| Oracle® Database Security Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10574-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Security Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10574-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter contains:
See Also:
"Guidelines for Auditing" for general guidelines to follow for auditing your systemThis section contains:
See Also:
Oracle Audit Vault Administrator's Guide for information about Oracle Audit Vault, which provides advanced auditing featuresAuditing is the monitoring and recording of selected user database actions, from both database users and nondatabase usersFoot 1 . You can base auditing on individual actions, such as the type of SQL statement executed, or on combinations of data that can include the user name, application, time, and so on. You can audit both successful and failed activities. To use auditing, you enable it, and then configure what must be audited. The actions that you audit are recorded in either data dictionary tables or in operating system files.
Oracle recommends that you enable and configure auditing. Auditing is an effective method of enforcing strong internal controls so that your site can meet its regulatory compliance requirements, as defined in the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. This enables you to monitor business operations, and find any activities that may deviate from company policy. Doing so translates into tightly controlled access to your database and the application software, ensuring that patches are applied on schedule and preventing ad hoc changes. By enabling auditing by default, you can generate an audit record for audit and compliance personnel. Be selective with auditing and ensure that it meets your business compliance needs.
You typically use auditing to perform the following activities:
Enable accountability for actions. These include actions taken in a particular schema, table, or row, or affecting specific content.
Deter users (or others, such as intruders) from inappropriate actions based on their accountability.
Investigate suspicious activity. For example, if a user is deleting data from tables, then a security administrator might decide to audit all connections to the database and all successful and unsuccessful deletions of rows from all tables in the database.
Notify an auditor of the actions of an unauthorized user. For example, an unauthorized user could be changing or deleting data, or the user has more privileges than expected, which can lead to reassessing user authorizations.
Monitor and gather data about specific database activities. For example, the database administrator can gather statistics about which tables are being updated, how many logical I/Os are performed, or how many concurrent users connect at peak times.
Detect problems with an authorization or access control implementation. For example, you can create audit policies that you expect will never generate an audit record because the data is protected in other ways. However, if these policies generate audit records, then you will know the other security controls are not properly implemented.
Address auditing requirements for compliance. Regulations such as the following have common auditing-related requirements:
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards: a Revised Framework (Basel II)
Japan Privacy Law
European Union Directive on Privacy and Electronic Communications
When auditing for suspicious database activity, you should protect the integrity of the audit trail records to guarantee the accuracy and completeness of the auditing information.
Oracle Database writes the database audit trail to the SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables. Audit records generated as a result of object audit options set for the SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables can only be deleted from the audit trail by someone who has connected with administrator privileges. Remember that administrators are also audited for unauthorized use. See "Auditing SYS Administrative Users" for more information.
Other ways to protect the database audit trail are as follows:
Set the O7_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBILITY initialization parameter to FALSE (the default). This way, only users who have the SYSDBA privilege can perform DML actions on the audit data in the SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables. In a default installation, O7_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBILITY is set to FALSE.
If you have Oracle Database Vault installed, create a realm around the SYSTEM.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables. In an Oracle Database Vault environment, when Oracle Label Security is enabled, the AUD$ table is moved to the SYSTEM schema. The synonym SYS.AUD$ is created to refer to the SYSTEM.AUD$ table. See Oracle Database Vault Administrator's Guide for more information about realms in Oracle Database Vault.
When standard auditing is enabled (that is, you set AUDIT_TRAIL to DB or DB,EXTENDED), Oracle Database audits all data manipulation language (DML) operations, such as INSERT, UPDATE, MERGE, and DELETE on the SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables by non-SYS users. (It performs this audit even if you have not set audit options for the AUD$ and FGA_LOGS$ tables.) Typically, non-SYS users do not have access to these tables, except if they have been explicitly granted access. If a non-SYS user tampers with the data in the SYS.FGA_LOG$ and SYS.AUD$ tables, then Oracle Database writes an audit record for each action.
Oracle Database always audits certain database-related operations and writes them to the operating system audit files. It includes the actions of any user who is logged in with the SYSDBA or SYSOPER privilege. This is called mandatory auditing. Even if you have enabled the database audit trail (that is, setting the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter to DB), Oracle Database still writes mandatory records to operating system files.
By default, the operating system files are in the $ORACLE_HOME/admin/$ORACLE_SID/adump directory on UNIX systems. On Windows systems, Oracle Database writes this information to the Windows Event Viewer. You can change the location of this directory by setting the AUDIT_FILE_DEST initialization parameter, which is described in "Specifying a Directory for the Operating System Audit Trail".
Mandatory auditing includes the following operations:
Database startup. An audit record is generated that lists the operating system user starting the instance, the user terminal identifier, and the date and time stamp. This data is stored in the operating system audit trail because the database audit trail is not available until after the startup has successfully completed.
SYSDBA and SYSOPER logins. Oracle Database records all SYSDBA and SYSOPER connections.
Database shutdown. An audit record is generated that lists the operating system user shutting down the instance, the user terminal identifier, and the date and time stamp.
Note:
If you set theAUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL initialization parameter, mandatory actions are written the to the UNIX syslog. See "Using the Syslog Audit Trail on UNIX Systems" for more information about the syslog audit trail. See also your operating system-specific Oracle Database documentation for more information about the operating system and syslog audit trail.Auditing is site autonomous. An instance audits only the statements issued by directly connected users. A local Oracle Database node cannot audit actions that take place in a remote database.
Follow these best practices guidelines:
As a general rule, design your auditing strategy to collect the amount of information that you need to meet compliance requirements, but being sure to focus on activities that cause the greatest security concerns. For example, auditing every table in the database is not practical, but auditing table columns that contain sensitive data, such as salaries, is. With both standard and fine-grained auditing, there are mechanisms you can use to design audit policies that focus on specific activities to audit.
Periodically archive and purge the audit trail data. See "Purging Audit Trail Records" for more information.
See Also:
"Guidelines for Auditing" for general guidelines to follow for auditing your systemTable 9-1 provides a roadmap for selecting and using the different audit options available.
Table 9-1 Selecting an Auditing Type
| What Do You Want to Audit? | About This Type of Auditing |
|---|---|
|
General activities |
You can audit SQL statements, privileges, schema objects, functions, procedures, packages, triggers, and network activity. For example, you can audit each time a particular user performs an Location of audit records: Oracle Database writes these audit records to the location based on the General steps:
|
|
Default, security-relevant SQL statements and privileges |
Oracle Database provides a set of default audit settings that you can enable for commonly used security-relevant SQL statements and privileges. Location of audit records: Oracle Database writes these audit records to the location based on the General steps:
|
|
Specific, fine-grained activities |
You can audit at the most granular level, data access, and actions based on content, using Boolean measures, such as Location of audit records: You can write the audit records to either the database audit trail or an operating system audit trail in XML format. See also "About Audit Records". General steps:
|
|
|
You can audit the top-level SQL statements issued by users who have connected using the Location of audit records: Oracle Database writes these audit records to an operating system audit trail only. On Windows, Oracle Database writes the General steps:
|
This section contains:
Configuring Standard Auditing with the AUDIT_TRAIL Initialization Parameter
What Do the Operating System and Database Audit Trails Have in Common?
Auditing SQL Statements and Privileges in a Multitier Environment
See Also:
"Auditing SYS Administrative Users" to learn how to use standard auditing to audit SYS users
Oracle Database 2 Day + Security Guide for a tutorial on creating a standard audit trail
This section contains:
In standard auditing, you audit SQL statements, privileges, schema objects, and network activity. You configure standard auditing by using the AUDIT SQL statement and NOAUDIT to remove this configuration. You can write the audit records to either the database audit trail or to operating system audit files.
Any user can configure auditing for the objects in his or her own schema, by using the AUDIT statement. To undo the audit configuration for this object, the user can use the NOAUDIT statement. No additional privileges are needed to perform this task. Users can run AUDIT statements to set auditing options regardless of the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter setting. If auditing has been disabled, the next time it is enabled, Oracle Database will record the auditing activities set by the AUDIT statements. "Enabling or Disabling the Standard Audit Trail" explains how to enable standard auditing.
Note the following:
To audit objects in another schema, the user must have the AUDIT ANY system privilege.
To audit system privileges, the user must have the AUDIT SYSTEM privilege.
If the O7_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBILITY initialization parameter has been set to FALSE (the default), then only users who have the SYSDBA privilege can perform DML actions on the audit data in the SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables. For greater security, set the O7_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBILITY parameter to FALSE so that non-SYSDBA users cannot audit SYS objects.
You, as the security administrator, enable or disable standard auditing for the entire database. If it is disabled, then no audit records are created. Configuring audit options is described in the previous section, "Who Can Perform Standard Auditing?"
When auditing is enabled in the database and an action configured to be audited occurs, Oracle Database generates an audit record during or after the execution phase of the SQL statement. Oracle Database individually audits SQL statements inside PL/SQL program units, as necessary, when the program unit is run.
The generation and insertion of an audit trail record is independent of a user transaction being committed. That is, even if a user transaction is rolled back, the audit trail record remains committed.
Statement and privilege audit options in effect at the time a database user connects to the database remain in effect for the duration of the session. When the session is already active, setting or changing statement or privilege audit options does not take effect in that session. The modified statement or privilege audit options take effect only when the current session ends and a new session is created.
In contrast, changes to schema object audit options become immediately effective for current sessions.
See Also:
Oracle Database Concepts for information about the different phases of SQL statement processing and shared SQLThis section contains:
You enable the standard audit trail by setting the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter. This setting determines whether to create the audit trail in the database audit trail, write the audit activities to an operating system file, or to disable auditing.
To enable or disable the standard audit trail, log in to SQL*Plus with administrative privileges, and use the ALTER SYSTEM statement. Afterwards, you need to restart the database instance.
To check the current value of the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter, use the SHOW PARAMETER command in SQL*Plus.
Example 9-1 shows how to check the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter setting.
Example 9-1 Checking the Current Value of the AUDIT_TRAIL Initialization Parameter
SHOW PARAMETER AUDIT_TRAIL NAME TYPE VALUE ------------------------------------ ----------- ------- audit_trail string DB
Example 9-2 shows how to log onto SQL*Plus, enable the standard audit trail, and then restart the database instance.
Example 9-2 Enabling the Standard Audit Trail
CONNECT SYSTEM Enter password: password ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL=DB SCOPE=SPFILE; System altered. CONNECT SYS/AS SYSOPER Enter password: password SHUTDOWN Database closed. Database dismounted. ORACLE instance shut down. STARTUP ORACLE instance started.
This example uses the SCOPE clause because the database instance had been started using a server parameter file (SPFILE). Starting the database with a server parameter file is the preferred way of starting a database instance. See Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information about creating configuring server parameter files.
Table 9-2 lists the settings you can use for the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter.
Table 9-2 AUDIT_TRAIL Initialization Parameter Settings
| AUDIT_TRAIL Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Directs audit records to the database audit trail (the If the database was started in read-only mode with See also "Managing the Database Audit Trail". |
|
Behaves the same as
If the database was started in read-only mode with You can specify ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL=DB, EXTENDED SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL='DB','EXTENDED' SCOPE=SPFILE; However, do not enclose ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL='DB, EXTENDED' SCOPE=SPFILE; |
|
|
|
Directs all audit records to an operating system file. Oracle recommends that you use the If you set
|
|
Writes to the operating system audit record file in XML format. Records all elements of the See also "Advantages of the Operating System Audit Trail" and Example 9-4, "XML File Operating System Audit Trail". If you set the In addition to XML files, Oracle Database creates a text index file that lists the XML files that were generated by the XML auditing. The file is named The You can control the output for
|
|
|
Behaves the same as You can specify ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL=XML, EXTENDED SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL='XML','EXTENDED' SCOPE=SPFILE; However, do not enclose ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL='XML, EXTENDED' SCOPE=SPFILE; See also the following sections: |
|
|
|
Note the following:
You do not need to restart the database after you run the AUDIT or NOAUDIT statements. You only need to restart the database if you made a universal change, such as changing the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter.
You do not need to set AUDIT_TRAIL to enable either fine-grained auditing or SYS auditing. For fine-grained auditing, you add and remove fine-grained audit policies as necessary, applying them to the specific operations or objects you want to monitor. To enable SYS auditing, set the AUDIT_SYS_OPERATIONS parameter to TRUE.
The operating system and database audit trails both capture many of the same types of actions. Table 9-3 lists the operating system audit trail records. Most map to equivalent columns in the DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL view. For a description of these columns, see Oracle Database Reference.
Table 9-3 Common Audited Actions in the Operating System and Database Audit Trails
| Operating System Audit Record | Equivalent DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL View Column |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indicates what audit option was set with |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Does not have an equivalent in the |
|
|
Does not have an equivalent in the |
Footnote 1 For example, if the ACTION value is 104 (for AUDIT) or 105 (for NOAUDIT), then the SYS$OPTIONS number represents an audit option listed in the STMT_AUDIT_OPTION_MAP table. If the ACTION value is 108 (for GRANT) or 109 (for REVOKE), then the number represents a privilege listed in the SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_MAP table.
This section contains:
As an alternative to creating standard audit records in the DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL (SYS.AUD$ table), you can create standard audit records in operating system files. The operating system file that contains the audit trail can include any of the following data:
Database audit trail records
Mandatory audit records (that is, database actions that are always audited)
Audit records for administrative users (SYS)
You can write the operating system audit records to either a text file or an XML file.
The operating system audit trail files are in either text or XML file format. Be aware that the contents of the text and XML operating system files have some differences, and that the formats may change across different releases. With each release of Oracle Database, new enhancements, such as the audit type, have been made to the XML file, but not the text file. The text operating system file has a different presentation for the timestamp, for example:
Wed May 6 00:57:36 2009 -07:00
However, this timestamp does not appear in the event log or syslog, which have their own format for timestamps. The timestamp string only appears in the text operating system audit files.
Example 9-3 shows a typical text operating system audit trail for a logon operation on an Oracle database that is installed on Microsoft Windows. (The text in the actual record wraps around, but for this manual, each item is separated onto its own line for easier readability.)
Example 9-3 Text File Operating System Audit Trail
Audit trail: LENGTH: "349" SESSIONID:[5] "43464" ENTRYID:[1] "1" STATEMENT:[1] "1" USERID:[6] "DBSNMP" USERHOST:[7] "SHOBEEN" TERMINAL:[3] "MAU" ACTION:[3] "100" RETURNCODE:[1] "0" COMMENT$TEXT:[97] "Authenticated by: DATABASE; Client address: (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=192.0.2.4)(PORT=2955))" OS$USERID:[19] "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" DBID:[10] "1212547373" PRIV$USED:[1] "5"
In this example:
LENGTH refers to the total number of bytes used in this audit record. This number includes the trailing newline bytes (\n), if any, at the end of the audit record.
[] brackets indicate the length of each value for each audit entry. For example, the USERID entry, DBSNMP, is 6 bytes long.
SESSIONID indicates the audit session ID number. You can also find the session ID by querying the AUDSID column in the V$SESSION data dictionary view.
ENTRYID indicates the current audit entry number, assigned to each audit trail record. The audit ENTRYID sequence number is shared between fine-grained audit records and regular audit records.
STATEMENT is a numeric ID assigned to the statement the user runs. It appears for each statement issued during the user session, because a statement can result in multiple audit records.
ACTION is a numeric value representing the action the user performed. The corresponding name of the action type is in the AUDIT_ACTIONS table. For example, action 100 refers to LOGON.
RETURNCODE indicates if the audited action was successful. 0 indicates success. If the action fails, the return code lists the Oracle Database error number. For example, if you try to drop a non-existent table, the error number is ORA-00903 invalid table name, which in turn translates to 903 in the RETURNCODE setting.
COMMENT$TEXT indicates additional comments about the audit record. For example, for LOGON audit records, it can indicate the authentication method.It corresponds to the COMENT_TEXT column of the DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
DBID is a database identifier calculated when the database is created. It corresponds to the DBID column of the V$DATABASE data dictionary view.
ECONTEXT_ID indicates the application execution context identifier.
PRIVS$USED refers to the privilege that was used to perform an action. To find the privilege, query the SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_MAP table. For example, privilege 5 refers to -5 in this table, which means CREATE SESSION. PRIVS$USED corresponds to the PRIV_USED column in the DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL, which lists the privilege by name.
Other possible values are as follows:
SCN (for example, SCN:8934328925) indicates the System Change Number (SCN). Use this value if you want to perform a flashback query to find the value of a setting (for example, a column) at a time in the past. For example, to find the value of the ORDER_TOTAL column of the OE.ORDERS table based on the SCN number, use the following SELECT statement:
SELECT ORDER_TOTAL FROM OE.ORDERS AS OF SCN = 8934328925 WHERE ORDER_TOTAL = 86;
SES_ACTIONS indicates the actions that took place during the session. This field is present only if the event was audited with the BY SESSION clause. Because this field does not explain in detail the actions that occurred during the session, you should configure the audit event with the BY ACCESS clause.
The SES_ACTIONS field contains 16 characters. Positions 14, 15, and 16 are reserved for future use. In the first 12 characters, each position indicates the result of an action. They are: ALTER, AUDIT, COMMENT, DELETE, GRANT, INDEX, INSERT, LOCK, RENAME, SELECT, UPDATE, and FLASHBACK. For example, if the user had successfully run the ALTER statement, the SES_ACTIONS setting is as follows:
S---------------
The S, in the first position (for ALTER), indicates success. Had the ALTER statement failed, the letter F would have appeared in its place. If the action resulted in both a success and failure, then the letter is B.
SES$TID indicates the ID of the object affected by the audited action.
SPARE2 indicates whether the user modified SYS.AUD$ table. 0 means the user modified SYS.AUD$; otherwise, the value is NULL.
Similarly, Example 9-4 shows how an XML audit trail record appears. The text wraps around in the actual record, but for this manual, each element appears on its own line for easier readability. To find all the tags that appear in the XML audit file, you can view its schema in a Web browser at
http://www.oracle.com/technology/oracleas/schema/dbserver_audittrail-11_2.xsd
Example 9-4 XML File Operating System Audit Trail
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Audit xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/oracleas/schema/dbserver_audittrail-11_2.xsd"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.oracle.com/oracleas/schema/dbserver_audittrail-11_2.xsd">
<Version>11.2</Version>
<AuditRecord>
<Audit_Type>1</Audit_Type>
<Session_Id>43535</Session_Id>
<StatementId>1</StatementId>
<EntryId>1</EntryId>
<Extended_Timestamp>2009-04-29T18:32:26.062000Z</Extended_Timestamp>
<DB_User>SYSMAN</DB_User>
<OS_User>SYSTEM</OS_User>
<Userhost>shobeen</Userhost>
<OS_Process>3164:3648</OS_Process>
<Terminal>mau</Terminal>
<Instance_Number>0</Instance_Number>
<Action>100</Action>
<TransactionId>0000000000000000</TransactionId>
<Returncode>0</Returncode>
<Comment_Text>Authenticated by: DATABASE; Client address: (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=192.0.2.4)(PORT=3536))</Comment_Text>
<Priv_Used>5</Priv_Used>
</AuditRecord>
</Audit>
In this example:
AuditRecord element contains the entire audit record. (See Example 9-3 for more information about the elements within the Audit_Record element.)
Audit_Type indicates the type of audit trail. Possible values are as follows:
1: Standard audit record
2: Fine-grained audit record
4: SYS audit record
8: Mandatory audit record
This field only appears in the XML audit files, not the OS text audit files.
Extended_Timestamp indicates the time of the audited operation (timestamp of user login for entries created by AUDIT SESSION) in the time zone of the session, in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) or Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). This field only appears in the XML audit files, not the OS text audit files.
Instance_Number indicates the instance number to which the user is connected, for an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment. In this example, the number is 0, which is used for single-instance database installations. The INSTANCE_NUMBER initialization parameter specifies this number.
The following values can appear if you set the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter to XML, EXTENDED. Both are listed in the DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
Sql_Bind (for example, <Sql_Bind>#1(5):89</Sql_Bind>) shows the value of the bind variable. The syntax is as follows:
VariablePosition(LengthOfVariableValue):ValueofBindVariable
The example #1(5):89 indicates that there is 1 bind variable; its value is 5 characters long; and the value of the bind variable is 89.
Sql_Text (for example, <Sql_Text>begin procedure_one(:num); end; </Sql_Text>) appears if you have set the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter to XML, EXTENDED. It shows the SQL text that the user entered.
Using the operating system audit trail offers these advantages:
It reduces the likelihood of a denial-of-service (DoS) attack.
It makes it easier to secure the audit trail. If the auditor is distinct from the database administrator, then you must use the OS, XML, or XML, EXTENDED setting. Otherwise, a database administrator can view and modify any auditing information that is stored in the database.
Because you are writing the audit trail to a specific location that you can restrict to specific users, the operating system audit trail enforces separation of duty concepts.
Writing the audit trail to an operating system file results in the least amount of overhead on the database. For this reason, it is excellent for very large databases.
Audit records stored in operating system files can be more secure than database-stored audit records because access can require file permissions that database administrators do not have. Greater availability is another advantage to operating system storage for audit records, because they remain available even if the database is temporarily inaccessible.
If the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter is set to XML (or XML, EXTENDED), then Oracle Database writes audit records to the operating system as XML files. You can use the V$XML_AUDIT_TRAIL view to make XML audit records available to database administrators through a SQL query, providing enhanced usability.
The DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL view includes the standard and fine grained audit trails written to database tables, XML-format audit trail records, and the contents of the V$XML_AUDIT_TRAIL dynamic view (standard, fine grained, SYS and mandatory).
Using your operating system audit trail can enable you to consolidate audit records from multiple sources, including Oracle Database and other applications. Examining system activity can be more efficient with all audit records in one place. If you use XML audit records, then you can use of any standard XML editing tool to review or extract information from those records.
The operating system audit trail writes the audit data to an operating system file. You can enable this feature by setting the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter to one of the following values:
OS: Writes the audit trail records to a text operating system file on UNIX systems and to the applications Event Viewer on Microsoft Windows.
XML: Writes the audit trail records to an XML file.
XML, EXTENDED: Writes the audit trail records to an XML file and includes SQL text and SQL bind information in the operating system XML audit files.
The AUDIT_FILE_DEST initialization parameter sets the location of the operating system audit file. If you want to audit top-level statements issued by users who log in to the database with the SYSDBA or SYSOPER privilege, then set the AUDIT_SYS_OPERATIONS parameter to TRUE. See Table 9-2, "AUDIT_TRAIL Initialization Parameter Settings" for more information about these settings.
The records that are written to an operating system file are not recorded to the SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables. You can still view the contents of the XML operating system audit files by querying the DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary views. Querying this view parses all XML files (all files with an .xml extension) in the AUDIT_FILE_DEST directory, and then presents them in relational table format. Because XML is a standard document format, many utilities are available to parse and analyze XML data. Consult the operating system-specific Oracle Database documentation to find if this feature has been implemented on your operating system.
Use the AUDIT_FILE_DEST initialization parameter to specify an operating system directory into which the audit trail is written, when the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter is set to OS, XML, or XML, EXTENDED. You must set AUDIT_FILE_DEST to a valid directory with permissions restricted to the owner of the Oracle software and the DBA group. Mandatory auditing information also goes into that directory, as do audit records for user SYS if the AUDIT_SYS_OPERATIONS initialization parameter is specified. You can change the AUDIT_FILE_DEST parameter by using the following ALTER SYSTEM statement, which enables the new destination to be effective for all subsequent sessions.
ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_FILE_DEST = directory_path DEFERRED;
To find the current setting of the AUDIT_FILE_DEST parameter, issue the following command:
SHOW PARAMETER AUDIT_FILE_DEST
The location of the operating system files depends on the following:
If the database is not running and you have not set the AUDIT_FILE_DEST parameter, then the operating system files are placed in the first default location $ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/adump directory.
If the database is not running and the first default location, the $ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/adump directory, is inaccessible or cannot be written to, or the Oracle process cannot identify the environment variables, then the second default location, $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/audit is used.
When the database is open and Oracle Database reads the initialization file (initSID.ora) for the database instance, the value of AUDIT_FILE_DEST parameter is used as the operating system audit file directory.
For UNIX and Solaris systems, all operating system files are written to a directory in the operating system. For Windows, the operating system text records are available from the Windows Event Viewer, but operating system XML files are available from an operating system directory, as explained in the preceding bulleted items.
Notes:
For platforms other than UNIX, Solaris, and Windows, check the platform documentation to learn the correct target directory for operating system files.On UNIX systems, you can audit the activities of users, including privileged users, and record these activities in a syslog file by creating a syslog audit trail.
This section contains:
A potential security vulnerability for the operating system audit trail is that a privileged user, such as a database administrator, can modify or delete database audit records. To minimize this risk, you can use a syslog audit trail. Syslog is a standard protocol on UNIX-based systems for logging information from different components of a network. Applications call the syslog() function to log information to the syslog daemon, which then determines where to log the information. You can configure syslog to log information to a file or to a dedicated host by editing the syslog.conf file. You can also configure syslog to alert a specified set of users when information is logged.
Because applications, such as an Oracle process, use the syslog() function to log information to the syslog daemon, a privileged user would not have permissions to the file system where syslog messages are logged. For this reason, audit records stored using a syslog audit trail can be more secure than audit records stored using an operating system audit trail. In addition to restricting permissions to a file system for a privileged user, for a syslog audit trail to be secure, neither privileged users nor the Oracle process should have root access to the system where the audit records are written.
Caution:
You should have a strong understanding of how to work withsyslog before enabling syslog auditing. See the following references for more information about syslog:
Oracle Database Reference for information about the AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL initialization parameter
The UNIX man page for the syslogd utility for more information about the facility.priority settings and their directory paths
Similar to the operating system audit trail records, Oracle Database encodes the syslog records to ensure greater security. If you have Oracle Audit Vault installed, you can use its Syslog Collector to extract and transfer syslog audit records to centralized Oracle Audit Vault server.
Example 9-5 shows how the syslog audit trail can appear. (For this example, the text has been reformatted for easier readability. In reality, the text is all on one line.) As with other Oracle Database audit trails, the brackets indicate the length of the value that was audited. For syslog audit trails, the text from (and including) LENGTH: is Oracle Database audit record. The prepended text (the date and Oracle Audit [10085] line) is added by the syslog utility.
To enable syslog auditing, follow these steps:
Assign the value of OS to the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter, as described in "Enabling or Disabling the Standard Audit Trail".
For example:
ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL=OS SCOPE=SPFILE;
Manually set the AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL parameter to the initialization parameter file, initsid.ora.
Set the AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL parameter to specify a facility and priority in the format AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL=facility.priority.
facility: Describes the part of the operating system that is logging the message. Accepted values are user, local0–local7, syslog, daemon, kern, mail, auth, lpr, news, uucp, and cron.
The local0–local7 values are predefined tags that enable you to sort the syslog message into categories. These categories can be log files or other destinations that the syslog utility can access. To find more information about these types of tags, refer to the syslog utility MAN page.
priority: Defines the severity of the message. Accepted values are notice, info, debug, warning, err, crit, alert, and emerg.
The syslog daemon compares the value assigned to the facility argument of the AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL parameter with the syslog.conf file to determine where to log information.
For example, the following statement identifies the facility as local1 with a priority level of warning:
AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL=local1.warning
See Oracle Database Reference for more information about AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL.
Log in to the computer that contains the syslog configuration file, /etc/syslog.conf, with the superuser (root) privilege.
Add the audit file destination to the syslog configuration file syslog.conf.
For example, assuming you had set the AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL to local1.warning, enter the following:
local1.warning /var/log/audit.log
This setting logs all warning messages to the /var/log/audit.log file.
Restart the syslog logger:
$/etc/rc.d/init.d/syslog restart
Now, all audit records will be captured in the file /var/log/audit.log through the syslog daemon.
Restart the database instance:
CONNECT SYS / AS SYSOPER
Enter password: password
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE
STARTUP
Auditing Statement Executions: Successful, Unsuccessful, or Both
Benefits of Using the BY ACCESS Clause in the AUDIT Statement
To configure the standard auditing option, use the AUDIT SQL statement.
Table 9-4 lists the categories in which you can use the AUDIT statement.
Table 9-4 Standard Auditing Levels and Their Effects
| Level | Effect |
|---|---|
|
Statement |
Audits specific SQL statements or groups of statements that affect a particular type of database object. For example, |
|
Privilege |
Audits SQL statements that are authorized by the specified system privilege. For example, |
|
Object |
Audits specific statements on specific objects, such as |
|
Network |
Audits unexpected errors in network protocol or internal errors in the network layer. |
For statement, privilege, and schema object auditing, Oracle Database permits the selective auditing of successful executions of statements, unsuccessful attempts to execute statements, or both. This enables you to monitor actions even if the audited statements do not complete successfully. Monitoring unsuccessful SQL statement can expose users who are snooping or acting maliciously, though most unsuccessful SQL statements are neither.
This method of auditing is also useful in that it reduces the audit trail, helping you to focus on specific actions. This can aid in maintaining good database performance.
The options are as follows:
WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL clause: This clause audits only successful executions of the audited statement.
WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL clause: This clause audits only unsuccessful executions of the audited statement.
Auditing an unsuccessful statement execution generates an audit report only if a valid SQL statement is issued but fails, because it lacks proper authorization or references a nonexistent schema object. Statements that fail to execute because they were not valid cannot be audited.
For example, an enabled privilege auditing option set to audit unsuccessful statement executions audits statements that use the target system privilege but failed for other reasons. One example is when a CREATE TABLE auditing condition is set, but some CREATE TABLE statements fail due to insufficient quota for the specified tablespace.
Omitting WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL or WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL: If you omit these clauses, then Oracle Database audits both successful and unsuccessful executions of the audited statement.
For example:
AUDIT CREATE TABLE BY ACCESS WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
Oracle Database generates an audit record for each execution of an audited statement or operation, as follows:
Each time the SQL statement for which auditing was configured is executed. This also includes the execution of the statements within PL/SQL procedures.
Each time the privilege for which auditing was configured is used
Each time the object for which auditing was configured is operated upon
For each execution of an auditable operation within a cursor, Oracle Database inserts one audit record into the audit trail. Events that cause cursors to be reused include the following:
An application, such as Oracle Forms, holding a cursor open for reuse
Subsequent execution of a cursor using new bind variables
Statements executed within PL/SQL loops where the PL/SQL engine optimizes the statements to reuse a single cursor
Auditing is not affected by whether or not a cursor is shared. Each user creates her or his own audit trail records on first execution of the cursor.
Oracle recommends that you include the BY ACCESS clause in your AUDIT statements. The benefits of using the BY ACCESS clause in the AUDIT statement are as follows:
The audit records generated through the BY ACCESS audit option have more information, such as execution status (return code), date and time of execution, the privileges used, the objects accessed, the SQL text itself and its bind values. In addition, the BY ACCESS audit option captures the SCN for each execution and this can help flashback queries.
Oracle Database records separately each execution of a PL/SQL statement, the use of a privilege, and access to the audited object. Given that the values for the return code, timestamp, SQL text recorded are accurate for each execution, this can help you find how many times the action was performed.
The BY ACCESS audit records have separate LOGON and LOGOFF entries, each with fine-grained timestamps.
For example:
AUDIT SELECT TABLE BY ACCESS;
In this scenario:
The user jward connects to the database and issues five SELECT statements against the table named departments and then disconnects from the database.
The user swilliams connects to the database and issues three SELECT statements against the departments table and then disconnects from the database.
The audit trail contains eight records, one recorded for each SELECT statement.
Statement and privilege audit options can audit statements issued by any user or statements issued by a specific list of users. By focusing on specific users, you can minimize the number of audit records generated.
Example 9-6 shows how to audit statements by users scott and blake when they query or update a table or view.
Example 9-6 Using AUDIT to Audit User Actions
AUDIT SELECT TABLE, UPDATE TABLE BY ACCESS
BY scott, blake;
See Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for additional information about auditing by user.
The NOAUDIT statement removes the audit option. Use it to reset statement and privilege audit options, and object audit options. A NOAUDIT statement that sets statement and privilege audit options can include the BY user or BY proxy option to specify a list of users to limit the scope of the statement and privilege audit options.
You can use the NOAUDIT statement to disable an audit option selectively using the WHENEVER clause. If the clause is not specified, then the auditing option is disabled entirely, for both successful and unsuccessful cases.
The NOAUDIT statement does not support the BY ACCESS clause. You can remove audit options, no matter how they were turned on, by using an appropriate NOAUDIT statement.
This section contains:
SQL statement auditing is the selective auditing of related groups of SQL statements regarding a particular type of database structure or schema object, but not a specifically named structure or schema object.
The statements that you can audit are in the following categories:
DDL statements. For example, AUDIT TABLE audits all CREATE and DROP TABLE statements
DML statements. For example, AUDIT SELECT TABLE audits all SELECT ... FROM TABLE/VIEW statements, regardless of the table or view
Statement auditing can be broad or focused, for example, by auditing the activities of all database users or of only a select list of activities.
Use the AUDIT statement to configure SQL statement auditing. You must have the AUDIT SYSTEM system privilege before you can enable auditing. Typically, only the security administrator is granted this system privilege.
Example 9-7 shows how to audit the SELECT TABLE SQL statement.
If you plan to audit all SQL statements, individual user connections, or references to non-existent objects, follow these guidelines:
Auditing all SQL statements for individual users. You can use the ALL STATEMENTS clause to audit only the top-level SQL statements. This way, the behavior of this audit option is different from other statement audit options. Hence, if the SQL statement is issued from inside a PL/SQL procedure, the AUDIT ALL STATEMENTS audit option does not audit it. Nor does the AUDIT ALL STATEMENTS statement record parse failures in the SQL statement. In addition, it does not affect any other AUDIT options you may have already set.
For example, to audit all successful statements issued by users jward and jsmith, enter the following:
AUDIT ALL STATEMENTS BY jward, jsmith BY ACCESS WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL;
Auditing all SQL statements for the current session, regardless of user. You can use the IN SESSION CURRENT clause for ALL STATEMENTS audit option to audit top-level SQL statements in the lifetime of the user session You cannot use the IN SESSION CURRENT clause for a specific user. You cannot use the NOAUDIT statement to cancel it, but the auditing lasts only as long as the user session lasts. When the user ends the session, the auditing ends.
For example, to audit all unsuccessful statements in any current user session:
AUDIT ALL STATEMENTS IN SESSION CURRENT BY ACCESS WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
You can use the AUDIT ALL STATEMENTS audit option with the IN SESSION CURRENT clause in a database logon trigger. The database logon trigger can use SYS_CONTEXT function to configure this auditing only under certain conditions, such as the time a user logs in between 6:30 p.m. to 9:00 a.m. This would enable you to capture SQL statements performed by users who log in to the database during non-work hours.
This type of auditing is useful to increase the collection of audit activity when you suspect this connection may not be secure or could pose an internal threat. For example, by using a database logon trigger, you can query contents of the connection context using the SYS_CONTEXT function.
The logon trigger functionality can establish that this connection should be audited more fully. Issue the following SQL command:
AUDIT ALL STATEMENTS IN SESSION CURRENT;
This type of auditing remains in effect until this session is terminated.
Auditing Login and Logoff Connections and Disconnections. The AUDIT SESSION statement generates an independent audit record for every login and logoff event. This enables you to audit all successful and unsuccessful connections to and disconnections from the database, regardless of user.
For example:
AUDIT SESSION BY ACCESS;
You can set this option selectively for individual users also, as in the following example:
AUDIT SESSION BY ACCESS BY jward, jsmith;
Auditing Statements That Fail Because an Object Does Not Exist. The NOT EXISTS option of the AUDIT statement specifies auditing of all SQL statements that fail because the target object does not exist.
For example:
AUDIT NOT EXISTS;
See Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for detailed information about the AUDIT SQL statement.
To remove SQL statement auditing, use the use the NOAUDIT SQL statement. (Privilege auditing will still be enabled.) You must have the AUDIT SYSTEM system privilege before you can remove SQL statement auditing. If you have configured the AUDIT ALL STATEMENTS option, then issuing the NOAUDIT AUDIT STATEMENTS statement does not affect other audit options you may have set. If you included the IN SESSION CURRENT clause in the AUDIT statement, you cannot remove this AUDIT statement using the NOAUDIT statement. (The audit setting discontinues when the user's session ends.)
Example 9-8 shows examples of using the NOAUDIT statement to remove auditing.
Example 9-8 Using NOAUDIT to Remove Session and SQL Statement Auditing
NOAUDIT session; NOAUDIT session BY preston, sebastian; NOAUDIT DELETE ANY TABLE; NOAUDIT SELECT TABLE, INSERT TABLE, DELETE TABLE, EXECUTE PROCEDURE;
Example 9-9 shows how to remove all statement auditing by using the NOAUDIT statement.
See Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for detailed information about the NOAUDIT statement.
This section contains:
Privilege auditing audits statements that use a system privilege, such as SELECT ANY TABLE. In this kind of auditing, SQL statements that require the audited privilege to succeed are recorded.
You can audit the use of any system privilege. Similar to statement auditing, privilege auditing audits the activities of all database users or only a specified list.
If you set similar audit options for both statement and privilege auditing, then only a single audit record is generated. For example, if the statement clause TABLE and the system privilege CREATE TABLE are both audited, then only a single audit record is generated each time a table is created.
Privilege auditing does not occur if the action is already permitted by the existing owner and object privileges. Privilege auditing is triggered only if the privileges are insufficient, that is, only if what makes the action possible is a system privilege. For example, suppose that user SCOTT has been granted the SELECT ANY TABLE privilege and the SELECT ANY TABLE is being audited. If SCOTT selects his own table (for example, SCOTT.EMP), then the SELECT ANY TABLE privilege is not used. Because he performed the SELECT statement within his own schema, no audit record is generated. On the other hand, if SCOTT selects from another schema (for example, the HR.EMPLOYEES table), then an audit record is generated. Because SCOTT selected a table outside his own schema, he needed to use the SELECT ANY TABLE privilege.
Privilege auditing is more focused than statement auditing, because each privilege auditing option audits only specific types of statements, not a related list of statements. For example, the statement auditing clause, TABLE, audits CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, and DROP TABLE statements. However, the privilege auditing option, CREATE TABLE, audits only CREATE TABLE statements, because only the CREATE TABLE statement requires the CREATE TABLE privilege.
See the listing of system privileges in the GRANT SQL statement section of Oracle Database SQL Language Reference.
Privilege audit options are the same as their corresponding system privileges. For example, the option to audit use of the DELETE ANY TABLE privilege is DELETE ANY TABLE.
Example 9-10 shows how to audit the DELETE ANY TABLE privilege.
Example 9-10 Using AUDIT to Configure Privilege Auditing
AUDIT DELETE ANY TABLE BY ACCESS WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
To audit all successful and unsuccessful uses of the DELETE ANY TABLE system privilege, enter the following statement:
AUDIT DELETE ANY TABLE BY ACCESS;
Example 9-11 shows how to audit all unsuccessful SELECT, INSERT, and DELETE statements on all tables and unsuccessful uses of the EXECUTE PROCEDURE system privilege, by all database users, and by individual audited statement.
The following statement removes all privilege audit options:
NOAUDIT ALL PRIVILEGES;
This example disables the audit settings from Example 9-11:
NOAUDIT SELECT TABLE, INSERT TABLE, DELETE TABLE, EXECUTE PROCEDURE;
To disable privilege auditing options, you must have the AUDIT SYSTEM system privilege. Usually, only the security administrator is granted this system privilege.
You can use the AUDIT statement to audit the activities of a client in a multitier environment. In a multitier environment, Oracle Database preserves the identity of a client through all tiers. Thus, you can audit actions taken on behalf of the client by a middle-tier application. To do so, use the BY PROXY clause in your AUDIT statement.
This clause allows you the following options:
Audit SQL statements issued by the specific proxy on its own behalf
Audit statements executed on behalf of a specified user or users
Audit all statements executed on behalf of any user
The middle tier can also set the user client identity in a database session, enabling the auditing of end-user actions through the middle-tier application. The end-user client identity then shows up in the audit trail.
Example 9-12 shows how to audit SELECT TABLE statements issued on behalf of client jackson by the proxy application server appserve.
Example 9-12 Using AUDIT to Audit a SQL Statement on Behalf of a Proxy User
AUDIT SELECT TABLE BY appserve ON BEHALF OF jackson;
You can audit user activity in a multitier environment. Once audited, you can verify these activities by querying the DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
Figure 9-1 illustrates how you can audit proxy users by querying the COMMENT_TEXT, PROXY_SESSIONID, ACTION_NAME, and SESSION_ID columns of the DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL view. In this scenario, both the database user and proxy user accounts are known to the database. Session pooling can be used.
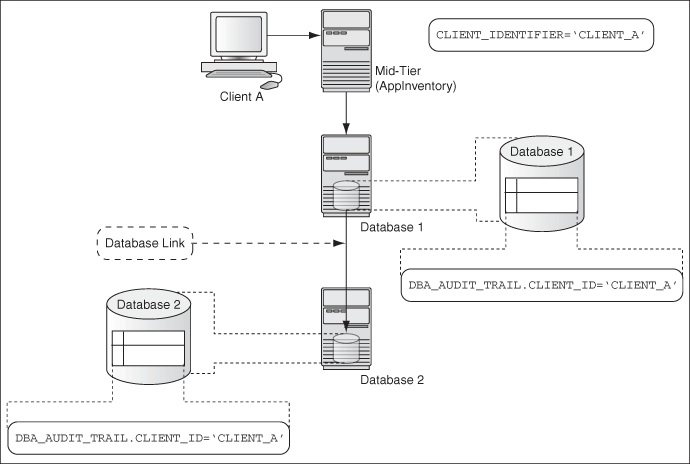
Figure 9-2 illustrates how you can audit client identifier information across multiple database sessions by querying the CLIENT_ID column of the DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view. In this scenario, the client identifier has been set to CLIENT_A. As with the proxy user-database user scenario described in Figure 9-1, session pooling can be used.
Figure 9-2 Auditing Client Identifier Information Across Sessions
See Also:
"Preserving User Identity in Multitiered Environments" for more information about user authentication in a multitiered environmentThis section contains:
Schema Object Audit Options for Views, Procedures, and Other Elements
Setting Audit Options for Objects That May Be Created in the Future
Schema object auditing monitors actions performed on the audited schema objects, such as tables or views. Object auditing applies to all users but is limited to the audited object only. Users can use the AUDIT and NOAUDIT statements on objects in their own schemas.
You can audit statements that refer to tables, views, sequences, standalone stored procedures or functions, and packages, but not individual procedures within packages. (See "Auditing Functions, Procedures, Packages, and Triggers" for more information about auditing these types of objects.)
You cannot directly audit statements that reference clusters, database links, indexes, or synonyms. However, you can indirectly audit access to these schema objects, by auditing the operations that affect the base table.
When you audit a schema object, the auditing applies to all users of the database. You cannot set these options for a specific list of users. You can set default schema object audit options for all auditable schema objects.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about auditable schema objectsWhen an editioned object has an audit policy, then it applies in all editions in which the object is visible. When an editioned object is actualized, any audit policies that are attached to it are newly attached to the new actual occurrence. When you newly apply an audit policy to an inherited editioned object, this action will actualize it.
You can find the editions in which audited objects appear by querying the OBJECT_NAME and OBJ_EDITION_NAME columns in the DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL and V$XML_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary views.
See Also:
Oracle Database Advanced Application Developer's Guide for detailed information about editionsThe definitions for views and procedures (including stored functions, packages, and triggers) reference underlying schema objects. Because of this dependency, some unique characteristics apply to auditing views and procedures, such as the likelihood of generating multiple audit records.
Views and procedures are subject to the enabled audit options on the base schema objects, including the default audit options. These options also apply to the resulting SQL statements.
Consider the following series of SQL statements:
AUDIT SELECT ON HR.EMPLOYEES BY ACCESS;
CREATE VIEW employees_departments AS
SELECT employee_id, last_name, department_id
FROM employees, departments
WHERE employees.department_id = departments.department_id;
AUDIT SELECT ON employees_departments BY ACCESS;
SELECT * FROM employees_departments;
As a result of the query on the employees_departments view, two audit records are generated: one for the query on the employees_departments view and one for the query on the base table employees (indirectly through the employees_departments view). The query on the base table departments does not generate an audit record because the SELECT audit option for this table is not enabled. All audit records pertain to the user that queried the employees_departments view.
In the given example, if the AUDIT SELECT ON HR.EMPLOYEES; statement is omitted, then using the employees_departments view does not generate an audit record for the EMPLOYEES table.
You can use the AUDIT statement to configure object auditing in the current edition. Oracle Database SQL Language Reference lists valid object audit options for AUDIT and the schema object types for which each option is available.
A user can set any object audit option for the objects contained in his or her schema. The AUDIT ANY system privilege is required to set an object audit option for an object contained in another user schema or to set the default object auditing option. Usually, only the security administrator is granted the AUDIT ANY privilege.
Figure 9-2 shows how to audit all successful and unsuccessful DELETE statements on the laurel.emp table.
Example 9-14 shows how to audit all successful SELECT, INSERT, and DELETE statements on the dept table owned by user jward.
Example 9-14 Auditing Successful Statements on a Schema Table
AUDIT SELECT, INSERT, DELETE
ON jward.dept
BY ACCESS
WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL;
Example 9-15 shows how you can use the ON DEFAULT clause to apply to any new objects (tables, views, and sequences) that are created after you set the AUDIT statement. In this example, new objects that are created in the future will be audited for all unsuccessful SELECT statements:
Example 9-15 Configuring Auditing for Any New Objects Using the DEFAULT Clause
AUDIT SELECT
ON DEFAULT
BY ACCESS
WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
Example 9-16 shows how to audit the execution of PL/SQL procedure or function.
Use the NOAUDIT statement to remove object auditing. The following statements turn off the corresponding auditing options:
NOAUDIT DELETE ON emp; NOAUDIT SELECT, INSERT, DELETE ON jward.dept;
To remove all object audit options on the emp table, enter the following statement:
NOAUDIT ALL ON emp;
To remove all default object audit options, enter the following statement:
NOAUDIT ALL ON DEFAULT;
All schema objects that are created before this NOAUDIT statement is issued continue to use the default object audit options in effect at the time of their creation, unless overridden by an explicit NOAUDIT statement after their creation.
To remove object audit options for a specific object, you must be the owner of the schema object. To remove the object audit options of an object in the schema of another user or to remove default object audit options, you must have the AUDIT ANY system privilege. A user with privileges to remove object audit options of an object can override the options set by any user.
You can create audit settings for objects that do not exist yet, such as the insertion and deletion of tables to be created. There are two approaches that you can take. One approach is to use the statement audit options in the AUDIT statement. For example, to audit all inserts on future tables, enter the following SQL statement:
AUDIT INSERT TABLE BY ACCESS;
The second approach is to invoke the AUDIT statement using the ON DEFAULT clause. For example:
AUDIT ALL ON DEFAULT BY ACCESS;
This statement audits by default all subsequent object creation statements. The ON keyword specifies object auditing. The ON DEFAULT clause configures auditing for subsequently created objects that are affected by the following statements:
ALTER |
EXECUTE |
INSERT |
SELECT |
AUDIT |
GRANT |
LOCK |
UPDATE |
COMMENT |
FLASHBACK |
READ |
|
DELETE |
INDEX |
RENAME |
To restrict ON DEFAULT to a specific action, enter a statement similar to the following:
AUDIT ALTER, DELETE ON DEFAULT BY ACCESS;
For more information about the audit options and the ON DEFAULT clause of the AUDIT SQL statement, see Oracle Database SQL Language Reference. To find objects audited by default, query the ALL_DEF_AUDIT_OPTS data dictionary view.
This section contains:
You can audit directory objects. For example, suppose you create a directory object that contains a preprocessor program that the ORACLE_LOADER access driver will use. You can audit anyone who runs this program within this directory object.
Use the AUDIT statement to enable object auditing. Example 9-17 shows how to audit the EXECUTE privilege on the directory object my_exec.
This section contains:
About Auditing Functions, Procedures, Packages, and Triggers
Configuring the Auditing of Functions, Procedures, Packages, and Triggers
Removing the Auditing of Functions, Procedures, Packages, and Triggers
You can audit functions, procedures, PL/SQL packages, and triggers. The areas that you can audit are as follows:
You can individually audit standalone functions, standalone procedures, and PL/SQL packages.
If you audit a PL/SQL package, Oracle Database audits all functions and procedures within the package.
If you enable auditing for all executions, Oracle Database audits all triggers in the database, as well as all the functions and procedures within PL/SQL packages.
You cannot audit individual functions or procedures within a PL/SQL package.
If you want to audit functions that are associated with Oracle Virtual Private database policies, note the following:
Dynamic policies: Oracle Database evaluates the policy function twice, once during SQL statement parsing and again during execution. As a result, two audit records are generated for each evaluation.
Static policies: Oracle Database evaluates the policy function once and then caches it in the SGA. As a result, only one audit record is generated.
Context-sensitive policies: Oracle Database executes the policy function once, during statement parsing. As a result, only one audit record is generated.
Example 9-18 shows how to audit the execution of any function, procedure, package, or trigger, by any user in the database.
Example 9-18 Auditing All Functions, Procedures, Packages, and Triggers
AUDIT EXECUTE PROCEDURE BY ACCESS;
Example 9-19 shows how to audit user psmith's successful and unsuccessful executions of functions, procedures, packages, and triggers.
Example 9-19 Auditing a User's Execution of Functions, Procedures, Packages, and Triggers
AUDIT EXECUTE PROCEDURE BY psmith BY ACCESS;
Example 9-20 shows how to audit a standalone procedure entitled check_work that is in the sales_data schema. This idea applies to standalone functions as well.
Use the NOAUDIT statement to remove the auditing of functions, procedures, and triggers. For example:
NOAUDIT EXECUTE PROCEDURE; NOAUDIT EXECUTE PROCEDURE BY psmith; NOAUDIT EXECUTE ON sales_data.checkwork;
This section contains:
You can use the AUDIT statement to audit unexpected errors in network protocol or internal errors in the network layer. Network auditing captures errors that occur during communication with the client on the network. These are errors thrown by the SQL*Net driver. There can be several causes of network errors. For example, an internal event set by a database engineer for testing purposes can cause a network error. Other causes include conflicting configuration settings for encryption, such as the network not finding the information required to create or process expected encryption. The errors that network auditing uncovers (such as ACTION 122 Network Error) are not connection failures: network auditing is only concerned with data as it travels across the network.
The audit record for network auditing lists the authentication type and SQL*Net address of the client (if available) in the COMMENT_TEXT field of the audit record, using the following format:
Authenticated by: authentication_type; Client Address: SQLNetAddress_of_client
The Client Address: SQLNetAddress_of_client portion only appears if this information is available.
Table 9-5 shows how to remedy four common error conditions.
Table 9-5 Auditable Network Error Conditions
| Error | Cause | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
|
After picking an algorithm, the server was unable to find an index for it in its table of algorithms. This should be impossible because the algorithm was chosen (indirectly) from that list. |
Turn on tracing for further details, and then rerun the operation. (Note that this error is not normally visible to the user.) If the error persists, then contact Oracle Support Services. |
|
|
An Oracle Advanced Security list-of-algorithms parameter was empty. |
Change the list to contain the name of at least one installed algorithm, or remove the list entirely if every installed algorithm is not acceptable. |
|
|
An Oracle Advanced Security list-of-algorithms parameter included an algorithm name that was not recognized. |
Remove that algorithm name, correct it if it was misspelled, or install the driver for the missing algorithm. |
|
|
The client and server have no algorithm in common for either encryption or data integrity or both. |
Choose sets of algorithms that overlap. In other words, add one of the client algorithm choices to the server list, or add one of the server list choices to the client algorithm. |
To configure network auditing, use the AUDIT statement. For example:
AUDIT NETWORK BY ACCESS;
When you use Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) to create a new database, Oracle Database configures the database to audit the most commonly used security-relevant SQL statements and privileges. It also sets the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter to DB. If you decide to use a different audit trail type (for example, OS if you want to write the audit trail records to operating system files), then you can do that: Oracle Database continues to audit the privileges that are audited by default. If you disable auditing by setting the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter to NONE, then no auditing takes place.
Oracle Database audits the following privileges by default:
ALTER ANY PROCEDURE |
CREATE ANY LIBRARY |
DROP ANY TABLE |
ALTER ANY TABLE |
CREATE ANY PROCEDURE |
DROP PROFILE |
ALTER DATABASE |
CREATE ANY TABLE |
DROP USER |
ALTER PROFILE |
CREATE EXTERNAL JOB |
EXEMPT ACCESS POLICY |
ALTER SYSTEM |
CREATE PUBLIC DATABASE LINK |
GRANT ANY OBJECT PRIVILEGE |
ALTER USER |
CREATE SESSION |
GRANT ANY PRIVILEGE |
AUDIT SYSTEM |
CREATE USER |
GRANT ANY ROLE |
CREATE ANY JOB |
DROP ANY PROCEDURE |
Oracle Database audits the following SQL shortcuts by default:
ROLE |
SYSTEM AUDIT |
PUBLIC SYNONYM |
DATABASE LINK |
PROFILE |
SYSTEM GRANT |
To individually control the auditing of SQL statements and privileges, use the AUDIT and NOAUDIT statements. For more information, see "Auditing SQL Statements" and "Auditing Privileges".
Note:
If your applications use the default audit settings from Oracle Database 10g Release 2 (10.2), then you can revert to these audit settings until you modify the applications to use the Release 11g audit settings. To do so, run theundoaud.sql script.
After you have modified your applications to conform to the Release 11g audit settings, then you can manually update your database to use the audit configuration that suits your business needs, or you can run the secconf.sql script to apply the Release 11g default audit settings.
The undoaud.sql and secconf.sql scripts are in the $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin directory. The undoaud.sql script affects audit settings only, and the secconf.sql script affects both audit and password settings. They have no effect on other security settings.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for detailed information about the SQL statements described in this section
sql_statement_shortcut in Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for a list of accepted SQL shortcuts you can use with the AUDIT statement
This section contains:
What Permissions Are Needed to Create a Fine-Grained Audit Policy?
Using the DBMS_FGA Package to Manage Fine-Grained Audit Policies
Tutorial: Adding an E-Mail Alert to a Fine-Grained Audit Policy
Fine-grained auditing enables you to create policies that define specific conditions that must take place for the audit to occur. This enables you to monitor data access based on content. It provides granular auditing of queries, and INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations. For example, a central tax authority must track access to tax returns to guard against employee snooping, with enough detail to determine what data was accessed. It is not enough to know that SELECT privilege was used by a specific user on a particular table. Fine-grained auditing provides this deeper functionality.
In general, fine-grained audit policies are based on simple, user-defined SQL predicates on table objects as conditions for selective auditing. During fetching, whenever policy conditions are met for a row, the query is audited.
You can use fine-grained auditing to audit the following types of actions:
Accessing a table between 9 p.m. and 6 a.m. or on Saturday and Sunday
Using an IP address from outside the corporate network
Selecting or updating a table column
Modifying a value in a table column
Fine-grained auditing creates a more meaningful audit trail, one that includes only very specific actions that you want to audit. It excludes unnecessary information that occurs if each table access was recorded. Fine-grained auditing has the following advantages over standard auditing:
It performs a Boolean condition check. If the Boolean condition you specify is met, for example, a table being accessed on a Saturday, then the audit takes place.
It captures the SQL that triggered the audit. You can capture both the SQL statement that caused the audit, and any associated bind variables. Be aware that you can only capture data from scalar column types. You cannot capture data from object columns, LOBs, or user-defined column types. For example, suppose you have the following query:
SELECT NAME FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE SSN = :1
If :1 is of integer type and the value for SSN is 987654321, then the audit trail can capture this information. However, the audit trail cannot capture this information if :1 is a BLOB, CLOB, object, or user-defined type.
This feature is available if you create the fine grained audit policy with the audit_trail parameter of the DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY PL/SQL procedure to DB+EXTENDED or XML+EXTENDED.
It adds extra protection to sensitive columns. You can audit specific relevant columns that may hold sensitive information, such as salaries or Social Security numbers.
It provides an event handler feature. For example, you can write a function that sends an e-mail alert to a security administrator when an audited column that should not be changed at midnight is updated.
You do not need to set initialization parameters to enable fine-grained auditing. Instead of setting initialization parameters such as AUDIT_TRAIL, you use the DBMS_FGA PL/SQL package to add and remove fine-grained auditing policies as necessary applying them to the specific operations or objects you want to monitor.
Fine-grained auditing records are stored in the SYS.FGA_LOG$ table. To find the records have been generated for the audit policies that are in effect, you can query the DBA_FGA_AUDIT_TRAIL view. The DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL view combines both standard and fine-grained audit log records. In addition, you can use the V$XML_AUDIT_TRAIL view to find fine-grained audit records that were written in XML formatted files. For detailed information about these views, see Oracle Database Reference.
Note:
Fine-grained auditing is supported only with cost-based optimization. For queries using rule-based optimization, fine-grained auditing checks before applying row filtering, which could result in an unnecessary audit event trigger.
Policies currently in force on an object involved in a flashback query are applied to the data returned from the specified flashback snapshot (based on time or system change number (SCN).
To create a fine-grained audit policy, you must have EXECUTE privileges on the DBMS_FGA PL/SQL package. The package is owned by the SYS user.
The SYS.AUD$ table records all data manipulation language (DML) statements, such as INSERT, UPDATE, MERGE, and DELETE, that are performed on the SYS.FGA_LOG$ table by non-SYS users. Oracle Database performs the audit even if auditing has not been configured for the SYS.FGA_LOG$ table, which is the table in which these activities occur. You can check these activities by querying the DBA_FGA_AUDIT_TRAIL and DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL views. See also "Activities That Are Always Written to the Standard and Fine-Grained Audit Records".
If you are preparing an application for edition-based redefinition, and you cover each table that the application uses with an editioning view, then you must move the fine-grained audit polices that protect these tables to the editioning view.
You designate the audit trail format for fine-grained auditing by setting the audit_trail parameter for the DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY policy (not to be confused with the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter) when you create the audit policy. Setting this parameter to XML or XML+EXTENDED writes the records to the operating system files in XML format. If you prefer to write the fine-grained audit records to the SYS.FGA_LOG$ table, then set the audit_trail parameter for the DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY parameter to DB or DB+EXTENDED. For a list of reasons why writing audit records to operating system files is beneficial, see "Advantages of the Operating System Audit Trail".
You can use the V$XML_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view to make audit records from XML files available to DBAs through a SQL query, providing enhanced usability. Querying this view causes all XML files (all files with an .xml extension) in the AUDIT_FILE_DEST directory to be parsed and presented in relational table format.
The DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL view includes the contents of the V$XML_AUDIT_TRAIL dynamic view for standard and fine-grained audit records.
Because the audit XML files are stored in files with the .xml extension on all platforms, the dynamic view presents audit information similarly on all platforms. See Oracle Database Reference for detailed information about the V$XML_AUDIT_TRAIL view contents.
Note:
If you audit tables that have sensitive data, remember thatDB+EXTENDED and XML+EXTENDED settings for the DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY audit_trail parameter will capture this data. See "Auditing Sensitive Information" for ways to handle this scenario.The fine-grained audit trail captures an audit record for each reference of a table or a view within a SQL statement. For example, if you run a UNION statement that references the HR.EMPLOYEES table twice, then an audit policy for statement generates two audit records, one for each access of the HR.EMPLOYEES table.
This section contains:
To manage a fine-grained audit policy, you use the DBMS_FGA PL/SQL package. This package enables you to add all combinations of SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements to one policy. You also can audit MERGE statements, by auditing the underlying actions of INSERT and UPDATE. To audit MERGE statements, configure fine-grained access on the INSERT and UPDATE statements. Only one record is generated for each policy for successful MERGE operations. To administer fine-grained audit policies, you must have the EXECUTE privilege on the DBMS_FGA package.
The audit policy is bound to the table for which you created it. This simplifies the management of audit policies because the policy only must be changed once in the database, not in each application. In addition, no matter how a user connects to the database—from an application, a Web interface, or through SQL*Plus or Oracle SQL Developer—Oracle Database records any actions that affect the policy.
If any rows returned from a query match the audit condition that you define, then Oracle Database inserts an audit entry into the fine-grained audit trail. This entry excludes all the information that is reported in the regular audit trail. In other words, only one row of audit information is inserted into the audit trail for every fine-grained audit policy that evaluates to true.
For detailed information about the syntax of the DBMS_FGA package, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference. See also Oracle Database Advanced Application Developer's Guide.
Note:
If you plan to use theDBMS_FGA package policy across different editions, then you can control the results of the policy: whether the results are uniform across all editions, or specific to the edition in which the policy is used. See "How Editions Affects the Results of a Global Application Context PL/SQL Package" for more information.To create a fine-grained audit policy, use the DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY procedure. This procedure creates an audit policy using the supplied predicate as the audit condition. Oracle Database executes the policy predicate with the privileges of the user who created the policy. The maximum number of fine-grained policies on any table or view object is 256. Oracle Database stores the policy in the data dictionary table, but you can create the policy on any table or view that is not in the SYS schema.
After you create the fine-grained audit policy, it does not reside in any specific schema, although the definition for the policy is stored in the SYS.FGA$ data dictionary table.
You cannot modify a fine-grained audit policy after you have created it. If you need to modify the policy, drop it and then recreate it.
The syntax for the ADD_POLICY procedure is:
DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY( object_schema VARCHAR2, object_name VARCHAR2, policy_name VARCHAR2, audit_condition VARCHAR2, audit_column VARCHAR2, handler_schema VARCHAR2, handler_module VARCHAR2, enable BOOLEAN, statement_types VARCHAR2, audit_trail BINARY_INTEGER IN DEFAULT, audit_column_opts BINARY_INTEGER IN DEFAULT);
In this specification:
object_schema: Specifies the schema of the object to be audited. (If NULL, the current log-on user schema is assumed.)
object_name: Specifies the name of the object to be audited.
policy_name: Specifies the name of the policy to be created. Ensure that this name is unique.
audit_condition: Specifies a Boolean condition in a row. NULL is allowed and acts as TRUE. See "Auditing Specific Columns and Rows" for more information. If you specify NULL or no audit condition, then any action on a table with that policy creates an audit record, whether or not rows are returned
audit_column: Specifies one or more columns to audit, including hidden columns. If set to NULL or omitted, all columns are audited. These can include Oracle Label Security hidden columns or object type columns. The default, NULL, causes audit if any column is accessed or affected.
handler_schema: If an alert is used to trigger a response when the policy is violated, specifies the name of the schema that contains the event handler. See also "Tutorial: Adding an E-Mail Alert to a Fine-Grained Audit Policy".
handler_module: Specifies the name of the event handler. Include the package the event handler is in. The default, NULL, uses the current schema.This function is invoked only after the first row that matches the audit condition in the query is processed. If the procedure fails with an exception, then the user SQL statement fails as well.
enable: Enables or disables the policy using true or false. If omitted, the policy is enabled. The default is TRUE.
statement_types: Specifies the SQL statements to be audited: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, or SELECT only.
audit_trail: Specifies the destination (DB or XML) of fine-grained audit records. Also specifies whether to populate LSQLTEXT and LSQLBIND in FGA_LOG$. However, be aware that sensitive data, such as credit card information, can be recorded in clear text. See "Auditing Sensitive Information" for how you can handle this scenario.
audit_column_opts: If you specify more than one column in the audit_column parameter, then this parameter determines whether to audit all or specific columns. See "Auditing Specific Columns and Rows" for more information.
See Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for additional details about the ADD_POLICY syntax.
Example 9-21 shows how to audit statements INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and SELECT on table HR.EMPLOYEES. Note that this example omits the audit_column_opts parameter, because it is not a mandatory parameter.
Example 9-21 Using DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY to Create a Fine-Grained Audit Policy
BEGIN DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY( object_schema => 'HR', object_name => 'EMPLOYEES', policy_name => 'chk_hr_employees', policy_owner => 'SEC_MGR', enable => TRUE, statement_types => 'INSERT, UPDATE, SELECT, DELETE', audit_trail => DBMS_FGA.DB); END; /
At this point, if you query the DBA_AUDIT_POLICIES view, you will find the new policy listed:
SELECT POLICY_NAME FROM DBA_AUDIT_POLICIES; POLICY_NAME ------------------------------- CHK_HR_EMPLOYEES
Afterwards, any of the following SQL statements log an audit event record.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM HR.EMPLOYEES WHERE COMMISSION_PCT = 20 AND SALARY > 4500; SELECT SALARY FROM HR.EMPLOYEES WHERE DEPARTMENT_ID = 50; DELETE FROM HR.EMPLOYEES WHERE SALARY > 1000000;
Auditing Specific Columns and Rows
You can fine-tune the audit behavior by targeting a specific column, referred to as a relevant column, to be audited if a condition is met. To accomplish this, you use the audit_column parameter to specify one or more sensitive columns. In addition, you can audit data in specific rows by using the audit_condition parameter to define a Boolean condition.
Example 9-21 performs an audit if anyone in Department 50 tries to access the salary and commission_pct columns.
audit_condition => 'DEPARTMENT_ID = 50', audit_column => 'SALARY,COMMISSION_PCT,'
As you can see, this feature is enormously beneficial. It not only enables you to pinpoint particularly important types of data to audit, but it provides increased protection for columns that contain sensitive data, such as Social Security numbers, salaries, patient diagnoses, and so on.
If the audit_column lists more than one column, you can use the audit_column_opts parameter to specify whether a statement is audited when the query references any column specified in the audit_column parameter or only when all columns are referenced. For example:
audit_column_opts => DBMS_FGA.ANY_COLUMNS, audit_column_opts => DBMS_FGA.ALL_COLUMNS,
If you do not specify a relevant column, then auditing applies to all columns.
You can disable a fine-grained audit policy by using the DBMS_FGA.DISABLE_POLICY procedure. The syntax for DISABLE_POLICY is:
DBMS_FGA.DISABLE_POLICY( object_schema VARCHAR2, object_name VARCHAR2, policy_name VARCHAR2 );
Example 9-22 shows how to disable the fine-grained audit policy created in Example 9-21.
Example 9-22 Disabling a Fine-Grained Audit Policy
DBMS_FGA.DISABLE_POLICY( object_schema => 'HR', object_name => 'EMPLOYEES' policy_name => 'chk_hr_employees'); /
For detailed information about the DISABLE_POLICY syntax, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference.
Example 9-23 show how to reenable the chk_hr_emp policy by using the DBMS_FGA.ENABLE_POLICY procedure:
Example 9-23 Enabling a Fine-Grained Audit Policy
DBMS_FGA.ENABLE_POLICY( object_schema => 'HR', object_name => 'EMPLOYEES', policy_name => 'chk_hr_employees' enable => 'TRUE'); /
For detailed information about the ENABLE_POLICY syntax, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference.
Oracle Database automatically drops the audit policy if you remove the object specified in the object_name parameter of the DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY procedure, or if you drop the user who created the audit policy.
Example 9-24 shows how to drop a fine-grained audit policy manually by using the DBMS_FGA.DROP_POLICY procedure.
Example 9-24 Dropping a Fine-Grained Audit Policy
DBMS_FGA.DROP_POLICY( object_schema => 'HR', object_name => 'EMPLOYEES', policy_name => 'chk_hr_employees');
See Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for detailed information about the DROP_POLICY syntax.
You can add an e-mail alert to a fine-grained audit policy that goes into effect when a user (or an intruder) violates the policy. To accomplish this, you first must create a procedure that generates the alert, and then use the following DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY parameters to call this function when someone violates this policy:
handler_schema: The schema in which the handler event is stored
handler_module: The name of the event handler
The alert can come in any form that best suits your environment: an e-mail or pager notification, updates to a particular file or table, and so on. Creating alerts also helps to meet certain compliance regulations, such as California Senate Bill 1386. In this tutorial, you will create an e-mail alert.
In this tutorial, you create an e-mail alert that notifies a security administrator that a Human Resources representative is trying to select or modify salary information in the HR.EMPLOYEES table. The representative is permitted to make changes to this table, but to meet compliance regulations, we want to create a record of all salary selections and modifications to the table.
In this tutorial:
Step 3: Configure an Access Control List File for Network Services
Step 5: Create and Test the Fine-Grained Audit Policy Settings
Log on as user SYS with the SYSDBA privilege.
sqlplus sys as sysdba
Enter password: password
Install the UTL_MAIL package.
@?/plsql/admin/utlmail.sql @?/plsql/admin/prvtmail.plb
The UTL_MAIL package enables you to manage e-mail. See Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for more information about UTL_MAIL.
Be aware that currently, the UTL_SMTP and UTL_MAIL PL/SQL packages do not support SSL servers.
Check the current value of the SMTP_OUT_SERVER initialization parameter, and make a note of this value so that you can restore it when you complete this tutorial.
For example:
SHOW PARAMETER SMTP_OUT_SERVER
If the SMTP_OUT_SERVER parameter has already been set, then output similar to the following appears:
NAME TYPE VALUE ----------------------- ----------------- ---------------------------------- SMTP_OUT_SERVER string some_imap_server.example.com
Issue the following ALTER SYSTEM statement:
ALTER SYSTEM SET SMTP_OUT_SERVER="imap_mail_server.example.com";
Replace imap_mail_server with the name of your SMTP server, which you can find in the account settings in your e-mail tool. Enclose these settings in quotation marks. For example:
ALTER SYSTEM SET SMTP_OUT_SERVER="my_imap_server.example.com"
Connect as SYS using the SYSOPER privilege and then restart the database.
CONNECT SYS/AS SYSOPER
Enter password: password
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE
STARTUP
Ensure that the SMTP_OUT_SERVER parameter setting is correct.
CONNECT SYS/AS SYSDBA
Enter password: password
SHOW PARAMETER SMTP_OUT_SERVER
Output similar to the following appears:
NAME TYPE VALUE ----------------------- ----------------- ---------------------------------- SMTP_OUT_SERVER string my_imap_server.example.com
Ensure that you are connected as SYS using the SYSDBA privilege, and then create the sysadmin_fga account, who will create the fine-grained audit policy.
For example:
CONNECT SYS/AS SYSDBA Enter password: password GRANT CREATE SESSION, DBA TO sysadmin_fga IDENTIFIED BY password; GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_FGA TO sysadmin_fga; GRANT CREATE PROCEDURE, DROP ANY PROCEDURE TO sysadmin_fga; GRANT EXECUTE ON UTL_TCP TO sysadmin_fga; GRANT EXECUTE ON UTL_SMTP TO sysadmin_fga; GRANT EXECUTE ON UTL_MAIL TO sysadmin_fga; GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN TO sysadmin_fga;
Replace password with a password that is secure. See "Minimum Requirements for Passwords" for more information.
The UTL_TCP, UTL_SMTP, UTL_MAIL, and DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN PL/SQL packages are used by the e-mail security alert that you create.
Connect as user SYSTEM.
CONNECT SYSTEM
Enter password: password
Ensure that the HR schema account is unlocked and has a password. If necessary, unlock HR and grant this user a password.
SELECT USERNAME, ACCOUNT_STATUS FROM DBA_USERS WHERE USERNAME = 'HR';
If the DBA_USERS view lists user HR as locked and expired, then enter the following statement to unlock the HR account and create a new password:
ALTER USER HR ACCOUNT UNLOCK IDENTIFIED BY password;
Enter a password that is secure. For greater security, do not give the HR account the same password from previous releases of Oracle Database. "Minimum Requirements for Passwords" for the minimum requirements for creating passwords.
Create a user account for Susan Mavris, who is an HR representative, and then grant this user access to the HR.EMPLOYEES table.
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO smavris IDENTIFIED BY password;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON HR.EMPLOYEES TO SMAVRIS;
Before you can use PL/SQL network utility packages such as UTL_MAIL, you must configure an access control list (ACL) file that enables fine-grained access to external network services. For detailed information about this topic, see "Managing Fine-Grained Access in PL/SQL Network Utility Packages".
To configure an access control list for the e-mail alert:
Connect to SQL*Plus as user sysadmin_fga.
CONNECT sysadmin_fga
Enter password: password
Create the following access control list and its privilege definitions.
BEGIN DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN.CREATE_ACL ( acl => 'email_server_permissions.xml', description => 'Enables network permissions for the e-mail server', principal => 'SYSADMIN_FGA', is_grant => TRUE, privilege => 'connect'); END; /
Ensure that you enter your exact user name for the principal setting, in upper-case letters. For this tutorial, enter SYSADMIN_FGA for the name of the principal.
Assign the access control list to the outgoing SMTP network host for your e-mail server.
BEGIN DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN.ASSIGN_ACL ( acl => 'email_server_permissions.xml', host => 'SMTP_OUT_SERVER_setting', lower_port => port); END; /
In this example:
SMTP_OUT_SERVER_setting: Enter the SMTP_OUT_SERVER setting that you set for the SMTP_OUT_SERVER parameter in "Step 1: Install and Configure the UTL_MAIL PL/SQL Package". This setting should match exactly the setting that your e-mail tool specifies for its outgoing server.
port: Enter the port number that your e-mail tool specifies for its outgoing server. Typically, this setting is 25. Enter this value for the lower_port setting. (Currently, the UTL_MAIL package does not support SSL. If your e-mail server is an SSL server, then enter 25 for the port number, even if the e-mail server uses a different port number.)
As user sysadmin_fga, create the following procedure:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE email_alert (sch varchar2, tab varchar2, pol varchar2)
AS
msg varchar2(20000) := 'HR.EMPLOYEES table violation. The time is: ';
BEGIN
msg := msg||to_char(SYSDATE, 'Day DD MON, YYYY HH24:MI:SS');
UTL_MAIL.SEND (
sender => 'youremail@example.com',
recipients => 'recipientemail@example.com',
subject => 'Table modification on HR.EMPLOYEES',
message => msg);
END email_alert;
/
|
In this example:
Lines 1 and 2: In the CREATE PROCEDURE statement, you must include a signature that describes the schema name (sch), table name (tab), and the name of the audit procedure (pol) that you will define in audit policy in the next step.
Lines 9 and 10: Replace youremail@example.com with your e-mail address, and recipientemail@example.com with the e-mail address of the person you want to receive the notification.
As user sysadmin_fga, create the chk_hr_emp policy fine-grained audit policy as follows.
BEGIN DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY ( object_schema => 'HR', object_name => 'EMPLOYEES', policy_name => 'CHK_HR_EMP', audit_column => 'SALARY', handler_schema => 'SYSADMIN_FGA', handler_module => 'EMAIL_ALERT', enable => TRUE, statement_types => 'SELECT, UPDATE', audit_trail => DBMS_FGA.DB + DBMS_FGA.EXTENDED); END; /
Commit the changes you have made to the database.
COMMIT;
Test the settings that you have created so far.
EXEC email_alert ('hr', 'employees', 'chk_hr_emp');
SQL*Plus should display a PL/SQL procedure successfully completed message, and in a moment, depending on the speed of your e-mail server, you should receive the e-mail alert.
If you receive an ORA-24247: network access denied by access control list (ACL) error followed by ORA-06512: at stringline string errors, then check the settings in the access control list file.
Connect to SQL*Plus as user smavris, check your salary, and give yourself a nice raise.
CONNECT smavris
Enter password: password
SELECT SALARY FROM HR.EMPLOYEES WHERE LAST_NAME = 'Mavris';
SALARY
-----------
6500
UPDATE HR.EMPLOYEES SET SALARY = 13000 WHERE LAST_NAME = 'Mavris';
Now select from a column other than SALARY in the HR.EMPLOYEES table.
SELECT FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME FROM HR.EMPLOYEES WHERE LAST_NAME = 'Raphaely';
The following output should appear:
FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME -------------------- -------------------- Den Raphaely
By now, depending on the speed of you e-mail server, you (or your recipient) should have received an e-mail with the subject header Table modification on HR.EMPLOYEES notifying you of the tampering of the HR.EMPLOYEES table.
As user sysadmin_fga, query the DBA_FGA_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view, which contains the Susan Mavris's audited activities.
CONNECT sysadmin_fga
Enter password: password
col dbuid format a10
col lsqltext format a66
col ntimestamp# format a15
SELECT DBUID, LSQLTEXT, NTIMESTAMP# FROM SYS.FGA_LOG$ WHERE POLICYNAME='CHK_HR_EMP';
Output similar to the following appears:
DBUID LSQLTEXT ---------- ------------------------------------------------------------------ NTIMESTAMP# -------------------------------------------------------------------------- SMAVRIS SELECT SALARY FROM HR.EMPLOYEES WHERE LAST_NAME = 'Mavris' 23-JUN-09 03.48.59.111000 PM SMAVRIS UPDATE HR.EMPLOYEES SET SALARY = 13000 WHERE LAST_NAME = 'Mavris' 23-JUN-09 03.49.07.330000 PM
The audit trail captures the two SQL statements that Susan Mavris ran that affected the SALARY column in the HR.EMPLOYEES table. The third statement she ran, in which she asked about Den Raphaely, was not recorded because it was not affected by the audit policy. This is because Oracle Database executes the audit function as an autonomous transaction, committing only the actions of the handler_module setting and not any user transaction. The function has no effect on any user SQL transaction.
Connect to SQL*Plus as user SYSTEM privilege, and then drop users sysadmin_fga (including the objects in the sysadmin_fga schema) and smavris.
CONNECT SYSTEM
Enter password: password
DROP USER sysadmin_fga CASCADE;
DROP USER smavris;
Connect as user HR and remove the loftiness of Susan Mavris's salary.
CONNECT HR
Enter password: password
UPDATE HR.EMPLOYEES SET SALARY = 6500 WHERE LAST_NAME = 'Mavris';
If you want, lock and expire HR, unless other users want to use this account:
ALTER USER HR PASSWORD EXPIRE ACCOUNT LOCK;
Connect as user SYS with the SYSDBA privilege, and drop the email_server_permissions.xml access control list.
BEGIN
DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN.DROP_ACL(
acl => 'email_server_permissions.xml');
END;
/
Access control lists reside in the SYS schema, not the schema of the user who created them.
This tutorial shows how to create a fine-grained audit policy that audits a nondatabase user's actions, based on the identity set in the client identifier.
In this tutorial:
Log on as user SYS with the SYSDBA privilege.
sqlplus SYS AS SYSDBA
Enter password: password
Create the sysadmin_fga account, who will create the fine-grained audit policy.
GRANT CREATE SESSION, DBA TO sysadmin_fga IDENTIFIED BY password;
GRANT SELECT ON OE.ORDERS TO sysadmin_fga;
GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_FGA TO sysadmin_fga;
GRANT SELECT ON SYS.FGA_LOG$ TO sysadmin_fga;
Replace password with a password that is secure. See "Minimum Requirements for Passwords" for more information.
The sample user OE will also be used in this tutorial, so query the DBA_USERS data dictionary view to ensure that OE is not locked or expired.
SELECT USERNAME, ACCOUNT_STATUS FROM DBA_USERS WHERE USERNAME = 'OE';
If the DBA_USERS view lists user OE as locked and expired, log in as user SYSTEM and then enter the following statement to unlock the OE account and create a new password:
ALTER USER OE ACCOUNT UNLOCK IDENTIFIED BY password;
Enter a password that is secure. For greater security, do not give the OE account the same password from previous releases of Oracle Database. "Minimum Requirements for Passwords" for the minimum requirements for creating passwords.
Connect to SQL*Plus as user sysadmin_fga.
CONNECT sysadmin_fga
Enter password: password
BEGIN
DBMS_FGA.ADD_POLICY(OBJECT_SCHEMA => 'OE',
OBJECT_NAME => 'ORDERS',
POLICY_NAME => 'ORDERS_FGA_POL',
AUDIT_CONDITION => 'SYS_CONTEXT(''USERENV'', ''CLIENT_IDENTIFIER'') = ''Robert''',
HANDLER_SCHEMA => NULL,
HANDLER_MODULE => NULL,
ENABLE => True,
STATEMENT_TYPES => 'INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,SELECT',
AUDIT_TRAIL => DBMS_FGA.DB + DBMS_FGA.EXTENDED,
AUDIT_COLUMN_OPTS => DBMS_FGA.ANY_COLUMNS);
END;
/
In this example, the AUDIT_CONDITION parameter assumes the nondatabase user is named Robert. The policy will monitor any INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and SELECT statements Robert will attempt.
Connect as user OE and select from the OE.ORDERS table.
CONNECT OE
Enter password: password
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ORDERS;
The following output appears:
COUNT(*)
----------
105
Connect as user sysadmin_fga and then check if any audit records were generated.
CONNECT sysadmin_fga
Enter password: password
SELECT DBUID, LSQLTEXT FROM SYS.FGA_LOG$ WHERE POLICYNAME='ORDERS_FGA_POL';
The following output appears:
no rows selected
Because no nondatabase users were logged in to query the OE.ORDERS table, the audit trail is empty.
Reconnect as user OE, set the client identifier to Robert, and then reselect from the OE.ORDERS table.
CONNECT OE
Enter password: password
EXEC DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER('Robert');
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ORDERS;
The following output should appear:
COUNT(*)
----------
105
Reconnect as user sysadmin_fga and then check the audit trail again.
CONNECT sysadmin_fga
Enter password: password
SELECT DBUID, LSQLTEXT FROM SYS.FGA_LOG$ WHERE POLICYNAME='ORDERS_FGA_POL';
This time, because Robert has made his appearance and queried the OE.ORDERS table, the audit trail captures his actions:
DBUID LSQLTEXT ---------------- ---------------------------- OE SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ORDERS;
Connect to SQL*Plus as user SYSTEM, and then drop user sysadmin_fga (including the objects in the sysadmin_fga schema).
CONNECT SYSTEM
Enter password: password
DROP USER sysadmin_fga CASCADE;
If you want, lock and expire OE, unless other users want to use this account:
ALTER USER OE PASSWORD EXPIRE ACCOUNT LOCK;
You can fully audit sessions for users who connect as SYS, including all users connecting using the SYSDBA or SYSOPER privileges. This enables you to write the actions of administrative users to an operating system file, even if the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter is set to NONE, DB, or DB, EXTENDED. Writing the actions of administrator users to an operating system audit file is safer than writing to the SYS.AUD$ table, because administrative users can remove rows from this table that indicate their bad behavior.
To configure audit settings for SYSDBA and SYSOPER users:
Set the AUDIT_SYS_OPERATIONS initialization parameter to TRUE.
ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_SYS_OPERATIONS=TRUE SCOPE=SPFILE;
This setting records the top-level operations directly issued by users who have connected to the database using the SYSDBA or SYSOPER privilege. It writes the audit records to the operation system audit trail. The SQL text of every statement is written to the ACTION field in the operating system audit trail record.
If you want to write system administrator activities to XML files, then set the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter to either XML or XML, EXTENDED.
For example:
ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_TRAIL=XML, EXTENDED SCOPE=SPFILE;
In all operating systems, if you set AUDIT_TRAIL to either XML or XML,EXTENDED, then audit records are written as XML files in the directory specified by the AUDIT_FILE_DEST initialization parameter. By default, Oracle Database writes the audit records to operating system files.
See Table 9-2, "AUDIT_TRAIL Initialization Parameter Settings" for more information about these settings. See also "Enabling or Disabling the Standard Audit Trail".
Restart the database.
After you restart the database, Oracle Database audits all successful actions performed by SYSDBA and SYSOPER users, and writes these audit records to the operating system audit trail, and not to the SYS.AUD$ table.
In Windows, if you have set the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter OS, then Oracle Database writes audit records as events to the Event Viewer log file.
Note:
The$ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/adump directory is the first default location used if the AUDIT_FILE_DEST initialization parameter is not set or does not point to a valid directory. If writing to that first default location fails or the database is closed, then Oracle Database uses the $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/audit directory as the backup default location. If that attempt fails, then the audited operation fails and a message is written to the alert log.
When AUDIT_TRAIL is set to OS, audit file names continue to be in the following form:
$ORACLE_SID_short_form_process_name_processid_sequence_number.aud
The sequence number starts from number 1.
For example, the short process name ora is used for dedicated server processes, and the names s001, s002, and so on are used for shared server processes.
When AUDIT_TRAIL is set to XML or XML, EXTENDED, the same audit file names have the extension xml instead of aud.
If you do not specify the AUDIT_FILE_DEST initialization parameter, then the default location is $ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/adump in Linux and Solaris, and %ORACLE_BASE%\admin\%ORACLE_SID%\adump for Microsoft Windows. For other operating systems, refer to their audit trail documentation.
Oracle Database audits all SYS-issued SQL statements indiscriminately and regardless of the setting of the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter.
Consider the following SYS session:
CONNECT SYS/AS SYSDBA;
Enter password: password
ALTER SYSTEM FLUSH SHARED_POOL;
UPDATE salary SET base=1000 WHERE name='laurel';
When SYS auditing is enabled, both the ALTER SYSTEM and UPDATE statements are displayed in the operating system audit file, similar to the following output. (Be aware that this format may change in different Oracle Database releases.)
Tue May 5 04:53:37 2009 -07:00 LENGTH : '159' ACTION :[7] 'CONNECT' DATABASE USER:[1] '/' PRIVILEGE :[6] 'SYSDBA' CLIENT USER:[7] 'laurelh' CLIENT TERMINAL:[5] 'pts/0' STATUS:[1] '0' DBID:[9] '561542328' Tue May 5 04:53:40 2009 -07:00 LENGTH : '183' ACTION :[30] 'ALTER SYSTEM FLUSH SHARED_POOL' DATABASE USER:[1] '/' PRIVILEGE :[6] 'SYSDBA' CLIENT USER:[7] 'laurelh' CLIENT TERMINAL:[5] 'pts/0' STATUS:[1] '0' DBID:[9] '561542328' Tue May 5 04:53:49 2009 -07:00 LENGTH : '200' ACTION :[47] 'UPDATE salary SET base=1000 WHERE name='laurel'' DATABASE USER:[1] '/' PRIVILEGE :[6] 'SYSDBA' CLIENT USER:[7] 'laurelh' CLIENT TERMINAL:[5] 'pts/0' STATUS:[1] '0' DBID:[9] '561542328'
The brackets indicate the length of the value. For example, PRIVILEGE is set to SYSDBA, which uses 6 characters. In addition, the values are in single quotes for SYS and mandatory audit records.
Because of the superuser privileges available to users who connect as SYSDBA, Oracle recommends that database administrators rarely use this connection and only when necessary. Database administrators can usually perform normal day-to-day maintenance activity. These database administrators are typical database users with the DBA role, or have been granted privileges that are the equivalent of a DBA role (for example, mydba or jr_dba) that your organization customizes.
You can use triggers to supplement the built-in auditing features of Oracle Database. The trigger that you create records user actions to a separate database table. When an activity fires the trigger, the trigger records the action in this table. Triggers are useful when you want to record customized information such as before-and-after changes to a table. For detailed information about creating triggers, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference.
You do not need to have auditing enabled for the trigger to work, nor does it matter what type of auditing you do have enabled. The trigger works outside of the database audit functionality.
Follow these guidelines if you want to create audit triggers:
Never write the trigger so that it writes data to the SYS.AUD$ table. In fact, you should never modify the SYS.AUD$ table contents. If you try to write values to SYS.AUD$ and the trigger does not work as expected, then it could adversely affect standard auditing. The SYS.AUD$ table is an Oracle Database-owned table, and only Oracle Database should write to it.
If possible, create the trigger as an AFTER trigger. The triggering statement is subjected to any applicable constraints. If no records are found, then the AFTER trigger does not fire, and audit processing is not carried out unnecessarily.
Create the trigger as either an AFTER row or AFTER statement trigger. Choosing between AFTER row and AFTER statement triggers depends on the information being audited. For example, row triggers provide value-based auditing for each table row. Triggers can also require you to supply a reason code for issuing the audited SQL statement, which can be useful in both row and statement-level auditing situations.
Table 9-6 provides a comparison of trigger-based auditing and the built-in database auditing features.
Table 9-6 Comparison of Built-in Auditing and Trigger-Based Auditing
| Audit Feature | Description |
|---|---|
|
DML and DDL auditing |
Standard auditing options permit auditing of DML and DDL statements regarding all types of schema objects and structures. Comparatively, triggers permit auditing of DML statements entered against tables, and DDL auditing at |
|
Centralized audit trail |
All database audit information is recorded centrally and automatically using the auditing features of the database. |
|
Declarative method |
Auditing features enabled using the standard database features are easier to declare and maintain, and less prone to errors, when compared to auditing functions defined by triggers. |
|
Auditing options can be audited |
Any changes to existing auditing options can also be audited to guard against malicious database activity. |
|
Session and execution time auditing |
Using the database auditing features, records are generated once every time an audited statement is entered. With triggers, an audit record is generated each time a trigger-audited table is referenced. |
|
Auditing of unsuccessful data access |
Database auditing can be set to audit when unsuccessful data access occurs. However, unless autonomous transactions are used, any audit information generated by a trigger is rolled back if the triggering statement is rolled back. For more information about autonomous transactions, see Oracle Database Concepts. |
|
Sessions can be audited |
Connections, disconnections, and session activity (physical I/Os, logical I/Os, deadlocks, and so on) can be recorded using standard database auditing. |
In Example 9-25, a trigger audits modifications to the emp_tab table for specific rows. The trigger writes the old and new values to the emp_audit_tab table, including the user who performed the update and the time the update took place.
Example 9-25 Audit Trigger to Record Before and After Changes to a Table
/* 1. Create the following table: */ CREATE TABLE emp_tab ( empno NUMBER(4), ename VARCHAR2(10), job VARCHAR2(9), mgr NUMBER(4), hiredate DATE, sal NUMBER(8,2), deptno NUMBER(2)); /* 2. Create a table to capture the audit data. */ CREATE TABLE emp_audit_tab ( oldname VARCHAR2(10), oldjob VARCHAR2(9), oldsal NUMBER (8,2), newname VARCHAR2(10), newjob VARCHAR2(9), newsal NUMBER(8,2), user1 varchar2(10), systemdate TIMESTAMP); /* 3. Create a trigger to record the old and new values, the author of the change, and when the change took place. */ CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER emp_audit_trig AFTER INSERT OR DELETE OR UPDATE ON emp_tab FOR EACH ROW BEGIN INSERT INTO emp_audit_tab ( oldname, oldjob, oldsal, newname, newjob, newsal, user1, systemdate ) VALUES ( :OLD.ename, :OLD.job, :OLD.sal, :NEW.ename, :NEW.job, :NEW.sal, user, sysdate ); END; /
To test this trigger, add a row to the emp_tab table, and then change the value the ename, job, or sal column in the emp_tab table. Then query the emp_audit_tab table to find the audit data.
This section contains:
Audit records include information about the operation that was audited, the user who performed the operationFoot 2 , and the date and time of the operation. Depending on the type of auditing you choose, you can write audit records to data dictionary tables, called the database audit trail, or in operating system files, called the operating system audit trail.
If you choose to write audit records to the database audit trail, Oracle Database writes the audit records to the SYS.AUD$ table for default and standard auditing, and to the SYS.FGA_LOG$ table for fine-grained auditing. Both of these tables reside in the SYSTEM tablespace and are owned by the SYS schema. You can check the contents of these tables by querying the following data dictionary views:
DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL for the SYS.AUD$ contents
DBA_FGA_AUDIT_TRAIL for the SYS.FGA_LOG$ contents
DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL for both SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ contents
"Finding Information About Audited Activities" describes more data dictionary views that you can use to view to contents of the SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables.
If you choose to write audit records to an operating system file, you can write them to either a text file or to an XML file. You can check the contents of the audit XML files by querying the V$XML_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
This section contains:
See Also:
"Purging Audit Trail Records"The database audit trail is a pair of tables, AUD$ (for standard auditing) and FGA_LOG$ (for fine-grained auditing), in the SYS schema of each Oracle Database data dictionary. It records both standard and fine-grained audit activities. Several data dictionary views can help you use the information in this table. "Finding Information About Audited Activities" lists all the auditing-related views.
The database audit trail record contains different types of information, depending on the events audited and the auditing options set. For example, if you have set the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter to DB, EXTENDED or XML, EXTENDED, then the SQL_BIND and SQL_TEXT columns show any SQL bind variables used for a SQL statement and SQL text that triggered the audit, respectively. For full details about the contents of these views, refer to Oracle Database Reference. However, be aware that the format and columns of the DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL view may change across Oracle Database releases.
Note:
If theAUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter is set to XML or XML, EXTENDED, then Oracle Database sends standard audit records to operating system files in XML format. Because XML is a standard document format, many utilities are available to parse and analyze XML data.If the database destination for audit records becomes full or unavailable, and, therefore, unable to accept new records, then an audited action cannot complete. Instead, Oracle Database generates an error message and does not audit the action. You can control the size of the audit trail to make it more manageable. (In fact, Oracle strongly recommends that you do so.) See "Controlling the Size of the Database Audit Trail" for more information. See also "Keeping Audited Information Manageable".
The audit trail does not store information about any data values that might be involved in the audited statement. For example, old and new data values of updated rows are not stored when an UPDATE statement is audited. However, you can perform this specialized type of auditing by using fine-grained auditing methods.
You can use the Flashback Query feature to show the old and new values of the updated rows, subject to any auditing policy presently in force. The current policies are enforced even if the flashback is to an old query that was originally subject to a different policy. Current business access rules always apply.
See Also:
"Auditing Specific Activities with Fine-Grained Auditing" for more information about methods of fine-grained auditing
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information about auditing table changes by using Flashback Transaction Query
Flashback entries in the table of system privileges listed in the GRANT SQL statement section of Oracle Database SQL Language Reference
If the database audit trail is full and no more audit records can be inserted, then underlying statement cannot complete successfully until you purge the audit trail. Oracle Database issues errors to all users who issue statements that cause the audit. Therefore, you must control the growth and size of the audit trail.
When auditing is enabled and audit records are being generated, the audit trail increases according to two factors:
The number of audit options turned on
The frequency of execution of audited statements
To control the growth of the audit trail, you can use the following methods:
Enable and disable database auditing. If it is enabled, then audit records are generated and stored in the audit trail. If it is disabled, then audit records are not generated. (Remember that some activities are always audited.)
Be selective about the audit options that are turned on. If more selective auditing is performed, then useless or unnecessary audit information is not generated and stored in the audit trail. You can use fine-grained auditing to selectively audit only certain conditions.
Tightly control the ability to perform object auditing. You can accomplish this in the following ways:
A security administrator owns all objects and never grants the AUDIT ANY system privilege to any other user. Alternatively, all schema objects can belong to a schema for which the corresponding user does not have CREATE SESSION privilege.
All objects are contained in schemas that do not correspond to real database users (that is, the CREATE SESSION privilege is not granted to the corresponding user). The security administrator is the only user granted the AUDIT ANY system privilege.
In both scenarios, a security administrator controls entirely object auditing.
The maximum size of the database audit trail tables (AUD$ and FGA_LOG$) is determined by the default storage parameters of the SYSTEM tablespace, in which it is stored by default. If you are concerned that a too-large database audit trail will affect the SYSTEM table performance, then consider moving the database audit trail tables to a different tablespace.
See Also:
Operating system-specific Oracle Database documentation for more information about managing the operating system audit trail when directing audit records to that locationBy default, the SYSTEM tablespace stores the database audit trail SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables. You can change this default location to another tablespace, such as the SYSAUX tablespace or a user-created tablespace. You may want to move the database audit trail tables to a different tablespace if the SYSTEM tablespace is too busy. Another reason for moving these audit trail tables to a different tablespace is if you plan to purge them by using the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package procedures.
Be aware that moving the database audit trail tables to a different tablespace can take a long time, depending on the amount of audit data in the audit tables, so you may want to do this during a time when database activity is slow.
To move the database audit trail from SYSTEM to a different tablespace:
Log in to SQL*Plus as an administrator who has the EXECUTE privilege on the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package.
For more information about the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference.
Check the tablespace to which you want to move the database audit trail tables.
You may need to optimize and allocate more space to this tablespace, including the SYSAUX auxiliary tablespace. For more information, see Oracle Database Performance Tuning Guide.
Run the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_LOCATION PL/SQL procedure to specify the name of the destination tablespace.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_LOCATION( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, AUDIT_TRAIL_LOCATION_VALUE => 'AUD_AUX'); END;
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Refers to the database audit trail type. Enter one of the following values:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD: Standard audit trail table, AUD$.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD: Fine-grained audit trail table, FGA_LOG$.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_STD: Both standard and fine-grained audit trail tables.
AUDIT_TRAIL_LOCATION_VALUE: Specifies the destination tablespace. This example specifies a tablespace named AUD_AUX.
At times an application must give the SYS.AUD$ system table access to regular users (non-SYSDBA users). For example, an audit report generator needs access to AUD$ table to generate daily reports on possible violations. Also, many installations have a distinct auditor role to achieve separation of duty.
In this case, be aware that DML statements such as INSERT, UPDATE, MERGE, and DELETE are always audited and recorded in the SYS.AUD$ table. You can check these activities by querying the DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL and DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL views.
If a user has SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE privileges on SYS.AUD$ and executes a SELECT operation, then the audit trail will have a record of that operation. That is, SYS.AUD$ will have a row identifying the SELECT action on itself, as for example row 1.
If a user later tries to delete this row from SYS.AUD$, then the DELETE operation succeeds, because the user has the privilege to perform this action. However, this DELETE action on SYS.AUD$ is also recorded in the audit trail. Setting up this type of auditing acts as a safety feature, potentially revealing unusual or unauthorized actions.
Note:
DELETE, INSERT, UPDATE, and MERGE operations on SYS.AUD$ table are always audited. These audit records are not allowed to be deleted.See Also:
"Auditing Sensitive Information"You should periodically archive and then purge the audit trail to prevent it from growing too large. Archiving and purging both frees audit trail space and facilitates the purging of the database audit trail. See "Purging Audit Trail Records" for different ways of purging the audit trail records.
You can create an archive of the database audit trail by using one of the following methods:
Oracle Audit Vault. You install Oracle Audit Vault separately from Oracle Database. For more information, see Oracle Audit Vault Administrator's Guide.
Oracle Data Warehouse. Oracle Data Warehouse is automatically installed with Oracle Database. For more information, see Oracle Warehouse Builder Installation and Administration Guide.
After you complete the archive, you can purge the database audit trail contents. See "Purging Audit Trail Records" for more information.
To archive standard and fine-grained audit records, you can copy the relevant records to a normal database table. For example:
INSERT INTO table SELECT ... FROM SYS.AUD$ ...; INSERT INTO table SELECT ... FROM SYS.FGA_LOG$ ...;
To purge the database audit trail, see the following sections:
See Also:
Be aware that an operating system audit trail or file system, including the Windows Event Log, can become full, and therefore, unable to accept new records, including audit records from Oracle Database. In this case, Oracle Database cancels and rolls back the operation being performed, including operations that normally are always audited. (See "Activities That Are Always Audited for All Platforms".) If the operating system audit trail becomes full, then set the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter to use database audit trail (such as DB or DB, EXTENDED). This prevents the audited actions from completing if their audit records cannot be stored. You should periodically archive and purge the operating system audit file to prevent these types of failures.
If you plan to use operating system auditing, then ensure that the operating system audit trail or the file system does not fill completely. Most operating systems provide administrators with sufficient information and warning to ensure this does not occur. If you configure auditing to use the database audit trail, you can prevent this potential loss of audit information. Oracle Database prevents audited events from occurring if the audit trail is unable to accept the database audit record for the statement.
Periodically archive and then purge the operating system audit trail. See "Archiving the Operating System Audit Trail" and "Purging Audit Trail Records"for more information.
To control the size of the operating system audit trail, set the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE property by using the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY PL/SQL procedure. Remember that you must have the EXECUTE privilege for the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package before you can use it. When the operating system file meets the size limitation you set, Oracle Database stops adding records to the current file and then creates a new operating system file for the subsequent records. For more information about the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference.
If you set both the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE and the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_AGE (described in "Setting the Age of the Operating System Audit Trail") properties, then Oracle Database performs the action based the property value limit that is met first.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE => 102400); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Specifies the operating system audit trail. Enter one of the following values:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS: Operating system audit trail files with the .aud extension. (This setting does not apply to Windows Event Log entries. Nor does it apply to syslog audit records, when the AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL initialization parameter is set.)
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML: XML audit trail files.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FILES: Both operating system and XML audit trail files.
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY: Specifies the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE property, which sets the maximum size. To find the status of the current property settings, query the PARAMETER_NAME and PARAMETER_VALUE columns of the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CONFIG_PARAMS data dictionary view.
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE: Sets the maximum size to 102400 kilobytes, that is, 10 megabytes. The default setting is 10,000 kilobytes (approximately 10 megabytes). Do not exceed 2 gigabytes.
Clearing the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE Setting
To clear the maximum file size setting, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAR_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY procedure.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAR_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE, USE_DEFAULT_VALUES => TRUE ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Specifies the operating system audit trail. Enter one of the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE values described in "Setting the Size of the Operating System Audit Trail".
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY: Specifies the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE property. You can query the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CONFIG_PARAMS data dictionary view to find the current status of this property.
USE_DEFAULT_VALUES: Enter one of the following values:
TRUE: Clears the current value and uses the default value, 10,000 kilobytes, instead.
FALSE: Oracle Database does not use a default maximum size for the operating system or XML file growth. The files will continue to grow without limitation unless you configure the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_AGE property. The default setting is FALSE.
To control the age of the operating system audit trail, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY PL/SQL procedure. Remember that you must have the EXECUTE privilege for the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package before you can use it. When the operating system file meets the age limitation you set, Oracle Database stops adding records to the current file and then creates a new operating system file for the subsequent records. For more information about the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference.
If you set both the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_AGE and the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE (described in "Setting the Size of the Operating System Audit Trail") properties, then Oracle Database controls the growth of the Audit file based on the property value limit that is met first.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_AGE, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE => 10 ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Specifies the operating system audit trail. Enter one of the following values:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS: Operating system audit trail files with the .aud extension. (This setting does not apply to Windows Event Log entries. Nor does it apply to syslog audit records, when the AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL initialization parameter is set.)
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML: XML audit trail files.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FILES: Both operating system and XML audit trail files.
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY: Specifies the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_AGE property to set the maximum age. To find the status of the current property setting, query the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CONFIG_PARAMS data dictionary view.
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE: Sets the maximum age to 10 days. Enter a value between 1 and 495. The default age is 5 days.
Clearing the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_AGE Setting
To clear the maximum file age setting, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAR_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY procedure.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAR_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_AGE, USE_DEFAULT_VALUES => TRUE ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Specifies operating system audit trail. Enter one of the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE values listed in "Setting the Age of the Operating System Audit Trail".
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY: Specifies the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_AGE property. Query the PARAMETER_NAME and PARAMETER_VALUE columns of the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CONFIG_PARAMS data dictionary view to find the current status of this property.
USE_DEFAULT_VALUES: Specify one of the following values:
TRUE: Clears the current value and uses the default value, 5 days, instead.
FALSE: Oracle Database does not use a default maximum age for the operating system or XML file growth. In this case, the files will continue to age without limitation unless you configure the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.OS_FILE_MAX_SIZE property. The default setting is FALSE.
You should periodically archive the operating system audit trail. Use your platform-specific operating system tools to create an archive of the operating system audit files.
Use the following methods to archive the operating system audit files:
Use Oracle Audit Vault. You install Oracle Audit Vault separately from Oracle Database. For more information, see Oracle Audit Vault Administrator's Guide.
Create tape or disc backups. You can create a compressed file of the audit files, and then store it on tapes or discs. Consult your operating system documentation for more information.
Afterwards, you should purge (delete) the operating system audit records both to free audit trail space and to facilitate audit trail management. See "Purging Audit Trail Records" for different ways that you can use to purge the operating system audit trail records.
This section contains:
You should periodically archive and then delete (purge) audit trail records, because the audit trail cannot accept new records if it grows too large. This section describes a variety of ways that you can use to purge both the database and operating system audit trail records. You can purge a subset of database audit trail records. For both database and operating system audit trail types, you can manually purge the records or create a purge job that performs at a specified time interval. In that case, the purge operation either purges the audit trail records that were created before the archive timestamp, or it purges all audit trail records.
To perform the audit trail purge tasks, in most cases, you use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package. You must have the EXECUTE privilege for DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT before you can use it.
If you have Oracle Audit Vault installed, the audit trail purge process differs from the procedures described in this manual. For example, Oracle Audit Vault archives the audit trail for you. See Oracle Audit Vault Administrator's Guide.
Note:
Oracle Database audits all deletions from the audit trail, without exception. See "Auditing the Database Audit Trail" and "Auditing SYS Administrative Users".See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for more information about the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package
Oracle Database Reference for detailed information about the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT-related views
Table 9-7 provides a roadmap for selecting an audit trail purge method.
Table 9-7 Selecting an Audit Trail Purge Method
| What Do You Want to Purge? | About This Type of Purge Method |
|---|---|
|
All audit records, or audit records created before a specified timestamp, on a regularly scheduled basis |
You can schedule a purge operation to occur an specific times. For example, you can schedule it for every Saturday at 2 a.m. General steps:
See "Scheduling an Automatic Purge Job for the Audit Trail" for more information. |
|
All audit records, or records that were created before a specified timestamp, when you want |
You can manually purge the audit records right away in a one-time operation, rather than creating a purge schedule. General steps:
See "Manually Purging the Audit Trail" for more information. |
|
Just a subset of the audit records from the database audit trail |
You can manually purge just a subset of the audit records. For example, you can delete all audit records that were created between May 14, 2009 and June 14, 2009. General steps:
See "Purging a Subset of Records from the Database Audit Trail" for more information. |
You can purge the entire audit trail, or only a portion of the audit trail that was created before a timestamp. For the database audit trail, the individual audit records created before the timestamp can be purged. For the operating system audit trail, you purge audit files that were created before the timestamp.
Be aware that purging the audit trail, particularly a large one, can take a while to complete. Consider scheduling the purge job so that it runs during a time when the database is not busy.
You can create multiple purge jobs for different audit trail types, so long as they do not conflict. For example, you can create a purge job for the standard audit trail table and then the fine-grained audit trail table. However, you cannot then create a purge job for both or all types, that is, by using the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_STD or DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_ALL property.
To create and schedule an automatic purge job:
Step 1: If Necessary, Tune Online and Archive Redo Log Sizes
Step 4: Optionally, Set an Archive Timestamp for Audit Records
Step 6: Optionally, Configure the Audit Trail Records to be Deleted in Batches
The purge process may generate additional redo logs. Before you run this process, you may need to tune online and archive redo log sizes to accommodate the additional records generated during the audit table purge process. For more information about tuning log files, see Oracle Database Performance Tuning Guide and Oracle Database Administrator's Guide.
You must record the timestamp of the database and operating system audit records before you can archive them. You can check the timestamp date by querying the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_LAST_ARCH_TS data dictionary view. Later on, when the purge takes place, Oracle Database purges only the audit trail records that were created before the date of this timestamp. See "Step 4: Optionally, Set an Archive Timestamp for Audit Records" for more information.
After you have timestamped the records, you are ready to archive them. See the following sections for more information:
Before you can purge the audit trail by using the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL PL/SQL procedure, you must initialize the audit trail for the cleanup operation. For the database audit trail, if you have not moved the database audit trail tables (SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$) from the SYSTEM tablespace to another tablespace, this process moves these tables to the SYSAUX tablespace or to the tablespace that you specified in "Moving the Database Audit Trail to a Different Tablespace". Be aware that moving these tables takes a while, so you may want to schedule the initialization process during time when the database is not busy.
To initialize the audit trail cleanup operation:
Log in to SQL*Plus as an administrative user who has the EXECUTE privilege on the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT PL/SQL package.
If you have not done so already, initialize the audit trail cleanup operation by running the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.INIT_CLEANUP procedure. (You only need to perform this step once.
You can check if the audit trail has been initialized for cleanup by running the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.IS_CLEANUP_INITIALIZED function. See "Verifying That the Audit Trail Is Initialized for Cleanup".)
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.INIT_CLEANUP( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD, DEFAULT_CLEANUP_INTERVAL => 12 ); END; /
In this specification:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Enter one of the following values:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD: Standard audit trail table, AUD$.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD: Fine-grained audit trail table, FGA_LOG$.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_STD: Both standard and fine-grained audit trail tables.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS: Operating system audit trail files with the .aud extension. (This setting does not apply to Windows Event Log entries.)
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML: XML Operating system audit trail files.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FILES: Both operating system and XML audit trail files.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_ALL: All audit trail records, that is, both database audit trail and operating system audit trail types.
DEFAULT_CLEANUP_INTERVAL: Specify the desired default hourly purge interval (for example, 12 for every 12 hours). The DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT procedures use this value to determine how to purge audit records. The timing begins when you run the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.INIT_CLEANUP procedure. To update this value later, set the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_UP_INTERVAL property of the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY procedure.
The DEFAULT_CLEANUP_INTERVAL setting must indicate the frequency in which DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL is called. If you are uncertain about the frequency, set it to an approximate value. You can change this value later on by using the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY procedure.
If you want to delete all of the audit trail, you can bypass this step.
You can set a timestamp when the last audit record was archived. Setting an archive timestamp provides a hint to the cleanup infrastructure that the cleanup operation will be invoked every 6 hours.
For the database audit trail, you must set the timestamp after you have initialized the audit trail cleanup operation. To find the last archive timestamps for the audit trail, you can query the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_LAST_ARCH_TS data dictionary view. After you set the timestamp, all audit records in the audit trail that indicate a time earlier than that timestamp are purged when you run the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL PL/SQL procedure. If you want to clear the archive timestamp setting, see "Clearing the Archive Timestamp Setting".
For the operating system audit trail, remember that you cannot delete individual audit records in the operating system (including XML) audit files. Instead, Oracle Database removes the entire file that contains the timestamped records.
If you are using Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC), then use Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize the time on each computer where you have installed an Oracle Database instance. For example, suppose you set the time for one Oracle RAC instance node at 11:00:00 a.m. and then set the next Oracle RAC instance node at 11:00:05. As a result, the two nodes have inconsistent times. You can use Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize the times for these Oracle RAC instance nodes.
To set the timestamp, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_LAST_ARCHIVE_TIMESTAMP PL/SQL procedure.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_LAST_ARCHIVE_TIMESTAMP( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, LAST_ARCHIVE_TIME => '2009-05-28 06:30:00.00' RAC_INSTANCE_NUMBER => 0 ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Enter one of the following settings:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD: Specified the standard audit trail table, AUD$.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD: Specifies the fine-grained audit trail table, FGA_LOG$.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS: Operating system audit trail files with the .aud extension. (This setting does not apply to Windows Event Log entries.)
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML: Specifies XML audit trail files.
LAST_ARCHIVE_TIME: Enter the timestamp in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS.FF UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) format for AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD and AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD (standard and fine-grained audit trails), and in the Local Time Zone for AUDIT_TRAIL_OS and AUDIT_TRAIL_XML (operating system and XML audit trails).
RAC_INSTANCE_NUMBER: Specifies the instance number for an Oracle RAC installation. If you specified the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD or DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD audit trail types, you can omit the RAC_INSTANCE_NUMBER argument. This is because there is only one AUD$ and FGA_LOG$ table, even for a RAC installation. The default is 0, which is used for single-instance database installations.
Typically, after you set the timestamp, you can use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL PL/SQL procedure to remove the audit records that were created before the timestamp date.
Create and schedule the purge job by running the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CREATE_PURGE_JOB PL/SQL procedure.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CREATE_PURGE_JOB ( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD, AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_INTERVAL => 12, AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_NAME => 'Standard_Audit_Trail_PJ', USE_LAST_ARCH_TIMESTAMP => TRUE ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Enter one of the following values:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD: Standard audit trail table, AUD$
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD: Fine-grained audit trail table, FGA_LOG$
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_STD: Both standard and fine-grained audit trail tables
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS: Operating system audit trail files with the .aud extension. (This setting does not apply to Windows Event Log entries.)
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML: XML audit trail files
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FILES: Both operating system and XML audit trail files
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_ALL: All audit trail records, that is, both database audit trail and operating system audit trail types
AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_INTERVAL: Specify the hourly interval for this purge job to run. The timing begins when you run the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CREATE_PURGE_JOB procedure, in this case, 12 hours after you run this procedure. Later on, if you want to update this value, run the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_PURGE_JOB_INTERVAL procedure.
USE_LAST_ARCH_TIMESTAMP: Enter either of the following settings:
TRUE: Deletes audit records created before the last archive timestamp. To check the last recorded timestamp, query the LAST_ARCHIVE_TS column of the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_LAST_ARCH_TS data dictionary view. The default value is TRUE. Oracle recommends that you set USE_LAST_ARCH_TIMESTAMP to TRUE.
FALSE: Deletes all audit records without considering last archive timestamp. Be careful about using this setting, in case you inadvertently delete audit records that should have been deleted.
By default, the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT package procedures delete the database and operating system audit trail records in batches of 10000 database audit records, or 1000 operating system audit files. You can set this batch size to a different value if you want. Later on, when Oracle Database runs the purge job, it deletes each batch, rather than all records together. If the audit trail is very large (and they can grow quite large), deleting the records in batches facilitates the purge operation.
To find the current batch setting, you can query the PARAMETER_NAME and PARAMETER_VALUE columns of the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CONFIG_PARAMS data dictionary view. To set the batch size, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY procedure. If you later want to clear this setting, see "Clearing the Database Audit Trail Batch Size".
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.DB_DELETE_BATCH_SIZE, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE => 100000); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Specifies the audit trail type, which in this case is the database system audit trail. Enter one of the following values:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD: Standard audit trail table, AUD$.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD: Fine-grained audit trail table, FGA_LOG$.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS: Operating system audit files.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML: XML audit files.
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY: Uses the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.DB_DELETE_BATCH_SIZE property to indicate the database audit trail batch size setting. If you want to batch the operating system audit trail, then use the FILE_DELETE_BATCH_SIZE property.
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE: Sets the number of audit record files to be 100,000 for each batch. Enter a value between 100 and 1000000. To determine this number, consider the total number of records being purged, and the time interval in which the purge operation is performed. The default is 10000 for the database audit trail and 1000 for the operating system audit trail records.
You can manually purge the audit trail right away, without scheduling a purge job. Similar to a purge job, you can purge audit trail records that were created before an archive timestamp date or all the records in the audit trail.
Note the following about the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL PL/SQL procedure:
Only the current audit directory is cleaned up when you run this procedure.
On Microsoft Windows, because the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT package does not support cleanup of Windows Event Viewer, setting the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE property to DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS has no effect. This is because operating system audit records on Windows are written to Windows Event Viewer. The DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT package does not support this type of cleanup operation.
On UNIX platforms, if you set the AUDIT_SYSLOG_LEVEL initialization parameter to a valid value as listed in Oracle Database Reference, then Oracle Database writes the operating system log files to syslog files. If you set the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE property to DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS, then the procedure only removes .aud files under audit directory (This directory is specified by the AUDIT_FILE_DEST initialization parameter).
When the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE parameter is set to DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML, this procedure only cleans up XML audit files (.xml) in the current audit directory. Oracle Database maintains an index file, called adx_$ORACLE_SID.txt, which lists the XML files that were generated by the XML auditing. The cleanup procedure does not remove this file.
For database audit trails, you must initialize the cleanup infrastructure by running the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.INIT_CLEANUP procedure, and then purging the database audit trail by using the method described in "Purging a Subset of Records from the Database Audit Trail".
To manually purge the audit trail:
Follow these steps under "Scheduling an Automatic Purge Job for the Audit Trail":
Purge the audit trail records by running the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL PL/SQL procedure.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD, USE_LAST_ARCH_TIMESTAMP => TRUE ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Enter one of the following values:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD: Standard audit trail table, AUD$
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD: Fine-grained audit trail table, FGA_LOG$
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_STD: Both standard and fine-grained audit trail tables
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS: Operating system audit trail files with the .aud extension. (This setting does not apply to Windows Event Log entries.)
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML: XML audit trail files
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FILES: Both operating system and XML audit trail files
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_ALL: All audit trail records, that is, both database audit trail and operating system audit trail types
USE_LAST_ARCH_TIMESTAMP: Enter either of the following settings:
TRUE: Deletes audit records created before the last archive timestamp. To set the archive timestamp, see "Step 4: Optionally, Set an Archive Timestamp for Audit Records". The default (and recommended) value is TRUE. Oracle recommends that you set USE_LAST_ARCH_TIMESTAMP to TRUE.
FALSE: Deletes all audit records without considering last archive timestamp. Be careful about using this setting, in case you inadvertently delete audit records that should have been deleted.
You can manually remove records from the database audit trail tables. This method can be useful if you want to remove a specific subset of records. You can use this method if the database audit trail table is in any tablespace, including the SYSTEM tablespace.
For example, to delete audit records that were created later than the evening of February 28, 20098 but before March 28, 2009, enter the following statement:
DELETE FROM SYS.AUD$
WHERE NTIMESTAMP# > TO_TIMESTAMP ('28-FEB-09 09.07.59.907000 PM') AND
NTIMESTAMP# < TO_TIMESTAMP ('28-MAR-09 09.07.59.907000 PM');
Alternatively, to delete all audit records from the audit trail, enter the following statement:
DELETE FROM SYS.AUD$;
Only the user SYS or a user to whom SYS granted the DELETE privilege on SYS.AUD$ can delete records from the database audit trail.
Note:
If the audit trail is full and connections are being audited (that is, if theAUDIT SESSION statement is set), then typical users cannot connect to the database because the associated audit record for the connection cannot be inserted into the audit trail. In this case, connect as SYS with the SYSDBA privilege, and make space available in the audit trail. Remember that operations by SYS are not recorded in the standard audit trail, but they are audited if you set the AUDIT_SYS_OPERATIONS parameter to TRUE.After you delete the rows from the database audit trail table, the freed space is available for reuse by that table. (The SYS.AUD$ table is allocated only as many extents as are necessary to maintain current audit trail records.) You do not need to do anything to make this space available to the table for reuse. If you want to use this space for another table, then you can run the following statement to free the space to the tablespace so that other objects can allocate its space:
ALTER TABLE SYS.AUD$ SHRINK SPACE;
If you want to both delete all the rows from the database audit trail table and free the used space for other tablespace objects, use the TRUNCATE TABLE statement. For example:
TRUNCATE TABLE SYS.AUD$;
Note:
SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ are the only SYS objects that can ever be directly modified.This section contains:
Setting the Default Audit Trail Purge Interval for Any Audit Trail Type
Setting the Default Audit Trail Purge Job Interval for a Specified Purge Job
You can check if the audit trail has been initialized for cleanup by running the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.IS_CLEANUP_INITIALIZED function. If the audit trail has been initialized, then this function returns TRUE. If it is not, it returns FALSE.
For example:
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
BEGIN
IF
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.IS_CLEANUP_INITIALIZED(DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD)
THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('AUD$ is initialized for cleanup');
ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('AUD$ is not initialized for cleanup.');
END IF;
END;
/
This example verifies that the database standard audit trail has been initialized and returns a message indicating its status. To select a setting for a different audit trail, choose from the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE settings described in "Step 3: Initialize the Audit Trail Cleanup Operation".
You can set a default purge operation interval, in hours, that must pass before the next purge operation takes place for a specified audit trail type.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_UP_INTERVAL, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE => 24 ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Specifies the audit trail type, which in this case is the database standard audit trail. Choose from the following settings:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD: Standard audit trail table, AUD$
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD: Fine-grained audit trail table, FGA_LOG$
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_STD: Both standard and fine-grained audit trail tables
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS: Operating system audit trail files with the .aud extension. (This setting does not apply to Windows Event Log entries.)
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML: XML Operating system audit trail files
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FILES: Both operating system and XML audit trail files
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_ALL: All audit trail records, that is, both database audit trail and operating system audit trail types
You can set a default interval for multiple audit trail types, so long as they do not conflict. For example, you can set individual intervals for the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_AUD and DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD properties, but not for the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_DB_STD property.
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY: Sets the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_UP_INTERVAL property to indicate the purge operation interval setting. To find the current property settings, query the PARAMETER_NAME and PARAMETER_VALUE columns of the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CONFIG_PARAMS data dictionary view. The timing begins when you set the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_UP_INTERVAL property.
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE: Updates the default hourly interval set by the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.INIT_CLEANUP procedure. Enter a value between 1 and 999.
You can cancel the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.INIT_CLEANUP settings, that is, the default cleanup interval, by invoking the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.DEINIT_CLEANUP procedure.
For example, to cancel all purge settings for the standard audit trail:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.DEINIT_CLEANUP( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Enter one of the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE settings listed in "Step 3: Initialize the Audit Trail Cleanup Operation".
To enable or disable an audit trail purge job, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_PURGE_JOB_STATUS PL/SQL procedure.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_PURGE_JOB_STATUS( AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_NAME => 'OS_Audit_Trail_PJ', AUDIT_TRAIL_STATUS_VALUE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.PURGE_JOB_ENABLE); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_NAME: Specifies a purge job called OS_Audit_Trail_PJ. To find existing purge jobs, query the JOB_NAME and JOB_STATUS columns of the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CLEANUP_JOBS data dictionary view.
AUDIT_TRAIL_STATUS_VALUE: Enter one of the following properties:
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.PURGE_JOB_ENABLE: Enables the specified purge job.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.PURGE_JOB_DISABLE: Disables the specified purge job.
You can set a default purge operation interval, in hours, that must pass before the next purge job operation takes place. The interval setting that is used in the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CREATE_PURGE_JOB procedure takes precedence over this setting.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_PURGE_JOB_INTERVAL( AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_NAME => 'OS_Audit_Trail_PJ', AUDIT_TRAIL_INTERVAL_VALUE => 24 ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_NAME: Specifies the name of the audit trail purge job. To find a list of existing purge jobs, query the JOB_NAME and JOB_STATUS columns of the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CLEANUP_JOBS data dictionary view.
AUDIT_TRAIL_INTERVAL_VALUE: Updates the default hourly interval set by the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CREATE_PURGE_JOB procedure. Enter a value between 1 and 999. The timing begins when you run the purge job.
To delete an audit trail purge job, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.DROP_PURGE_JOB PL/SQL procedure. To find existing purge jobs, query the JOB_NAME and JOB_STATUS columns of the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CLEANUP_JOBS data dictionary view.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.DROP_PURGE_JOB( AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_NAME => 'FGA_Audit_Trail_PJ'); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_PURGE_NAME: Specifies a purge job called FGA_Audit_Trail_PJ.
To clear the archive timestamp setting, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAR_LAST_ARCHIVE_TIMESTAMP PL/SQL procedure.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAR_LAST_ARCHIVE_TIMESTAMP( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML', RAC_INSTANCE_NUMBER => 1 ); END; /
In this example:
RAC_INSTANCE_NUMBER: If the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE property is set to DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_OS or DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_XML, then you cannot set RAC_INSTANCE_NUMBER to 0. You can omit this setting or specify 1 to indicate an instance number.
You can omit the RAC_INSTANCE_NUMBER setting when AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE is DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD or DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_FGA_STD, or if the database is not an Oracle RAC database. Otherwise, specify the correct instance number. You can find the instance number by issuing the SHOW PARAMETER INSTANCE_NUMBER command in SQL*Plus.
To clear the batch size setting, use the DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAR_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY procedure.
For example:
BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAR_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.DB_DELETE_BATCH_SIZE, USE_DEFAULT_VALUES => TRUE ); END; /
In this example:
AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE: Specifies the audit trail type, which in this case is the database system audit trail. Enter one of the AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE values listed in "Step 6: Optionally, Configure the Audit Trail Records to be Deleted in Batches".
AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY: Specifies the DB_DELETE_BATCH_SIZE property. Query the DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CONFIG_PARAMS data dictionary view to find the current status of this property.
USE_DEFAULT_VALUES: Is set to TRUE, which clears the current audit record batch size and uses the default value, 10000, instead.
The pseudo code in Example 9-26 creates a database audit trail purge operation that the user calls by invoking the DBMS_ADUIT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL procedure. The purge operation deletes records that were created before the last archived timestamp by using a loop. The loop archives the audit records, calculates which audit records were archived and uses the SetCleanUpAuditTrail call to set the last archive timestamp, and then calls the CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL procedure. It deletes the database audit trail records in batches of 100,000 records each. In this example, major steps are in bold typeface.
Example 9-26 Directly Calling a Database Audit Trail Purge Operation
-- 1. Initialize the AUD$ table for cleanup: PROCEDURE CleanUpAuditTrailMain() BEGIN -- Connect to the database using appropriate login. CALL ConnectToDatabase(); -- The login used must have privileges to modify Audit settings. -- Currently, the DBA will be the authorized user DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.INIT_CLEANUP( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, DEFAULT_CLEANUP_INTERVAL => 12 ); END; /*PROCEDURE */ / -- 2. Optionally, set the batch size: BEGIN DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.DB_DELETE_BATCH_SIZE, AUDIT_TRAIL_PROPERTY_VALUE => 100000 /* delete batch size */); END; /*PROCEDURE */ / -- 3. Set the last archive timestamp: PROCEDURE SetCleanUpAuditTrail() BEGIN CALL FindLastArchivedTimestamp(AUD$); DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_LAST_ARCHIVE_TIMESTAMP( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, LAST_ARCHIVE_TIME => '20-AUG-2009 00:00:00'); END /* PROCEDURE */ / -- 4. Run a customized archive procedure to purge the audit trail records: BEGIN CALL MakeAuditSettings(); LOOP (/* How long to loop*/) -- Invoke function for audit record archival CALL DoAuditRecordArchival(AUD$); CALL SetCleanUpAuditTrail(); IF(/* Clean up is needed immediately */) DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL( AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_AUD_STD, USE_LAST_ARCH_TIMESTAMP => TRUE); END IF END LOOP /*LOOP*/ END; /* PROCEDURE */ /
This section contains:
Using Data Dictionary Views to Find Information About the Audit Trail
Using Audit Trail Views to Investigate Suspicious Activities
Tip:
To find error information about audit policies, check the trace files. TheUSER_DUMP_DEST initialization parameter sets the location of the trace files.Table 9-8 lists data dictionary views that provide auditing information. For detailed information about these views, see Oracle Database Reference.
Table 9-8 Data Dictionary Views That Display Information about the Database Audit Trail
| View | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Describes the fine-grained auditing policies on the tables and views accessible to the current user |
|
|
Describes the fine-grained auditing policy columns on the tables and views accessible to the current user. |
ALL_DEF_AUDIT_OPTS |
Lists default object-auditing options that are to be applied when objects are created |
AUDIT_ACTIONS |
Describes audit trail action type codes |
DBA_AUDIT_EXISTS |
Lists audit trail entries produced |
|
|
Displays the history of purge events. Periodically, as user DELETE FROM DBA_AUDIT_MGMT_CLEAN_EVENTS; |
|
|
Displays the currently configured audit trail purge jobs |
|
|
Displays the currently configured audit trail properties that are used by the |
|
|
Displays the last archive timestamps that have set for audit trail purges. |
DBA_AUDIT_OBJECT |
Lists audit trail records for all objects in the system |
|
|
Lists all the fine-grained auditing policies on the system |
DBA_AUDIT_SESSION |
Lists all audit trail records concerning |
|
|
Describes the fine-grained auditing policy columns on the tables and views throughout the database. |
|
|
Lists audit trail records concerning |
|
|
Lists all standard audit trail entries in the |
|
|
Combines standard and fine-grained audit log records, and includes |
|
|
Lists audit trail records for fine-grained auditing. |
|
|
Describes auditing options on all objects |
DBA_PRIV_AUDIT_OPTS |
Describes current system privileges being audited across the system and by user |
DBA_STMT_AUDIT_OPTS |
Describes current statement auditing options across the system and by user |
|
|
Lists audit trail records for statements concerning objects that are accessible to the current user |
|
|
Describes the fine-grained auditing policy columns on the tables and views accessible to the current user. |
|
|
Lists all audit trail records concerning connections and disconnections for the current user |
USER_AUDIT_STATEMENT |
Lists audit trail records concerning |
USER_AUDIT_TRAIL |
Lists all standard audit trail entries in the |
USER_OBJ_AUDIT_OPTS |
Describes auditing options on all objects owned by the current user |
|
|
Contains log history information. To query this view, you must have the |
|
|
Shows standard, fine-grained, |
This section provides examples that demonstrate how to examine and interpret the information in the audit trail. Suppose you want to audit the database for the following suspicious activities:
Passwords, tablespace settings, and quotas for some database users are altered without authorization.
A high number of deadlocks occur, most likely because of users acquiring exclusive table locks.
Rows are arbitrarily deleted from the emp table in laurel's schema.
You suspect the users jward and swilliams of several of these detrimental actions.
To investigate, you issue the following statements (in the order specified):
AUDIT ALTER, INDEX, RENAME ON DEFAULT;
CREATE VIEW laurel.employee AS SELECT * FROM laurel.emp;
AUDIT SESSION BY jward, swilliams;
AUDIT ALTER USER;
AUDIT LOCK TABLE
BY ACCESS
WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL;
AUDIT DELETE ON laurel.emp
BY ACCESS
WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL;
The following statements are subsequently issued by the user jward:
ALTER USER tsmith QUOTA 0 ON users; DROP USER djones;
The following statements are subsequently issued by the user swilliams:
LOCK TABLE laurel.emp IN EXCLUSIVE MODE;
DELETE FROM laurel.emp WHERE mgr = 7698;
ALTER TABLE laurel.emp ALLOCATE EXTENT (SIZE 100K);
CREATE INDEX laurel.ename_index ON laurel.emp (ename);
CREATE PROCEDURE laurel.fire_employee (empid NUMBER) AS
BEGIN
DELETE FROM laurel.emp WHERE empno = empid;
END;
/
EXECUTE laurel.fire_employee(7902);
The following sections display the information relevant to your investigation that can be viewed using the audit trail views in the data dictionary:
The following query returns all the statement audit options that are set:
SELECT * FROM DBA_STMT_AUDIT_OPTS;
Output similar to the following appears:
USER_NAME AUDIT_OPTION SUCCESS FAILURE -------------------- ------------------- ---------- --------- JWARD DROP ANY CLUSTER BY ACCESS BY ACCESS SWILLIAMS DEBUG PROCEDURE BY ACCESS BY ACCESS MSEDLAK ALTER RESOURCE COST BY ACCESS BY ACCESS
The following query returns all the privilege audit options that are set:
SELECT * FROM DBA_PRIV_AUDIT_OPTS;
Output similar to the following appears:
USER_NAME PRIVILEGE SUCCESS FAILURE ------------------- -------------------- --------- ---------- ALTER USER BY ACCESS BY ACCESS
The following query returns all audit options set for any objects with names that start with the characters emp and that are contained in the schema of laurel:
SELECT * FROM DBA_OBJ_AUDIT_OPTS
WHERE OWNER = 'LAUREL' AND OBJECT_NAME LIKE 'EMP%';
Output similar to the following appears:
OWNER OBJECT_NAME OBJECT_TY ALT AUD COM DEL GRA IND INS LOC ... ----- ----------- --------- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- ... LAUREL EMP TABLE S/S -/- -/- A/- -/- S/S -/- -/- ... LAUREL EMPLOYEE VIEW -/- -/- -/- A/- -/- S/S -/- -/- ...
The view returns information about all the audit options for the specified object. The information in the view is interpreted as follows:
A dash (-) indicates that the audit option is not set.
The S character indicates that the audit option is set BY SESSION.
The A character indicates that the audit option is set BY ACCESS.
Each audit option has two possible settings, WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL and WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL, separated by a slash (/). For example, the DELETE audit option for laurel.emp is set BY ACCESS for successful DELETE statements and not set at all for unsuccessful DELETE statements.
The following query returns all default object audit options:
SELECT * FROM ALL_DEF_AUDIT_OPTS;
Output similar to the following appears:
ALT AUD COM DEL GRA IND INS LOC REN SEL UPD REF EXE FBK REA --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- S/S -/- -/- -/- -/- S/S -/- -/- S/S -/- -/- -/- -/- /- -/-
Notice that the view returns information similar to the USER_OBJ_AUDIT_OPTS and DBA_OBJ_AUDIT_OPTS views (refer to previous example).
The following query lists audit records generated for all objects in the database:
SELECT * FROM DBA_AUDIT_OBJECT;
The following query lists audit information corresponding to the AUDIT SESSION statement audit option:
SELECT USERNAME, LOGOFF_TIME, LOGOFF_LREAD, LOGOFF_PREAD,
LOGOFF_LWRITE, LOGOFF_DLOCK
FROM DBA_AUDIT_SESSION;
Output similar to the following appears:
USERNAME LOGOFF_TI LOGOFF_LRE LOGOFF_PRE LOGOFF_LWR LOGOFF_DLO ---------- --------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- JWARD 02-AUG-91 53 2 24 0 SWILLIAMS 02-AUG-91 3337 256 630 0
Footnote Legend
Footnote 1: "Nondatabase users" refers to application users who are recognized in the database using theCLIENT_IDENTIFIER attribute. To audit this type of user, you can use a fine-grained audit policy. See "Auditing Specific Activities with Fine-Grained Auditing" for more information.SYS.AUD$ and SYS.FGA_LOG$ tables. The CLIENTID column in these tables records the name of the nondatabase user. The USERID column in the SYS.AUD$ table and the DBUID column of the SYS.FGA_LOG$ store the database user account. For nondatabase users, the USERID and DBUID columns store the database user account that was created to enable the nondatabase user access to the database. The DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL, DBA_FGA_AUDIT_TRAIL, and DBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL views store this information in the CLIENT_ID, USERNAME, and DB_USER columns.