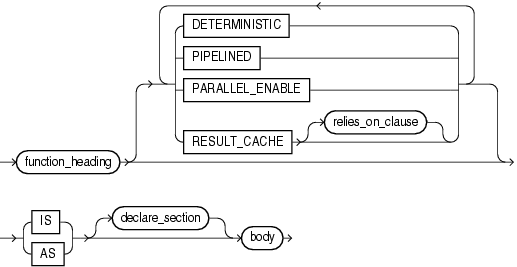
function_definition ::=
See:
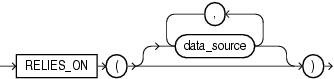
relies_on_clause ::=
Semantics
function_declaration
Declares a function, but does not define it. The definition must appear later in the same block, subprogram, or package as the declaration.
DETERMINISTIC
Specify DETERMINISTIC to indicate that the function returns the same result value whenever it is invoked with the same values for its parameters. This helps the optimizer avoid redundant function calls: If a stored function was invoked previously with the same arguments, the optimizer can elect to use the previous result.
Do not specify DETERMINISTIC for a function whose result depends on the state of session variables or schema objects, because results might vary across calls. Instead, consider making the function result-cached (see "Making Result-Cached Functions Handle Session-Specific Settings" and "Making Result-Cached Functions Handle Session-Specific Application Contexts").
Only DETERMINISTIC functions can be invoked from a function-based index or a materialized view that has query-rewrite enabled. For more information and possible limitations of the DETERMINISTIC option, see "CREATE FUNCTION Statement".
See Also:
CREATE INDEX statement in Oracle Database SQL Language Reference
PIPELINED
PIPELINED specifies to return the results of a table function iteratively. A table function returns a collection type (a nested table or varray) with elements that are SQL data types. You can query table functions using the TABLE keyword before the function name in the FROM clause of a SQL query. For more information, see "Performing Multiple Transformations with Pipelined Table Functions".
PARALLEL_ENABLE
Enables the function to be used safely in slave sessions of parallel DML evaluations.
RESULT_CACHE
Causes the results of the function to be cached. For more information, see "PL/SQL Function Result Cache".
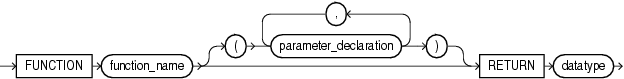
function_heading
function_name
The name that you give to the function that you are declaring or defining.
RETURN datatype
For datatype, specify the data type of the return value of the function. The return value can have any data type supported by PL/SQL.
Restriction on datatype You cannot constrain this data type (with NOT NULL, for example).
function_definition
Either defines a function that was declared earlier or both declares and defines a function.
declare_section
The optional declarative part of the function. Declarations are local to the function, can be referenced in body, and cease to exist when the function completes execution.
body
The required executable part of the function and, optionally, the exception-handling part of the function.
At least one execution path must lead to a RETURN statement in the executable part of the function; otherwise, a run-time error occurs.
relies_on_clause
Specifies the data sources on which the results of the function depend. Each data_source is the name of either a database table or view.
Note:
This clause is deprecated. As of Release 11.2, the database detects all data sources that are queried while a result-cached function is running, and relies_on_clause does nothing.
You cannot use relies_on_clause in a function declared in an anonymous block.
Examples
Related Topics
In this chapter:
In other chapters:
See Also:
Oracle Database Advanced Application Developer's Guide for information about restrictions on user-defined functions that are called from SQL statements and expressions