| Oracle® Database Utilities 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10701-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Utilities 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10701-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes the field-list portion of the SQL*Loader control file. The following topics are included:
The field-list portion of a SQL*Loader control file provides information about fields being loaded, such as position, datatype, conditions, and delimiters.
Example 10-1 shows the field list section of the sample control file that was introduced in Chapter 9.
Example 10-1 Field List Section of Sample Control File
. . . 1 (hiredate SYSDATE, 2 deptno POSITION(1:2) INTEGER EXTERNAL(2) NULLIF deptno=BLANKS, 3 job POSITION(7:14) CHAR TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE NULLIF job=BLANKS "UPPER(:job)", mgr POSITION(28:31) INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE, NULLIF mgr=BLANKS, ename POSITION(34:41) CHAR TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE "UPPER(:ename)", empno POSITION(45) INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE, sal POSITION(51) CHAR TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE "TO_NUMBER(:sal,'$99,999.99')", 4 comm INTEGER EXTERNAL ENCLOSED BY '(' AND '%' ":comm * 100" )
In this sample control file, the numbers that appear to the left would not appear in a real control file. They are keyed in this sample to the explanatory notes in the following list:
SYSDATE sets the column to the current system date. See Setting a Column to the Current Date.
POSITION specifies the position of a data field. See Specifying the Position of a Data Field.
INTEGER EXTERNAL is the datatype for the field. See Specifying the Datatype of a Data Field and Numeric EXTERNAL.
The NULLIF clause is one of the clauses that can be used to specify field conditions. See Using the WHEN, NULLIF, and DEFAULTIF Clauses.
In this sample, the field is being compared to blanks, using the BLANKS parameter. See Comparing Fields to BLANKS.
The TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE clause is one of the delimiters it is possible to specify for a field. See Specifying Delimiters.
The ENCLOSED BY clause is another possible field delimiter. See Specifying Delimiters.
To load data from the datafile, SQL*Loader must know the length and location of the field. To specify the position of a field in the logical record, use the POSITION clause in the column specification. The position may either be stated explicitly or relative to the preceding field. Arguments to POSITION must be enclosed in parentheses. The start, end, and integer values are always in bytes, even if character-length semantics are used for a datafile.
The syntax for the position specification (pos_spec) clause is as follows:
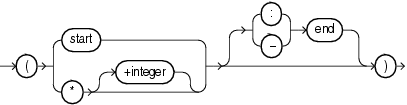
Table 10-1 describes the parameters for the position specification clause.
Table 10-1 Parameters for the Position Specification Clause
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The starting column of the data field in the logical record. The first byte position in a logical record is 1. |
|
|
The ending position of the data field in the logical record. Either |
|
|
Specifies that the data field follows immediately after the previous field. If you use |
|
+i |
You can use an offset, specified as +i |
You may omit POSITION entirely. If you do, the position specification for the data field is the same as if POSITION(*) had been used.
When you are determining field positions, be alert for tabs in the datafile. Suppose you use the SQL*Loader advanced SQL string capabilities to load data from a formatted report. You would probably first look at a printed copy of the report, carefully measure all character positions, and then create your control file. In such a situation, it is highly likely that when you attempt to load the data, the load will fail with multiple "invalid number" and "missing field" errors.
These kinds of errors occur when the data contains tabs. When printed, each tab expands to consume several columns on the paper. In the datafile, however, each tab is still only one character. As a result, when SQL*Loader reads the datafile, the POSITION specifications are wrong.
To fix the problem, inspect the datafile for tabs and adjust the POSITION specifications, or else use delimited fields.
See Also:
Specifying DelimitersIn a multiple table load, you specify multiple INTO TABLE clauses. When you specify POSITION(*) for the first column of the first table, the position is calculated relative to the beginning of the logical record. When you specify POSITION(*) for the first column of subsequent tables, the position is calculated relative to the last column of the last table loaded.
Thus, when a subsequent INTO TABLE clause begins, the position is not set to the beginning of the logical record automatically. This allows multiple INTO TABLE clauses to process different parts of the same physical record. For an example, see Extracting Multiple Logical Records.
A logical record might contain data for one of two tables, but not both. In this case, you would reset POSITION. Instead of omitting the position specification or using POSITION(*+n) for the first field in the INTO TABLE clause, use POSITION(1) or POSITION(n).
siteid POSITION (*) SMALLINT siteloc POSITION (*) INTEGER
If these were the first two column specifications, siteid would begin in column 1, and siteloc would begin in the column immediately following.
ename POSITION (1:20) CHAR empno POSITION (22-26) INTEGER EXTERNAL allow POSITION (*+2) INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY "/"
Column ename is character data in positions 1 through 20, followed by column empno, which is presumably numeric data in columns 22 through 26. Column allow is offset from the next position (27) after the end of empno by +2, so it starts in column 29 and continues until a slash is encountered.
You may load any number of a table's columns. Columns defined in the database, but not specified in the control file, are assigned null values.
A column specification is the name of the column, followed by a specification for the value to be put in that column. The list of columns is enclosed by parentheses and separated with commas as follows:
(columnspec,columnspec, ...)
Each column name (unless it is marked FILLER) must correspond to a column of the table named in the INTO TABLE clause. A column name must be enclosed in quotation marks if it is a SQL or SQL*Loader reserved word, contains special characters, or is case sensitive.
If the value is to be generated by SQL*Loader, the specification includes the RECNUM, SEQUENCE, or CONSTANT parameter. See Using SQL*Loader to Generate Data for Input.
If the column's value is read from the datafile, the data field that contains the column's value is specified. In this case, the column specification includes a column name that identifies a column in the database table, and a field specification that describes a field in a data record. The field specification includes position, datatype, null restrictions, and defaults.
It is not necessary to specify all attributes when loading column objects. Any missing attributes will be set to NULL.
A filler field, specified by BOUNDFILLER or FILLER is a datafile mapped field that does not correspond to a database column. Filler fields are assigned values from the data fields to which they are mapped.
Keep the following in mind regarding filler fields:
The syntax for a filler field is same as that for a column-based field, except that a filler field's name is followed by FILLER.
Filler fields have names but they are not loaded into the table.
Filler fields can be used as arguments to init_specs (for example, NULLIF and DEFAULTIF).
Filler fields can be used as arguments to directives (for example, SID, OID, REF, and BFILE).
To avoid ambiguity, if a Filler field is referenced in a directive, such as BFILE, and that field is declared in the control file inside of a column object, then the field name must be qualified with the name of the column object. This is illustrated in the following example:
LOAD DATA INFILE * INTO TABLE BFILE1O_TBL REPLACE FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' ( emp_number char, emp_info_b column object ( bfile_name FILLER char(12), emp_b BFILE(constant "SQLOP_DIR", emp_info_b.bfile_name) NULLIF emp_info_b.bfile_name = 'NULL' ) ) BEGINDATA 00001,bfile1.dat, 00002,bfile2.dat, 00003,bfile3.dat,
Filler fields can be used in field condition specifications in NULLIF, DEFAULTIF, and WHEN clauses. However, they cannot be used in SQL strings.
Filler field specifications cannot contain a NULLIF or DEFAULTIF clause.
Filler fields are initialized to NULL if TRAILING NULLCOLS is specified and applicable. If another field references a nullified filler field, an error is generated.
Filler fields can occur anyplace in the datafile, including inside the field list for an object or inside the definition of a VARRAY.
SQL strings cannot be specified as part of a filler field specification, because no space is allocated for fillers in the bind array.
A sample filler field specification looks as follows:
field_1_count FILLER char,
field_1 varray count(field_1_count)
(
filler_field1 char(2),
field_1 column object
(
attr1 char(2),
filler_field2 char(2),
attr2 char(2),
)
filler_field3 char(3),
)
filler_field4 char(6)
The datatype specification of a field tells SQL*Loader how to interpret the data in the field. For example, a datatype of INTEGER specifies binary data, while INTEGER EXTERNAL specifies character data that represents a number. A CHAR field can contain any character data.
Only one datatype can be specified for each field; if a datatype is not specified, CHAR is assumed.
SQL*Loader Datatypes describes how SQL*Loader datatypes are converted into Oracle datatypes and gives detailed information about each SQL*Loader datatype.
Before you specify the datatype, you must specify the position of the field.
SQL*Loader datatypes can be grouped into portable and nonportable datatypes. Within each of these two groups, the datatypes are subgrouped into value datatypes and length-value datatypes.
Portable versus nonportable refers to whether the datatype is platform dependent. Platform dependency can exist for several reasons, including differences in the byte ordering schemes of different platforms (big-endian versus little-endian), differences in the number of bits in a platform (16-bit, 32-bit, 64-bit), differences in signed number representation schemes (2's complement versus 1's complement), and so on. In some cases, such as with byte ordering schemes and platform word length, SQL*Loader provides mechanisms to help overcome platform dependencies. These mechanisms are discussed in the descriptions of the appropriate datatypes.
Both portable and nonportable datatypes can be values or length-values. Value datatypes assume that a data field has a single part. Length-value datatypes require that the data field consist of two subfields where the length subfield specifies how long the value subfield can be.
Nonportable datatypes are grouped into value datatypes and length-value datatypes. The nonportable value datatypes are as follows:
INTEGER(n)
SMALLINT
FLOAT
DOUBLE
BYTEINT
ZONED
(packed) DECIMAL
The nonportable length-value datatypes are as follows:
VARGRAPHIC
VARCHAR
VARRAW
LONG VARRAW
The syntax for the nonportable datatypes is shown in the syntax diagram for datatype_spec.
The data is a full-word binary integer, where n is an optionally supplied length of 1, 2, 4, or 8. If no length specification is given, then the length, in bytes, is based on the size of a LONG INT in the C programming language on your particular platform.
INTEGERs are not portable because their byte size, their byte order, and the representation of signed values may be different between systems. However, if the representation of signed values is the same between systems, SQL*Loader may be able to access INTEGER data with correct results. If INTEGER is specified with a length specification (n), and the appropriate technique is used (if necessary) to indicate the byte order of the data, then SQL*Loader can access the data with correct results between systems. If INTEGER is specified without a length specification, then SQL*Loader can access the data with correct results only if the size of a LONG INT in the C programming language is the same length in bytes on both systems. In that case, the appropriate technique must still be used (if necessary) to indicated the byte order of the data.
Specifying an explicit length for binary integers is useful in situations where the input data was created on a platform whose word length differs from that on which SQL*Loader is running. For instance, input data containing binary integers might be created on a 64-bit platform and loaded into a database using SQL*Loader on a 32-bit platform. In this case, use INTEGER(8) to instruct SQL*Loader to process the integers as 8-byte quantities, not as 4-byte quantities.
By default, INTEGER is treated as a SIGNED quantity. If you want SQL*Loader to treat it as an unsigned quantity, specify UNSIGNED. To return to the default behavior, specify SIGNED.
See Also:
Loading Data Across Different PlatformsThe data is a half-word binary integer. The length of the field is the length of a half-word integer on your system. By default, it is treated as a SIGNED quantity. If you want SQL*Loader to treat it as an unsigned quantity, specify UNSIGNED. To return to the default behavior, specify SIGNED.
SMALLINT can be loaded with correct results only between systems where a SHORT INT has the same length in bytes. If the byte order is different between the systems, use the appropriate technique to indicate the byte order of the data. See Byte Ordering.
The data is a single-precision, floating-point, binary number. If you specify end in the POSITION clause, end is ignored. The length of the field is the length of a single-precision, floating-point binary number on your system. (The datatype is FLOAT in C.) This length cannot be overridden in the control file.
FLOAT can be loaded with correct results only between systems where the representation of FLOAT is compatible and of the same length. If the byte order is different between the two systems, use the appropriate technique to indicate the byte order of the data. See Byte Ordering.
The data is a double-precision, floating-point binary number. If you specify end in the POSITION clause, end is ignored. The length of the field is the length of a double-precision, floating-point binary number on your system. (The datatype is DOUBLE or LONG FLOAT in C.) This length cannot be overridden in the control file.
DOUBLE can be loaded with correct results only between systems where the representation of DOUBLE is compatible and of the same length. If the byte order is different between the two systems, use the appropriate technique to indicate the byte order of the data. See Byte Ordering.
The decimal value of the binary representation of the byte is loaded. For example, the input character x"1C" is loaded as 28. The length of a BYTEINT field is always 1 byte. If POSITION(start:end) is specified, end is ignored. (The datatype is UNSIGNED CHAR in C.)
An example of the syntax for this datatype is:
(column1 position(1) BYTEINT, column2 BYTEINT, ... )
ZONED data is in zoned decimal format: a string of decimal digits, one per byte, with the sign included in the last byte. (In COBOL, this is a SIGN TRAILING field.) The length of this field equals the precision (number of digits) that you specify.
The syntax for the ZONED datatype is:
In this syntax, precision is the number of digits in the number, and scale (if given) is the number of digits to the right of the (implied) decimal point. The following example specifies an 8-digit integer starting at position 32:
sal POSITION(32) ZONED(8),
The Oracle database uses the VAX/VMS zoned decimal format when the zoned data is generated on an ASCII-based platform. It is also possible to load zoned decimal data that is generated on an EBCDIC-based platform. In this case, Oracle uses the IBM format as specified in the ESA/390 Principles of Operations, version 8.1 manual. The format that is used depends on the character set encoding of the input datafile. See CHARACTERSET Parameter for more information.
DECIMAL data is in packed decimal format: two digits per byte, except for the last byte, which contains a digit and sign. DECIMAL fields allow the specification of an implied decimal point, so fractional values can be represented.
The syntax for the DECIMAL datatype is:
The precision parameter is the number of digits in a value. The length of the field in bytes, as computed from digits, is (N+1)/2 rounded up.
The scale parameter is the scaling factor, or number of digits to the right of the decimal point. The default is zero (indicating an integer). The scaling factor can be greater than the number of digits but cannot be negative.
An example is:
sal DECIMAL (7,2)
This example would load a number equivalent to +12345.67. In the data record, this field would take up 4 bytes. (The byte length of a DECIMAL field is equivalent to (N+1)/2, rounded up, where N is the number of digits in the value, and 1 is added for the sign.)
The data is a varying-length, double-byte character set (DBCS). It consists of a length subfield followed by a string of double-byte characters. The Oracle database does not support double-byte character sets; however, SQL*Loader reads them as single bytes and loads them as RAW data. Like RAW data, VARGRAPHIC fields are stored without modification in whichever column you specify.
Note:
The size of the length subfield is the size of the SQL*LoaderSMALLINT datatype on your system (C type SHORT INT). See SMALLINT for more information.VARGRAPHIC data can be loaded with correct results only between systems where a SHORT INT has the same length in bytes. If the byte order is different between the systems, use the appropriate technique to indicate the byte order of the length subfield. See Byte Ordering.
The syntax for the VARGRAPHIC datatype is:
The length of the current field is given in the first 2 bytes. A maximum length specified for the VARGRAPHIC datatype does not include the size of the length subfield. The maximum length specifies the number of graphic (double-byte) characters. It is multiplied by 2 to determine the maximum length of the field in bytes.
The default maximum field length is 2 KB graphic characters, or 4 KB (2 * 2KB). To minimize memory requirements, specify a maximum length for such fields whenever possible.
If a position specification is specified (using pos_spec) before the VARGRAPHIC statement, it provides the location of the length subfield, not of the first graphic character. If you specify pos_spec(start:end), the end location determines a maximum length for the field. Both start and end identify single-character (byte) positions in the file. Start is subtracted from (end + 1) to give the length of the field in bytes. If a maximum length is specified, it overrides any maximum length calculated from the position specification.
If a VARGRAPHIC field is truncated by the end of the logical record before its full length is read, a warning is issued. Because the length of a VARGRAPHIC field is embedded in every occurrence of the input data for that field, it is assumed to be accurate.
VARGRAPHIC data cannot be delimited.
A VARCHAR field is a length-value datatype. It consists of a binary length subfield followed by a character string of the specified length. The length is in bytes unless character-length semantics are used for the datafile. In that case, the length is in characters. See Character-Length Semantics.
VARCHAR fields can be loaded with correct results only between systems where a SHORT data field INT has the same length in bytes. If the byte order is different between the systems, or if the VARCHAR field contains data in the UTF16 character set, use the appropriate technique to indicate the byte order of the length subfield and of the data. The byte order of the data is only an issue for the UTF16 character set. See Byte Ordering.
Note:
The size of the length subfield is the size of the SQL*LoaderSMALLINT datatype on your system (C type SHORT INT). See SMALLINT for more information.The syntax for the VARCHAR datatype is:
A maximum length specified in the control file does not include the size of the length subfield. If you specify the optional maximum length for a VARCHAR datatype, then a buffer of that size, in bytes, is allocated for these fields. However, if character-length semantics are used for the datafile, the buffer size in bytes is the max_length times the size in bytes of the largest possible character in the character set. See Character-Length Semantics.
The default maximum size is 4 KB. Specifying the smallest maximum length that is needed to load your data can minimize SQL*Loader's memory requirements, especially if you have many VARCHAR fields.
The POSITION clause, if used, gives the location, in bytes, of the length subfield, not of the first text character. If you specify POSITION(start:end), the end location determines a maximum length for the field. Start is subtracted from (end + 1) to give the length of the field in bytes. If a maximum length is specified, it overrides any length calculated from POSITION.
If a VARCHAR field is truncated by the end of the logical record before its full length is read, a warning is issued. Because the length of a VARCHAR field is embedded in every occurrence of the input data for that field, it is assumed to be accurate.
VARCHAR data cannot be delimited.
VARRAW is made up of a 2-byte binary length subfield followed by a RAW string value subfield.
VARRAW results in a VARRAW with a 2-byte length subfield and a maximum size of 4 KB (that is, the default). VARRAW(65000) results in a VARRAW with a length subfield of 2 bytes and a maximum size of 65000 bytes.
VARRAW fields can be loaded between systems with different byte orders if the appropriate technique is used to indicate the byte order of the length subfield. See Byte Ordering.
LONG VARRAW is a VARRAW with a 4-byte length subfield instead of a 2-byte length subfield.
LONG VARRAW results in a VARRAW with 4-byte length subfield and a maximum size of 4 KB (that is, the default). LONG VARRAW(300000) results in a VARRAW with a length subfield of 4 bytes and a maximum size of 300000 bytes.
LONG VARRAW fields can be loaded between systems with different byte orders if the appropriate technique is used to indicate the byte order of the length subfield. See Byte Ordering.
The portable datatypes are grouped into value datatypes and length-value datatypes. The portable value datatypes are as follows:
CHAR
Datetime and Interval
GRAPHIC
GRAPHIC EXTERNAL
Numeric EXTERNAL (INTEGER, FLOAT, DECIMAL, ZONED)
RAW
The portable length-value datatypes are as follows:
VARCHARC
VARRAWC
The syntax for these datatypes is shown in the diagram for datatype_spec.
The character datatypes are CHAR, DATE, and the numeric EXTERNAL datatypes. These fields can be delimited and can have lengths (or maximum lengths) specified in the control file.
The data field contains character data. The length, which is optional, is a maximum length. Note the following regarding length:
If a length is not specified, it is derived from the POSITION specification.
If a length is specified, it overrides the length in the POSITION specification.
If no length is given and there is no POSITION specification, CHAR data is assumed to have a length of 1, unless the field is delimited:
For a delimited CHAR field, if a length is specified, that length is used as a maximum.
For a delimited CHAR field for which no length is specified, the default is 255 bytes.
For a delimited CHAR field that is greater than 255 bytes, you must specify a maximum length. Otherwise you will receive an error stating that the field in the datafile exceeds maximum length.
The syntax for the CHAR datatype is:
See Also:
Specifying DelimitersBoth datetimes and intervals are made up of fields. The values of these fields determine the value of the datatype.
DATE
TIME
TIME WITH TIME ZONE
TIMESTAMP
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE
TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE
Values of datetime datatypes are sometimes called datetimes. In the following descriptions of the datetime datatypes you will see that, except for DATE, you are allowed to optionally specify a value for fractional_second_precision. The fractional_second_precision specifies the number of digits stored in the fractional part of the SECOND datetime field. When you create a column of this datatype, the value can be a number in the range 0 to 9. The default is 6.
The interval datatypes are:
INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH
INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND
Values of interval datatypes are sometimes called intervals. The INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH datatype lets you optionally specify a value for year_precision. The year_precision value is the number of digits in the YEAR datetime field. The default value is 2.
The INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND datatype lets you optionally specify values for day_precision and fractional_second_precision. The day_precision is the number of digits in the DAY datetime field. Accepted values are 0 to 9. The default is 2. The fractional_second_precision specifies the number of digits stored in the fractional part of the SECOND datetime field. When you create a column of this datatype, the value can be a number in the range 0 to 9. The default is 6.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more detailed information about specifying datetime and interval datatypes, including the use offractional_second_precision, year_precision, and day_precisionThe DATE field contains character data that should be converted to an Oracle date using the specified date mask. The syntax for the DATE field is:
For example:
LOAD DATA INTO TABLE dates (col_a POSITION (1:15) DATE "DD-Mon-YYYY") BEGINDATA 1-Jan-2008 1-Apr-2008 28-Feb-2008
Whitespace is ignored and dates are parsed from left to right unless delimiters are present. (A DATE field that consists entirely of whitespace is loaded as a NULL field.)
The length specification is optional, unless a varying-length date mask is specified. The length is in bytes unless character-length semantics are used for the datafile. In that case, the length is in characters. See Character-Length Semantics.
In the preceding example, the date mask, "DD-Mon-YYYY" contains 11 bytes, with byte-length semantics. Therefore, SQL*Loader expects a maximum of 11 bytes in the field, so the specification works properly. But, suppose a specification such as the following is given:
DATE "Month dd, YYYY"
In this case, the date mask contains 14 bytes. If a value with a length longer than 14 bytes is specified, such as "September 30, 2008", a length must be specified.
Similarly, a length is required for any Julian dates (date mask "J"). A field length is required any time the length of the date string could exceed the length of the mask (that is, the count of bytes in the mask).
If an explicit length is not specified, it can be derived from the POSITION clause. It is a good idea to specify the length whenever you use a mask, unless you are absolutely sure that the length of the data is less than, or equal to, the length of the mask.
An explicit length specification, if present, overrides the length in the POSITION clause. Either of these overrides the length derived from the mask. The mask may be any valid Oracle date mask. If you omit the mask, the default Oracle date mask of "dd-mon-yy" is used.
The length must be enclosed in parentheses and the mask in quotation marks.
A field of datatype DATE may also be specified with delimiters. For more information, see Specifying Delimiters.
The TIME datatype stores hour, minute, and second values. It is specified as follows:
TIME [(fractional_second_precision)]
The TIME WITH TIME ZONE datatype is a variant of TIME that includes a time zone displacement in its value. The time zone displacement is the difference (in hours and minutes) between local time and UTC (coordinated universal time, formerly Greenwich mean time). It is specified as follows:
TIME [(fractional_second_precision)] WITH [LOCAL] TIME ZONE
If the LOCAL option is specified, then data stored in the database is normalized to the database time zone, and time zone displacement is not stored as part of the column data. When the data is retrieved, it is returned in the user's local session time zone.
The TIMESTAMP datatype is an extension of the DATE datatype. It stores the year, month, and day of the DATE datatype, plus the hour, minute, and second values of the TIME datatype. It is specified as follows:
TIMESTAMP [(fractional_second_precision)]
If you specify a date value without a time component, the default time is 12:00:00 a.m. (midnight).
The TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE datatype is a variant of TIMESTAMP that includes a time zone displacement in its value. The time zone displacement is the difference (in hours and minutes) between local time and UTC (coordinated universal time, formerly Greenwich mean time). It is specified as follows:
TIMESTAMP [(fractional_second_precision)] WITH TIME ZONE
The TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE datatype is another variant of TIMESTAMP that includes a time zone offset in its value. Data stored in the database is normalized to the database time zone, and time zone displacement is not stored as part of the column data. When the data is retrieved, it is returned in the user's local session time zone. It is specified as follows:
TIMESTAMP [(fractional_second_precision)] WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE
The INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH datatype stores a period of time using the YEAR and MONTH datetime fields. It is specified as follows:
INTERVAL YEAR [(year_precision)] TO MONTH
The data is in the form of a double-byte character set (DBCS). The Oracle database does not support double-byte character sets; however, SQL*Loader reads them as single bytes. Like RAW data, GRAPHIC fields are stored without modification in whichever column you specify.
The syntax for the GRAPHIC datatype is:
For GRAPHIC and GRAPHIC EXTERNAL, specifying POSITION(start:end) gives the exact location of the field in the logical record.
If you specify a length for the GRAPHIC (EXTERNAL) datatype, however, then you give the number of double-byte graphic characters. That value is multiplied by 2 to find the length of the field in bytes. If the number of graphic characters is specified, then any length derived from POSITION is ignored. No delimited data field specification is allowed with GRAPHIC datatype specification.
If the DBCS field is surrounded by shift-in and shift-out characters, use GRAPHIC EXTERNAL. This is identical to GRAPHIC, except that the first and last characters (the shift-in and shift-out) are not loaded.
The syntax for the GRAPHIC EXTERNAL datatype is:
GRAPHIC indicates that the data is double-byte characters. EXTERNAL indicates that the first and last characters are ignored. The graphic_char_length value specifies the length in DBCS (see GRAPHIC).
For example, let [ ] represent shift-in and shift-out characters, and let # represent any double-byte character.
To describe ####, use POSITION(1:4) GRAPHIC or POSITION(1) GRAPHIC(2).
To describe [####], use POSITION(1:6) GRAPHIC EXTERNAL or POSITION(1) GRAPHIC EXTERNAL(2).
The numeric EXTERNAL datatypes are the numeric datatypes (INTEGER, FLOAT, DECIMAL, and ZONED) specified as EXTERNAL, with optional length and delimiter specifications. The length is in bytes unless character-length semantics are used for the datafile. In that case, the length is in characters. See Character-Length Semantics.
These datatypes are the human-readable, character form of numeric data. The same rules that apply to CHAR data regarding length, position, and delimiters apply to numeric EXTERNAL data. See CHAR for a complete description of these rules.
The syntax for the numeric EXTERNAL datatypes is shown as part of datatype_spec.
Note:
The data is a number in character form, not binary representation. Therefore, these datatypes are identical toCHAR and are treated identically, except for the use of DEFAULTIF. If you want the default to be null, use CHAR; if you want it to be zero, use EXTERNAL. See Using the WHEN, NULLIF, and DEFAULTIF Clauses.FLOAT EXTERNAL data can be given in either scientific or regular notation. Both "5.33" and "533E-2" are valid representations of the same value.
When raw, binary data is loaded "as is" into a RAW database column, it is not converted by the Oracle database. If it is loaded into a CHAR column, the Oracle database converts it to hexadecimal. It cannot be loaded into a DATE or number column.
The syntax for the RAW datatype is as follows:
The length of this field is the number of bytes specified in the control file. This length is limited only by the length of the target column in the database and by memory resources. The length is always in bytes, even if character-length semantics are used for the datafile. RAW data fields cannot be delimited.
The datatype VARCHARC consists of a character length subfield followed by a character string value-subfield.
The declaration for VARCHARC specifies the length of the length subfield, optionally followed by the maximum size of any string. If byte-length semantics are in use for the datafile, then the length and the maximum size are both in bytes. If character-length semantics are in use for the datafile, then the length and maximum size are in characters. If a maximum size is not specified, 4 KB is the default regardless of whether byte-length semantics or character-length semantics are in use.
For example:
VARCHARC results in an error because you must at least specify a value for the length subfield.
VARCHARC(7) results in a VARCHARC whose length subfield is 7 bytes long and whose maximum size is 4 KB (the default) if byte-length semantics are used for the datafile. If character-length semantics are used, it results in a VARCHARC with a length subfield that is 7 characters long and a maximum size of 4 KB (the default). Remember that when a maximum size is not specified, the default of 4 KB is always used, regardless of whether byte-length or character-length semantics are in use.
VARCHARC(3,500) results in a VARCHARC whose length subfield is 3 bytes long and whose maximum size is 500 bytes if byte-length semantics are used for the datafile. If character-length semantics are used, it results in a VARCHARC with a length subfield that is 3 characters long and a maximum size of 500 characters.
The datatype VARRAWC consists of a RAW string value subfield.
For example:
VARRAWC results in an error.
VARRAWC(7) results in a VARRAWC whose length subfield is 7 bytes long and whose maximum size is 4 KB (that is, the default).
VARRAWC(3,500) results in a VARRAWC whose length subfield is 3 bytes long and whose maximum size is 500 bytes.
There are several ways to specify a length for a field. If multiple lengths are specified and they conflict, then one of the lengths takes precedence. A warning is issued when a conflict exists. The following rules determine which field length is used:
The size of SMALLINT, FLOAT, and DOUBLE data is fixed, regardless of the number of bytes specified in the POSITION clause.
If the length specified (or precision) of a DECIMAL, INTEGER, ZONED, GRAPHIC, GRAPHIC EXTERNAL, or RAW field conflicts with the size calculated from a POSITION(start:end) specification, then the specified length (or precision) is used.
If the maximum size specified for a character or VARGRAPHIC field conflicts with the size calculated from a POSITION(start:end) specification, then the specified maximum is used.
For example, assume that the native datatype INTEGER is 4 bytes long and the following field specification is given:
column1 POSITION(1:6) INTEGER
In this case, a warning is issued, and the proper length (4) is used. The log file shows the actual length used under the heading "Len" in the column table:
Column Name Position Len Term Encl Datatype ----------------------- --------- ----- ---- ---- --------- COLUMN1 1:6 4 INTEGER
A control file can specify a maximum length for the following length-value datatypes: VARCHAR, VARCHARC, VARGRAPHIC, VARRAW, and VARRAWC. The specified maximum length is in bytes if byte-length semantics are used for the field, and in characters if character-length semantics are used for the field. If no length is specified, the maximum length defaults to 4096 bytes. If the length of the field exceeds the maximum length, the record is rejected with the following error:
Variable length field exceed maximum length
The datatype specifications in the control file tell SQL*Loader how to interpret the information in the datafile. The server defines the datatypes for the columns in the database. The link between these two is the column name specified in the control file.
SQL*Loader extracts data from a field in the input file, guided by the datatype specification in the control file. SQL*Loader then sends the field to the server to be stored in the appropriate column (as part of an array of row inserts).
SQL*Loader or the server does any necessary data conversion to store the data in the proper internal format. This includes converting data from the datafile character set to the database character set when they differ.
Note:
When you use SQL*Loader conventional path to load character data from the data file into aLONG RAW column, the character data is interpreted has a HEX string. SQL converts the HEX string into its binary representation. Be aware that any string longer than 4000 bytes exceeds the byte limit for the SQL HEXTORAW conversion operator. Therefore, SQL returns the Oracle error ORA-01461. SQL*Loader will reject that row and continue loading.The datatype of the data in the file does not need to be the same as the datatype of the column in the Oracle table. The Oracle database automatically performs conversions, but you need to ensure that the conversion makes sense and does not generate errors. For instance, when a datafile field with datatype CHAR is loaded into a database column with datatype NUMBER, you must ensure that the contents of the character field represent a valid number.
Note:
SQL*Loader does not contain datatype specifications for Oracle internal datatypes such asNUMBER or VARCHAR2. The SQL*Loader datatypes describe data that can be produced with text editors (character datatypes) and with standard programming languages (native datatypes). However, although SQL*Loader does not recognize datatypes like NUMBER and VARCHAR2, any data that the Oracle database can convert can be loaded into these or other database columns.Table 10-2 shows which conversions between Oracle database datatypes and SQL*Loader control file datetime and interval datatypes are supported and which are not.
In the table, the abbreviations for the Oracle Database Datatypes are as follows:
N = NUMBER
C = CHAR or VARCHAR2
D = DATE
T = TIME and TIME WITH TIME ZONE
TS = TIMESTAMP and TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE
YM = INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH
DS = INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND
For the SQL*Loader datatypes, the definitions for the abbreviations in the table are the same for D, T, TS, YM, and DS. However, as noted in the previous section, SQL*Loader does not contain datatype specifications for Oracle internal datatypes such as NUMBER,CHAR, and VARCHAR2. However, any data that the Oracle database can convert can be loaded into these or other database columns.
For an example of how to read this table, look at the row for the SQL*Loader datatype DATE (abbreviated as D). Reading across the row, you can see that datatype conversion is supported for the Oracle database datatypes of CHAR, VARCHAR2, DATE, TIMESTAMP, and TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE datatypes. However, conversion is not supported for the Oracle database datatypes NUMBER, TIME, TIME WITH TIME ZONE, INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH, or INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND datatypes.
Table 10-2 Datatype Conversions for Datetime and Interval Datatypes
| SQL*Loader Datatype | Oracle Database Datatype (Conversion Support) |
|---|---|
|
N |
N (Yes), C (Yes), D (No), T (No), TS (No), YM (No), DS (No) |
|
C |
N (Yes), C (Yes), D (Yes), T (Yes), TS (Yes), YM (Yes), DS (Yes) |
|
D |
N (No), C (Yes), D (Yes), T (No), TS (Yes), YM (No), DS (No) |
|
T |
N (No), C (Yes), D (No), T (Yes), TS (Yes), YM (No), DS (No) |
|
TS |
N (No), C (Yes), D (Yes), T (Yes), TS (Yes), YM (No), DS (No) |
|
YM |
N (No), C (Yes), D (No), T (No), TS (No), YM (Yes), DS (No) |
|
DS |
N (No), C (Yes), D (No), T (No), TS (No), YM (No), DS (Yes) |
The boundaries of CHAR, datetime, interval, or numeric EXTERNAL fields can also be marked by delimiter characters contained in the input data record. The delimiter characters are specified using various combinations of the TERMINATED BY, ENCLOSED BY, and OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY clauses (the TERMINATED BY clause, if used, must come first). The delimiter specification comes after the datatype specification.
For a description of how data is processed when various combinations of delimiter clauses are used, see How Delimited Data Is Processed.
Note:
TheRAW datatype can also be marked by delimiters, but only if it is in an input LOBFILE, and only if the delimiter is TERMINATED BY EOF (end of file).The following diagram shows the syntax for termination_spec and enclosure_spec.
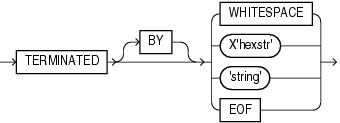

Table 10-3 describes the syntax for the termination and enclosure specifications used to specify delimiters.
Table 10-3 Parameters Used for Specifying Delimiters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Data is read until the first occurrence of a delimiter. |
|
|
An optional word to increase readability. |
|
|
Delimiter is any whitespace character including spaces, tabs, blanks, line feeds, form feeds, or carriage returns. (Only used with |
|
|
Data can be enclosed by the specified character. If SQL*Loader finds a first occurrence of the character, it reads the data value until it finds the second occurrence. If the data is not enclosed, the data is read as a terminated field. If you specify an optional enclosure, you must specify a |
|
|
The data will be found between two delimiters. |
|
|
The delimiter is a string. |
|
|
The delimiter is a string that has the value specified by |
|
|
Specifies a trailing enclosure delimiter that may be different from the initial enclosure delimiter. If |
|
|
Indicates that the entire file has been loaded into the LOB. This is valid only when data is loaded from a LOB file. Fields terminated by |
Here are some examples, with samples of the data they describe:
TERMINATED BY ',' a data string,
ENCLOSED BY '"' "a data string"
TERMINATED BY ',' ENCLOSED BY '"' "a data string",
ENCLOSED BY '(' AND ')' (a data string)
Sometimes the punctuation mark that is a delimiter must also be included in the data. To make that possible, two adjacent delimiter characters are interpreted as a single occurrence of the character, and this character is included in the data. For example, this data:
(The delimiters are left parentheses, (, and right parentheses, )).)
with this field specification:
ENCLOSED BY "(" AND ")"
puts the following string into the database:
The delimiters are left parentheses, (, and right parentheses, ).
For this reason, problems can arise when adjacent fields use the same delimiters. For example, with the following specification:
field1 TERMINATED BY "/" field2 ENCLOSED by "/"
the following data will be interpreted properly:
This is the first string/ /This is the second string/
But if field1 and field2 were adjacent, then the results would be incorrect, because
This is the first string//This is the second string/
would be interpreted as a single character string with a "/" in the middle, and that string would belong to field1.
The default maximum length of delimited data is 255 bytes. Therefore, delimited fields can require significant amounts of storage for the bind array. A good policy is to specify the smallest possible maximum value if the fields are shorter than 255 bytes. If the fields are longer than 255 bytes, then you must specify a maximum length for the field, either with a length specifier or with the POSITION clause.
For example, if you have a string literal that is longer than 255 bytes, then in addition to using SUBSTR(), use CHAR() to specify the longest string in any record for the field. An example of how this would look is as follows, assuming that 600 bytes is the longest string in any record for field1:
field1 CHAR(600) SUBSTR(:field, 1, 240)
Trailing blanks are not loaded with nondelimited datatypes unless you specify PRESERVE BLANKS. If a data field is 9 characters long and contains the value DANIELbbb, where bbb is three blanks, it is loaded into the Oracle database as "DANIEL" if declared as CHAR(9).
If you want the trailing blanks, you could declare it as CHAR(9) TERMINATED BY ':', and add a colon to the datafile so that the field is DANIELbbb:. This field is loaded as "DANIEL ", with the trailing blanks. You could also specify PRESERVE BLANKS without the TERMINATED BY clause and obtain the same results.
To specify delimiters, field definitions can use various combinations of the TERMINATED BY, ENCLOSED BY, and OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY clauses. The following sections describe the processing that takes place in each case:
Each of these scenarios is described in the following sections.
If TERMINATED BY is specified for a field without ENCLOSED BY, the data for the field is read from the starting position of the field up to, but not including, the first occurrence of the TERMINATED BY delimiter. If the terminator delimiter is found in the first column position of a field, the field is null. If the end of the record is found before the TERMINATED BY delimiter, then all data up to the end of the record is considered part of the field.
If TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE is specified, data is read until the first occurrence of a whitespace character (spaces, tabs, blanks, line feeds, form feeds, or carriage returns). Then the current position is advanced until no more adjacent whitespace characters are found. This allows field values to be delimited by varying amounts of whitespace. However, unlike non-whitespace terminators, if a whitespace terminator is found in the first column position of a field, the field is not treated as null and can result in record rejection or fields loaded into incorrect columns.
The following steps take place when a field uses an ENCLOSED BY clause without also using a TERMINATED BY clause.
Any whitespace at the beginning of the field is skipped.
The first non-whitespace character found must be the start of a string that matches the first ENCLOSED BY delimiter. If it is not, the row is rejected.
If the first ENCLOSED BY delimiter is found, the search for the second ENCLOSED BY delimiter begins.
If two of the second ENCLOSED BY delimiters are found adjacent to each other, they are interpreted as a single occurrence of the delimiter and included as part of the data for the field. The search then continues for another instance of the second ENCLOSED BY delimiter.
If the end of the record is found before the second ENCLOSED BY delimiter is found, then the row is rejected.
The following steps take place when a field uses an ENCLOSED BY clause and also uses a TERMINATED BY clause.
Any whitespace at the beginning of the field is skipped.
The first non-whitespace character found must be the start of a string that matches the first ENCLOSED BY delimiter. If it is not, then the row is rejected.
If the first ENCLOSED BY delimiter is found, the search for the second ENCLOSED BY delimiter begins.
If two of the second ENCLOSED BY delimiters are found adjacent to each other, they are interpreted as a single occurrence of the delimiter and included as part of the data for the field. The search then continues for the second instance of the ENCLOSED BY delimiter.
If the end of the record is found before the second ENCLOSED BY delimiter is found, then the row is rejected.
If the second ENCLOSED BY delimiter is found, the parser looks for the TERMINATED BY delimiter. If the TERMINATED BY delimiter is anything other than WHITESPACE, then whitespace found between the end of the second ENCLOSED BY delimiter and the TERMINATED BY delimiter is skipped over.
Note:
OnlyWHITESPACE is allowed between the second ENCLOSED BY delimiter and the TERMINATED BY delimiter. Any other characters will cause an error.The row is not rejected if the end of the record is found before the TERMINATED BY delimiter is found.
The following steps take place when a field uses an OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY clause and a TERMINATED BY clause.
Any whitespace at the beginning of the field is skipped.
The parser checks to see if the first non-whitespace character found is the start of a string that matches the first OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiter. If it is not, and the OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiters are not present in the data, then the data for the field is read from the current position of the field up to, but not including, the first occurrence of the TERMINATED BY delimiter. If the TERMINATED BY delimiter is found in the first column position, the field is null. If the end of the record is found before the TERMINATED BY delimiter, then all data up to the end of the record is considered part of the field.
If the first OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiter is found, the search for the second OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiter begins.
If two of the second OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiters are found adjacent to each other, they are interpreted as a single occurrence of the delimiter and included as part of the data for the field. The search then continues for the second OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiter.
If the end of the record is found before the second OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiter is found, then the row is rejected.
If the OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiter are present in the data, the parser looks for the TERMINATED BY delimiter. If the TERMINATED BY delimiter is anything other than WHITESPACE, then whitespace found between the end of the second OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiter and the TERMINATED BY delimiter is skipped over.
The row is not rejected if the end of record is found before the TERMINATED BY delimiter is found.
Caution:
Be careful when you specify whitespace characters as theTERMINATED BY delimiter and are also using OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY. SQL*Loader strips off leading whitespace when looking for an OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY delimiter. If the data contains two adjacent TERMINATED BY delimiters in the middle of a record (usually done to set a field in the record to NULL), then the whitespace for the first TERMINATED BY delimiter will be used to terminate a field, but the remaining whitespace will be considered as leading whitespace for the next field rather than the TERMINATED BY delimiter for the next field. If you want to load a NULL value, you must include the ENCLOSED BY delimiters in the data.A control file can specify multiple lengths for the character-data fields CHAR, DATE, and numeric EXTERNAL. If conflicting lengths are specified, one of the lengths takes precedence. A warning is also issued when a conflict exists. This section explains which length is used.
If you specify a starting position and ending position for one of these fields, then the length of the field is determined by these specifications. If you specify a length as part of the datatype and do not give an ending position, the field has the given length. If starting position, ending position, and length are all specified, and the lengths differ, then the length given as part of the datatype specification is used for the length of the field, as follows:
POSITION(1:10) CHAR(15)
In this example, the length of the field is 15.
If a delimited field is specified with a length, or if a length can be calculated from the starting and ending positions, then that length is the maximum length of the field. The specified maximum length is in bytes if byte-length semantics are used for the field, and in characters if character-length semantics are used for the field. If no length is specified or can be calculated from the start and end positions, the maximum length defaults to 255 bytes. The actual length can vary up to that maximum, based on the presence of the delimiter.
If delimiters and also starting and ending positions are specified for the field, then only the position specification has any effect. Any enclosure or termination delimiters are ignored.
If the expected delimiter is absent, then the end of record terminates the field. If TRAILING NULLCOLS is specified, remaining fields are null. If either the delimiter or the end of record produces a field that is longer than the maximum, SQL*Loader rejects the record and returns an error.
The length of a date field depends on the mask, if a mask is specified. The mask provides a format pattern, telling SQL*Loader how to interpret the data in the record. For example, assume the mask is specified as follows:
"Month dd, yyyy"
Then "May 3, 2008" would occupy 11 bytes in the record (with byte-length semantics), while "January 31, 2009" would occupy 16.
If starting and ending positions are specified, however, then the length calculated from the position specification overrides a length derived from the mask. A specified length such as DATE(12) overrides either of those. If the date field is also specified with terminating or enclosing delimiters, then the length specified in the control file is interpreted as a maximum length for the field.
A field condition is a statement about a field in a logical record that evaluates as true or false. It is used in the WHEN, NULLIF, and DEFAULTIF clauses.
Note:
If a field used in a clause evaluation has a NULL value, then that clause will always evaluate to FALSE. This feature is illustrated in Example 10-5.A field condition is similar to the condition in the CONTINUEIF clause, with two important differences. First, positions in the field condition refer to the logical record, not to the physical record. Second, you can specify either a position in the logical record or the name of a field in the datafile (including filler fields).
Note:
A field condition cannot be based on fields in a secondary datafile (SDF).The syntax for the field_condition clause is as follows:
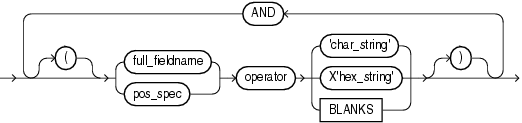
The syntax for the pos_spec clause is as follows:

Table 10-4 describes the parameters used for the field condition clause. For a full description of the position specification parameters, see Table 10-1.
Table 10-4 Parameters for the Field Condition Clause
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the starting and ending position of the comparison field in the logical record. It must be surrounded by parentheses. Either The starting location can be specified as a column number, or as If you omit an ending position, the length of the field is determined by the length of the comparison string. If the lengths are different, the shorter field is padded. Character strings are padded with blanks, hexadecimal strings with zeros. |
|
|
Specifies the starting position of the comparison field in the logical record. |
|
|
Specifies the ending position of the comparison field in the logical record. |
|
|
|
|
|
A comparison operator for either equal or not equal. |
|
|
A string of characters enclosed in single or double quotation marks that is compared to the comparison field. If the comparison is true, the current record is inserted into the table. |
|
|
A string of hexadecimal digits, where each pair of digits corresponds to one byte in the field. It is enclosed in single or double quotation marks. If the comparison is true, the current record is inserted into the table. |
|
|
Enables you to test a field to see if it consists entirely of blanks. |
The BLANKS parameter makes it possible to determine if a field of unknown length is blank.
For example, use the following clause to load a blank field as null:
full_fieldname ... NULLIF column_name=BLANKS
The BLANKS parameter recognizes only blanks, not tabs. It can be used in place of a literal string in any field comparison. The condition is true whenever the column is entirely blank.
The BLANKS parameter also works for fixed-length fields. Using it is the same as specifying an appropriately sized literal string of blanks. For example, the following specifications are equivalent:
fixed_field CHAR(2) NULLIF fixed_field=BLANKS fixed_field CHAR(2) NULLIF fixed_field=" "
There can be more than one blank in a multibyte character set. It is a good idea to use the BLANKS parameter with these character sets instead of specifying a string of blank characters.
The character string will match only a specific sequence of blank characters, while the BLANKS parameter will match combinations of different blank characters. For more information about multibyte character sets, see Multibyte (Asian) Character Sets.
When a data field is compared to a literal string that is shorter than the data field, the string is padded. Character strings are padded with blanks, for example:
NULLIF (1:4)=" "
This example compares the data in position 1:4 with 4 blanks. If position 1:4 contains 4 blanks, then the clause evaluates as true.
Hexadecimal strings are padded with hexadecimal zeros, as in the following clause:
NULLIF (1:4)=X'FF'
This clause compares position 1:4 to hexadecimal 'FF000000'.
The following information applies to scalar fields. For nonscalar fields (column objects, LOBs, and collections), the WHEN, NULLIF, and DEFAULTIF clauses are processed differently because nonscalar fields are more complex.
The results of a WHEN, NULLIF, or DEFAULTIF clause can be different depending on whether the clause specifies a field name or a position.
If the WHEN, NULLIF, or DEFAULTIF clause specifies a field name, SQL*Loader compares the clause to the evaluated value of the field. The evaluated value takes trimmed whitespace into consideration. See Trimming Whitespace for information about trimming blanks and tabs.
If the WHEN, NULLIF, or DEFAULTIF clause specifies a position, SQL*Loader compares the clause to the original logical record in the datafile. No whitespace trimming is done on the logical record in that case.
Different results are more likely if the field has whitespace that is trimmed, or if the WHEN, NULLIF, or DEFAULTIF clause contains blanks or tabs or uses the BLANKS parameter. If you require the same results for a field specified by name and for the same field specified by position, use the PRESERVE BLANKS option. The PRESERVE BLANKS option instructs SQL*Loader not to trim whitespace when it evaluates the values of the fields.
The results of a WHEN, NULLIF, or DEFAULTIF clause are also affected by the order in which SQL*Loader operates, as described in the following steps. SQL*Loader performs these steps in order, but it does not always perform all of them. Once a field is set, any remaining steps in the process are ignored. For example, if the field is set in Step 5, SQL*Loader does not move on to Step 6.
SQL*Loader evaluates the value of each field for the input record and trims any whitespace that should be trimmed (according to existing guidelines for trimming blanks and tabs).
For each record, SQL*Loader evaluates any WHEN clauses for the table.
If the record satisfies the WHEN clauses for the table, or no WHEN clauses are specified, SQL*Loader checks each field for a NULLIF clause.
If a NULLIF clause exists, SQL*Loader evaluates it.
If the NULLIF clause is satisfied, SQL*Loader sets the field to NULL.
If the NULLIF clause is not satisfied, or if there is no NULLIF clause, SQL*Loader checks the length of the field from field evaluation. If the field has a length of 0 from field evaluation (for example, it was a null field, or whitespace trimming resulted in a null field), SQL*Loader sets the field to NULL. In this case, any DEFAULTIF clause specified for the field is not evaluated.
If any specified NULLIF clause is false or there is no NULLIF clause, and if the field does not have a length of 0 from field evaluation, SQL*Loader checks the field for a DEFAULTIF clause.
If a DEFAULTIF clause exists, SQL*Loader evaluates it.
If the DEFAULTIF clause is satisfied, then the field is set to 0 if the field in the datafile is a numeric field. It is set to NULL if the field is not a numeric field. The following fields are numeric fields and will be set to 0 if they satisfy the DEFAULTIF clause:
BYTEINT
SMALLINT
INTEGER
FLOAT
DOUBLE
ZONED
(packed) DECIMAL
Numeric EXTERNAL (INTEGER, FLOAT, DECIMAL, and ZONED)
If the DEFAULTIF clause is not satisfied, or if there is no DEFAULTIF clause, SQL*Loader sets the field with the evaluated value from Step 1.
The order in which SQL*Loader operates could cause results that you do not expect. For example, the DEFAULTIF clause may look like it is setting a numeric field to NULL rather than to 0.
Note:
As demonstrated in these steps, the presence ofNULLIF and DEFAULTIF clauses results in extra processing that SQL*Loader must perform. This can affect performance. Note that during Step 1, SQL*Loader will set a field to NULL if its evaluated length is zero. To improve performance, consider whether it might be possible for you to change your data to take advantage of this. The detection of NULLs as part of Step 1 occurs much more quickly than the processing of a NULLIF or DEFAULTIF clause.
For example, a CHAR(5) will have zero length if it falls off the end of the logical record or if it contains all blanks and blank trimming is in effect. A delimited field will have zero length if there are no characters between the start of the field and the terminator.
Also, for character fields, NULLIF is usually faster to process than DEFAULTIF (the default for character fields is NULL).
Example 10-2 through Example 10-5 clarify the results for different situations in which the WHEN, NULLIF, and DEFAULTIF clauses might be used. In the examples, a blank or space is indicated with a period (.). Assume that col1 and col2 are VARCHAR2(5) columns in the database.
Example 10-2 DEFAULTIF Clause Is Not Evaluated
The control file specifies:
(col1 POSITION (1:5), col2 POSITION (6:8) CHAR INTEGER EXTERNAL DEFAULTIF col1 = 'aname')
The datafile contains:
aname...
In Example 10-2, col1 for the row evaluates to aname. col2 evaluates to NULL with a length of 0 (it is ... but the trailing blanks are trimmed for a positional field).
When SQL*Loader determines the final loaded value for col2, it finds no WHEN clause and no NULLIF clause. It then checks the length of the field, which is 0 from field evaluation. Therefore, SQL*Loader sets the final value for col2 to NULL. The DEFAULTIF clause is not evaluated, and the row is loaded as aname for col1 and NULL for col2.
Example 10-3 DEFAULTIF Clause Is Evaluated
The control file specifies:
. . . PRESERVE BLANKS . . . (col1 POSITION (1:5), col2 POSITION (6:8) INTEGER EXTERNAL DEFAULTIF col1 = 'aname'
The datafile contains:
aname...
In Example 10-3, col1 for the row again evaluates to aname. col2 evaluates to '...' because trailing blanks are not trimmed when PRESERVE BLANKS is specified.
When SQL*Loader determines the final loaded value for col2, it finds no WHEN clause and no NULLIF clause. It then checks the length of the field from field evaluation, which is 3, not 0.
Then SQL*Loader evaluates the DEFAULTIF clause, which evaluates to true because col1 is aname, which is the same as aname.
Because col2 is a numeric field, SQL*Loader sets the final value for col2 to 0. The row is loaded as aname for col1 and as 0 for col2.
Example 10-4 DEFAULTIF Clause Specifies a Position
The control file specifies:
(col1 POSITION (1:5), col2 POSITION (6:8) INTEGER EXTERNAL DEFAULTIF (1:5) = BLANKS)
The datafile contains:
.....123
In Example 10-4, col1 for the row evaluates to NULL with a length of 0 (it is ..... but the trailing blanks are trimmed). col2 evaluates to 123.
When SQL*Loader sets the final loaded value for col2, it finds no WHEN clause and no NULLIF clause. It then checks the length of the field from field evaluation, which is 3, not 0.
Then SQL*Loader evaluates the DEFAULTIF clause. It compares (1:5) which is ..... to BLANKS, which evaluates to true. Therefore, because col2 is a numeric field (integer EXTERNAL is numeric), SQL*Loader sets the final value for col2 to 0. The row is loaded as NULL for col1 and 0 for col2.
Example 10-5 DEFAULTIF Clause Specifies a Field Name
The control file specifies:
(col1 POSITION (1:5), col2 POSITION(6:8) INTEGER EXTERNAL DEFAULTIF col1 = BLANKS)
The datafile contains:
.....123
In Example 10-5, col1 for the row evaluates to NULL with a length of 0 (it is ..... but the trailing blanks are trimmed). col2 evaluates to 123.
When SQL*Loader determines the final value for col2, it finds no WHEN clause and no NULLIF clause. It then checks the length of the field from field evaluation, which is 3, not 0.
Then SQL*Loader evaluates the DEFAULTIF clause. As part of the evaluation, it checks to see that col1 is NULL from field evaluation. It is NULL, so the DEFAULTIF clause evaluates to false. Therefore, SQL*Loader sets the final value for col2 to 123, its original value from field evaluation. The row is loaded as NULL for col1 and 123 for col2.
When a datafile created on one platform is to be loaded on a different platform, the data must be written in a form that the target system can read. For example, if the source system has a native, floating-point representation that uses 16 bytes, and the target system's floating-point numbers are 12 bytes, the target system cannot directly read data generated on the source system.
The best solution is to load data across an Oracle Net database link, taking advantage of the automatic conversion of datatypes. This is the recommended approach, whenever feasible, and means that SQL*Loader must be run on the source system.
Problems with interplatform loads typically occur with native datatypes. In some situations, it is possible to avoid problems by lengthening a field by padding it with zeros, or to read only part of the field to shorten it (for example, when an 8-byte integer is to be read on a system that uses 4-byte integers, or the reverse). Note, however, that incompatible datatype implementation may prevent this.
If you cannot use an Oracle Net database link and the datafile must be accessed by SQL*Loader running on the target system, it is advisable to use only the portable SQL*Loader datatypes (for example, CHAR, DATE, VARCHARC, and numeric EXTERNAL). Datafiles written using these datatypes may be longer than those written with native datatypes. They may take more time to load, but they transport more readily across platforms.
If you know in advance that the byte ordering schemes or native integer lengths differ between the platform on which the input data will be created and the platform on which SQL*loader will be run, then investigate the possible use of the appropriate technique to indicate the byte order of the data or the length of the native integer. Possible techniques for indicating the byte order are to use the BYTEORDER parameter or to place a byte-order mark (BOM) in the file. Both methods are described in Byte Ordering. It may then be possible to eliminate the incompatibilities and achieve a successful cross-platform data load. If the byte order is different from the SQL*Loader default, then you must indicate a byte order.
Note:
The information in this section is only applicable if you are planning to create input data on a system that has a different byte-ordering scheme than the system on which SQL*Loader will be run. Otherwise, you can skip this section.SQL*Loader can load data from a datafile that was created on a system whose byte ordering is different from the byte ordering on the system where SQL*Loader is running, even if the datafile contains certain nonportable datatypes.
By default, SQL*Loader uses the byte order of the system where it is running as the byte order for all datafiles. For example, on a Sun Solaris system, SQL*Loader uses big-endian byte order. On an Intel or an Intel-compatible PC, SQL*Loader uses little-endian byte order.
Byte order affects the results when data is written and read an even number of bytes at a time (typically 2 bytes, 4 bytes, or 8 bytes). The following are some examples of this:
The 2-byte integer value 1 is written as 0x0001 on a big-endian system and as 0x0100 on a little-endian system.
The 4-byte integer 66051 is written as 0x00010203 on a big-endian system and as 0x03020100 on a little-endian system.
Byte order also affects character data in the UTF16 character set if it is written and read as 2-byte entities. For example, the character 'a' (0x61 in ASCII) is written as 0x0061 in UTF16 on a big-endian system, but as 0x6100 on a little-endian system.
All Oracle-supported character sets, except UTF16, are written one byte at a time. So, even for multibyte character sets such as UTF8, the characters are written and read the same way on all systems, regardless of the byte order of the system. Therefore, data in the UTF16 character set is nonportable because it is byte-order dependent. Data in all other Oracle-supported character sets is portable.
Byte order in a datafile is only an issue if the datafile that contains the byte-order-dependent data is created on a system that has a different byte order from the system on which SQL*Loader is running. If SQL*Loader knows the byte order of the data, it swaps the bytes as necessary to ensure that the data is loaded correctly in the target database. Byte swapping means that data in big-endian format is converted to little-endian format, or the reverse.
To indicate byte order of the data to SQL*Loader, you can use the BYTEORDER parameter, or you can place a byte-order mark (BOM) in the file. If you do not use one of these techniques, SQL*Loader will not correctly load the data into the datafile.
See Also:
Case study 11, Loading Data in the Unicode Character Set, for an example of how SQL*Loader handles byte swapping. (See SQL*Loader Case Studies for information on how to access case studies.)To specify the byte order of data in the input datafiles, use the following syntax in the SQL*Loader control file:
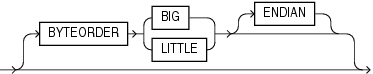
The BYTEORDER parameter has the following characteristics:
BYTEORDER is placed after the LENGTH parameter in the SQL*Loader control file.
It is possible to specify a different byte order for different datafiles. However, the BYTEORDER specification before the INFILE parameters applies to the entire list of primary datafiles.
The BYTEORDER specification for the primary datafiles is also used as the default for LOBFILEs and SDFs. To override this default, specify BYTEORDER with the LOBFILE or SDF specification.
The BYTEORDER parameter is not applicable to data contained within the control file itself.
The BYTEORDER parameter applies to the following:
Binary INTEGER and SMALLINT data
Binary lengths in varying-length fields (that is, for the VARCHAR, VARGRAPHIC, VARRAW, and LONG VARRAW datatypes)
Character data for datafiles in the UTF16 character set
FLOAT and DOUBLE datatypes, if the system where the data was written has a compatible floating-point representation with that on the system where SQL*Loader is running
The BYTEORDER parameter does not apply to any of the following:
Raw datatypes (RAW, VARRAW, or VARRAWC)
Graphic datatypes (GRAPHIC, VARGRAPHIC, or GRAPHIC EXTERNAL)
Character data for datafiles in any character set other than UTF16
ZONED or (packed) DECIMAL datatypes
Datafiles that use a Unicode encoding (UTF-16 or UTF-8) may contain a byte-order mark (BOM) in the first few bytes of the file. For a datafile that uses the character set UTF16, the values {0xFE,0xFF} in the first two bytes of the file are the BOM indicating that the file contains big-endian data. The values {0xFF,0xFE} are the BOM indicating that the file contains little-endian data.
If the first primary datafile uses the UTF16 character set and it also begins with a BOM, that mark is read and interpreted to determine the byte order for all primary datafiles. SQL*Loader reads and interprets the BOM, skips it, and begins processing data with the byte immediately after the BOM. The BOM setting overrides any BYTEORDER specification for the first primary datafile. BOMs in datafiles other than the first primary datafile are read and used for checking for byte-order conflicts only. They do not change the byte-order setting that SQL*Loader uses in processing the datafile.
In summary, the precedence of the byte-order indicators for the first primary datafile is as follows:
BOM in the first primary datafile, if the datafile uses a Unicode character set that is byte-order dependent (UTF16) and a BOM is present
BYTEORDER parameter value, if specified before the INFILE parameters
The byte order of the system where SQL*Loader is running
For a datafile that uses a UTF8 character set, a BOM of {0xEF,0xBB,0xBF} in the first 3 bytes indicates that the file contains UTF8 data. It does not indicate the byte order of the data, because data in UTF8 is not byte-order dependent. If SQL*Loader detects a UTF8 BOM, it skips it but does not change any byte-order settings for processing the datafiles.
SQL*Loader first establishes a byte-order setting for the first primary datafile using the precedence order just defined. This byte-order setting is used for all primary datafiles. If another primary datafile uses the character set UTF16 and also contains a BOM, the BOM value is compared to the byte-order setting established for the first primary datafile. If the BOM value matches the byte-order setting of the first primary datafile, SQL*Loader skips the BOM, and uses that byte-order setting to begin processing data with the byte immediately after the BOM. If the BOM value does not match the byte-order setting established for the first primary datafile, then SQL*Loader issues an error message and stops processing.
If any LOBFILEs or secondary datafiles are specified in the control file, SQL*Loader establishes a byte-order setting for each LOBFILE and secondary datafile (SDF) when it is ready to process the file. The default byte-order setting for LOBFILEs and SDFs is the byte-order setting established for the first primary datafile. This is overridden if the BYTEORDER parameter is specified with a LOBFILE or SDF. In either case, if the LOBFILE or SDF uses the UTF16 character set and contains a BOM, the BOM value is compared to the byte-order setting for the file. If the BOM value matches the byte-order setting for the file, SQL*Loader skips the BOM, and uses that byte-order setting to begin processing data with the byte immediately after the BOM. If the BOM value does not match, then SQL*Loader issues an error message and stops processing.
In summary, the precedence of the byte-order indicators for LOBFILEs and SDFs is as follows:
BYTEORDER parameter value specified with the LOBFILE or SDF
The byte-order setting established for the first primary datafile
Note:
If the character set of your datafile is a unicode character set and there is a byte-order mark in the first few bytes of the file, do not use theSKIP parameter. If you do, the byte-order mark will not be read and interpreted as a byte-order mark.A datafile in a Unicode character set may contain binary data that matches the BOM in the first bytes of the file. For example the integer(2) value 0xFEFF = 65279 decimal matches the big-endian BOM in UTF16. In that case, you can tell SQL*Loader to read the first bytes of the datafile as data and not check for a BOM by specifying the BYTEORDERMARK parameter with the value NOCHECK. The syntax for the BYTEORDERMARK parameter is:
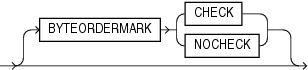
BYTEORDERMARK NOCHECK indicates that SQL*Loader should not check for a BOM and should read all the data in the datafile as data.
BYTEORDERMARK CHECK tells SQL*Loader to check for a BOM. This is the default behavior for a datafile in a Unicode character set. But this specification may be used in the control file for clarification. It is an error to specify BYTEORDERMARK CHECK for a datafile that uses a non-Unicode character set.
The BYTEORDERMARK parameter has the following characteristics:
It is placed after the optional BYTEORDER parameter in the SQL*Loader control file.
It applies to the syntax specification for primary datafiles, and also to LOBFILEs and secondary datafiles (SDFs).
It is possible to specify a different BYTEORDERMARK value for different datafiles; however, the BYTEORDERMARK specification before the INFILE parameters applies to the entire list of primary datafiles.
The BYTEORDERMARK specification for the primary datafiles is also used as the default for LOBFILEs and SDFs, except that the value CHECK is ignored in this case if the LOBFILE or SDF uses a non-Unicode character set. This default setting for LOBFILEs and secondary datafiles can be overridden by specifying BYTEORDERMARK with the LOBFILE or SDF specification.
Fields that are totally blank cause the record to be rejected. To load one of these fields as NULL, use the NULLIF clause with the BLANKS parameter.
If an all-blank CHAR field is surrounded by enclosure delimiters, then the blanks within the enclosures are loaded. Otherwise, the field is loaded as NULL.
A DATE or numeric field that consists entirely of blanks is loaded as a NULL field.
See Also:
Case study 6, Loading Data Using the Direct Path Load Method, for an example of how to load all-blank fields as NULL with the NULLIF clause. (See SQL*Loader Case Studies for information on how to access case studies.)
Blanks, tabs, and other nonprinting characters (such as carriage returns and line feeds) constitute whitespace. Leading whitespace occurs at the beginning of a field. Trailing whitespace occurs at the end of a field. Depending on how the field is specified, whitespace may or may not be included when the field is inserted into the database. This is illustrated in Figure 10-1, where two CHAR fields are defined for a data record.
The field specifications are contained in the control file. The control file CHAR specification is not the same as the database CHAR specification. A data field defined as CHAR in the control file simply tells SQL*Loader how to create the row insert. The data could then be inserted into a CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, or even a NUMBER or DATE column in the database, with the Oracle database handling any necessary conversions.
By default, SQL*Loader removes trailing spaces from CHAR data before passing it to the database. So, in Figure 10-1, both Field 1 and Field 2 are passed to the database as 3-byte fields. However, when the data is inserted into the table, there is a difference.
Column 1 is defined in the database as a fixed-length CHAR column of length 5. So the data (aaa) is left-justified in that column, which remains 5 bytes wide. The extra space on the right is padded with blanks. Column 2, however, is defined as a varying-length field with a maximum length of 5 bytes. The data for that column (bbb) is left-justified as well, but the length remains 3 bytes.
Table 10-5 summarizes when and how whitespace is removed from input data fields when PRESERVE BLANKS is not specified. See How the PRESERVE BLANKS Option Affects Whitespace Trimming for details on how to prevent whitespace trimming.
Table 10-5 Behavior Summary for Trimming Whitespace
| Specification | Data | Result | Leading Whitespace PresentFoot 1 | Trailing Whitespace PresentFootref 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Predetermined size |
__aa__ |
__aa |
Yes |
No |
|
Terminated |
__aa__, |
__aa__ |
Yes |
YesFoot 2 |
|
Enclosed |
"__aa__" |
__aa__ |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Terminated and enclosed |
"__aa__", |
__aa__ |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Optional enclosure (present) |
"__aa__", |
__aa__ |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Optional enclosure (absent) |
__aa__, |
aa__ |
No |
Yes |
|
Previous field terminated by whitespace |
__aa__ |
aaFoot 3 |
No |
Footnote 1 When an all-blank field is trimmed, its value is NULL.
Footnote 2 Except for fields that are terminated by whitespace.
Footnote 3 Presence of trailing whitespace depends on the current field's specification, as shown by the other entries in the table.
The rest of this section discusses the following topics with regard to trimming whitespace:
The information in this section applies only to fields specified with one of the character-data datatypes:
CHAR datatype
Datetime and interval datatypes
Numeric EXTERNAL datatypes:
INTEGER EXTERNAL
FLOAT EXTERNAL
(packed) DECIMAL EXTERNAL
ZONED (decimal) EXTERNAL
Note:
AlthoughVARCHAR and VARCHARC fields also contain character data, these fields are never trimmed. These fields include all whitespace that is part of the field in the datafile.There are two ways to specify field length. If a field has a constant length that is defined in the control file with a position specification or the datatype and length, then it has a predetermined size. If a field's length is not known in advance, but depends on indicators in the record, then the field is delimited, using either enclosure or termination delimiters.
If a position specification with start and end values is defined for a field that also has enclosure or termination delimiters defined, only the position specification has any effect. The enclosure and termination delimiters are ignored.
Fields that have a predetermined size are specified with a starting position and ending position, or with a length, as in the following examples:
loc POSITION(19:31) loc CHAR(14)
In the second case, even though the exact position of the field is not specified, the length of the field is predetermined.
Delimiters are characters that demarcate field boundaries.
Enclosure delimiters surround a field, like the quotation marks in the following example, where "__" represents blanks or tabs:
"__aa__"
Termination delimiters signal the end of a field, like the comma in the following example:
__aa__,
Delimiters are specified with the control clauses TERMINATED BY and ENCLOSED BY, as shown in the following example:
loc TERMINATED BY "." OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY '|'
This section describes how SQL*Loader determines the starting position of a field in the following situations:
When a starting position is not specified for a field, it begins immediately after the end of the previous field. Figure 10-2 illustrates this situation when the previous field (Field 1) has a predetermined size.
Figure 10-2 Relative Positioning After a Fixed Field
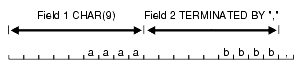
If the previous field (Field 1) is terminated by a delimiter, then the next field begins immediately after the delimiter, as shown in Figure 10-3.
Figure 10-3 Relative Positioning After a Delimited Field
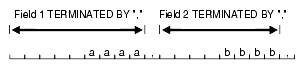
When a field is specified with both enclosure delimiters and a termination delimiter, then the next field starts after the termination delimiter, as shown in Figure 10-4. If a nonwhitespace character is found after the enclosure delimiter, but before the terminator, then SQL*Loader generates an error.
Figure 10-4 Relative Positioning After Enclosure Delimiters
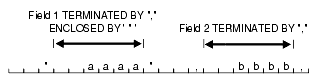
In Figure 10-4, both fields are stored with leading whitespace. Fields do not include leading whitespace in the following cases:
When the previous field is terminated by whitespace, and no starting position is specified for the current field
When optional enclosure delimiters are specified for the field, and the enclosure delimiters are not present
These cases are illustrated in the following sections.
If the previous field is TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE, then all whitespace after the field acts as the delimiter. The next field starts at the next nonwhitespace character. Figure 10-5 illustrates this case.
Figure 10-5 Fields Terminated by Whitespace
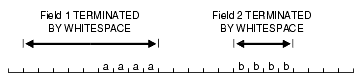
This situation occurs when the previous field is explicitly specified with the TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE clause, as shown in the example. It also occurs when you use the global FIELDS TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE clause.
Leading whitespace is also removed from a field when optional enclosure delimiters are specified but not present.
Whenever optional enclosure delimiters are specified, SQL*Loader scans forward, looking for the first enclosure delimiter. If an enclosure delimiter is not found, SQL*Loader skips over whitespace, eliminating it from the field. The first nonwhitespace character signals the start of the field. This situation is shown in Field 2 in Figure 10-6. (In Field 1 the whitespace is included because SQL*Loader found enclosure delimiters for the field.)
Figure 10-6 Fields Terminated by Optional Enclosure Delimiters

Unlike the case when the previous field is TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE, this specification removes leading whitespace even when a starting position is specified for the current field.
Note:
If enclosure delimiters are present, leading whitespace after the initial enclosure delimiter is kept, but whitespace before this delimiter is discarded. See the first quotation mark in Field 1, Figure 10-6.Trailing whitespace is always trimmed from character-data fields that have a predetermined size. These are the only fields for which trailing whitespace is always trimmed.
If a field is enclosed, or terminated and enclosed, like the first field shown in Figure 10-6, then any whitespace outside the enclosure delimiters is not part of the field. Any whitespace between the enclosure delimiters belongs to the field, whether it is leading or trailing whitespace.
To prevent whitespace trimming in all CHAR, DATE, and numeric EXTERNAL fields, you specify PRESERVE BLANKS as part of the LOAD statement in the control file. However, there may be times when you do not want to preserve blanks for all CHAR, DATE, and numeric EXTERNAL fields. Therefore, SQL*Loader also enables you to specify PRESERVE BLANKS as part of the datatype specification for individual fields, rather than specifying it globally as part of the LOAD statement.
In the following example, assume that PRESERVE BLANKS has not been specified as part of the LOAD statement, but you want the c1 field to default to zero when blanks are present. You can achieve this by specifying PRESERVE BLANKS on the individual field. Only that field is affected; blanks will still be removed on other fields.
c1 INTEGER EXTERNAL(10) PRESERVE BLANKS DEFAULTIF c1=BLANKS
In this example, if PRESERVE BLANKS were not specified for the field, it would result in the field being improperly loaded as NULL (instead of as 0).
There may be times when you want to specify PRESERVE BLANKS as an option to the LOAD statement and have it apply to most CHAR, DATE, and numeric EXTERNAL fields. You can override it for an individual field by specifying NO PRESERVE BLANKS as part of the datatype specification for that field, as follows:
c1 INTEGER EXTERNAL(10) NO PRESERVE BLANKS
The PRESERVE BLANKS option is affected by the presence of the delimiter clauses, as follows:
Leading whitespace is left intact when optional enclosure delimiters are not present
Trailing whitespace is left intact when fields are specified with a predetermined size
For example, consider the following field, where underscores represent blanks:
__aa__,
Suppose this field is loaded with the following delimiter clause:
TERMINATED BY ',' OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY '"'
In such a case, if PRESERVE BLANKS is specified, then both the leading whitespace and the trailing whitespace are retained. If PRESERVE BLANKS is not specified, then the leading whitespace is trimmed.
Now suppose the field is loaded with the following clause:
TERMINATED BY WHITESPACE
In such a case, if PRESERVE BLANKS is specified, it does not retain the space at the beginning of the next field, unless that field is specified with a POSITION clause that includes some of the whitespace. Otherwise, SQL*Loader scans past all whitespace at the end of the previous field until it finds a nonblank, nontab character.
See Also:
Trimming WhitespaceA wide variety of SQL operators can be applied to field data with the SQL string. This string can contain any combination of SQL expressions that are recognized by the Oracle database as valid for the VALUES clause of an INSERT statement. In general, any SQL function that returns a single value that is compatible with the target column's datatype can be used. SQL strings can be applied to simple scalar column types and also to user-defined complex types such as column object and collections. See the information about expressions in the Oracle Database SQL Language Reference.
The column name and the name of the column in a SQL string bind variable must, with the interpretation of SQL identifier rules, correspond to the same column. But the two names do not necessarily have to be written exactly the same way, as in the following example of specifying the control file:
LOAD DATA INFILE * APPEND INTO TABLE XXX ( "Last" position(1:7) char "UPPER(:\"Last\")" first position(8:15) char "UPPER(:first || :FIRST || :\"FIRST\")" ) BEGINDATA Phil Grant Jason Taylor
Note the following about the preceding example:
If, during table creation, a column identifier is declared using double quotation marks because it contains lowercase and/or special-case letters (as in the column named "Last" above), then the column name in the bind variable must exactly match the column name used in the CREATE TABLE statement.
If a column identifier is declared without double quotation marks during table creation (as in the column name first above), then because first, FIRST, and "FIRST" all point to the same column, any of these written formats in a SQL string bind variable would be acceptable.
The following requirements and restrictions apply when you are using SQL strings:
If your control file specifies character input that has an associated SQL string, SQL*Loader makes no attempt to modify the data. This is because SQL*Loader assumes that character input data that is modified using a SQL operator will yield results that are correct for database insertion.
The SQL string appears after any other specifications for a given column.
The SQL string must be enclosed in double quotation marks.
To enclose a column name in quotation marks within a SQL string, you must use escape characters.
In the preceding example, Last is enclosed in double quotation marks to preserve the mixed case, and the double quotation marks necessitate the use of the backslash (escape) character.
If a SQL string contains a column name that references a column object attribute, then the full object attribute name must be used in the bind variable. Each attribute name in the full name is an individual identifier. Each identifier is subject to the SQL identifier quoting rules, independent of the other identifiers in the full name. For example, suppose you have a column object named CHILD with an attribute name of "HEIGHT_%TILE". (Note that the attribute name is in double quotation marks.) To use the full object attribute name in a bind variable, any one of the following formats would work:
:CHILD.\"HEIGHT_%TILE\"
:child.\"HEIGHT_%TILE\"
Enclosing the full name (:\"CHILD.HEIGHT_%TILE\") generates a warning message that the quoting rule on an object attribute name used in a bind variable has changed. The warning is only to suggest that the bind variable be written correctly; it will not cause the load to abort. The quoting rule was changed because enclosing the full name in quotation marks would have caused SQL to interpret the name as one identifier rather than a full column object attribute name consisting of multiple identifiers.
The SQL string is evaluated after any NULLIF or DEFAULTIF clauses, but before a date mask.
If the Oracle database does not recognize the string, the load terminates in error. If the string is recognized, but causes a database error, the row that caused the error is rejected.
SQL strings are required when using the EXPRESSION parameter in a field specification.
The SQL string cannot reference fields that are loaded using OID, SID, REF, or BFILE. Also, it cannot reference filler fields.
In direct path mode, a SQL string cannot reference a VARRAY, nested table, or LOB column. This also includes a VARRAY, nested table, or LOB column that is an attribute of a column object.
The SQL string cannot be used on RECNUM, SEQUENCE, CONSTANT, or SYSDATE fields.
The SQL string cannot be used on LOBs, BFILEs, XML columns, or a file that is an element of a collection.
In direct path mode, the final result that is returned after evaluation of the expression in the SQL string must be a scalar datatype. That is, the expression may not return an object or collection datatype when performing a direct path load.
To refer to fields in the record, precede the field name with a colon (:). Field values from the current record are substituted. A field name preceded by a colon (:) in a SQL string is also referred to as a bind variable. Note that bind variables enclosed in single quotation marks are treated as text literals, not as bind variables.
The following example illustrates how a reference is made to both the current field and to other fields in the control file. It also illustrates how enclosing bind variables in single quotation marks causes them to be treated as text literals. Be sure to read the notes following this example to help you fully understand the concepts it illustrates.
LOAD DATA
INFILE *
APPEND INTO TABLE YYY
(
field1 POSITION(1:6) CHAR "LOWER(:field1)"
field2 CHAR TERMINATED BY ','
NULLIF ((1) = 'a') DEFAULTIF ((1)= 'b')
"RTRIM(:field2)"
field3 CHAR(7) "TRANSLATE(:field3, ':field1', ':1')",
field4 COLUMN OBJECT
(
attr1 CHAR(3) "UPPER(:field4.attr3)",
attr2 CHAR(2),
attr3 CHAR(3) ":field4.attr1 + 1"
),
field5 EXPRESSION "MYFUNC(:FIELD4, SYSDATE)"
)
BEGINDATA
ABCDEF1234511 ,:field1500YYabc
abcDEF67890 ,:field2600ZZghl
Notes About This Example:
In the following line, :field1 is not enclosed in single quotation marks and is therefore interpreted as a bind variable:
field1 POSITION(1:6) CHAR "LOWER(:field1)"
In the following line, ':field1' and ':1' are enclosed in single quotation marks and are therefore treated as text literals and passed unchanged to the TRANSLATE function:
field3 CHAR(7) "TRANSLATE(:field3, ':field1', ':1')"
For more information about the use of quotation marks inside quoted strings, see Specifying File Names and Object Names.
For each input record read, the value of the field referenced by the bind variable will be substituted for the bind variable. For example, the value ABCDEF in the first record is mapped to the first field :field1. This value is then passed as an argument to the LOWER function.
A bind variable in a SQL string need not reference the current field. In the preceding example, the bind variable in the SQL string for field FIELD4.ATTR1 references field FIELD4.ATTR3. The field FIELD4.ATTR1 is still mapped to the values 500 and 600 in the input records, but the final values stored in its corresponding columns are ABC and GHL.
field5 is not mapped to any field in the input record. The value that is stored in the target column is the result of executing the MYFUNC PL/SQL function, which takes two arguments. The use of the EXPRESSION parameter requires that a SQL string be used to compute the final value of the column because no input data is mapped to the field.
SQL operators are commonly used for the following tasks:
Loading external data with an implied decimal point:
field1 POSITION(1:9) DECIMAL EXTERNAL(8) ":field1/1000"
Truncating fields that could be too long:
field1 CHAR TERMINATED BY "," "SUBSTR(:field1, 1, 10)"
Multiple operators can also be combined, as in the following examples:
field1 POSITION(*+3) INTEGER EXTERNAL
"TRUNC(RPAD(:field1,6,'0'), -2)"
field1 POSITION(1:8) INTEGER EXTERNAL
"TRANSLATE(RTRIM(:field1),'N/A', '0')"
field1 CHAR(10)
"NVL( LTRIM(RTRIM(:field1)), 'unknown' )"
When a SQL string is used with a date mask, the date mask is evaluated after the SQL string. Consider a field specified as follows:
field1 DATE "dd-mon-yy" "RTRIM(:field1)"
SQL*Loader internally generates and inserts the following:
TO_DATE(RTRIM(<field1_value>), 'dd-mon-yyyy')
Note that when using the DATE field datatype, it is not possible to have a SQL string without a date mask. This is because SQL*Loader assumes that the first quoted string it finds after the DATE parameter is a date mask. For instance, the following field specification would result in an error (ORA-01821: date format not recognized):
field1 DATE "RTRIM(TO_DATE(:field1, 'dd-mon-yyyy'))"
In this case, a simple workaround is to use the CHAR datatype.
It is possible to use the TO_CHAR operator to store formatted dates and numbers. For example:
field1 ... "TO_CHAR(:field1, '$09999.99')"
This example could store numeric input data in formatted form, where field1 is a character column in the database. This field would be stored with the formatting characters (dollar sign, period, and so on) already in place.
You have even more flexibility, however, if you store such values as numeric quantities or dates. You can then apply arithmetic functions to the values in the database, and still select formatted values for your reports.
An example of using the SQL string to load data from a formatted report is shown in case study 7, Extracting Data from a Formatted Report. (See SQL*Loader Case Studies for information on how to access case studies.)
The ANYDATA database type can contain data of different types. To load the ANYDATA type using SQL*loader, it must be explicitly constructed by using a function call. The function is invoked using support for SQL strings as has been described in this section.
For example, suppose you have a table with a column named miscellaneous which is of type ANYDATA. You could load the column by doing the following, which would create an ANYDATA type containing a number.
LOAD DATA INFILE * APPEND INTO TABLE ORDERS ( miscellaneous CHAR "SYS.ANYDATA.CONVERTNUMBER(:miscellaneous)" ) BEGINDATA 4
There can also be more complex situations in which you create an ANYDATA type that contains a different type depending upon the values in the record. To do this, you could write your own PL/SQL function that would determine what type should be in the ANYDATA type, based on the value in the record, and then call the appropriate ANYDATA.Convert*() function to create it.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about the ANYDATA database type
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for more information about using ANYDATA with PL/SQL
The parameters described in this section provide the means for SQL*Loader to generate the data stored in the database record, rather than reading it from a datafile. The following parameters are described:
It is possible to use SQL*Loader to generate data by specifying only sequences, record numbers, system dates, constants, and SQL string expressions as field specifications.
SQL*Loader inserts as many records as are specified by the LOAD statement. The SKIP parameter is not permitted in this situation.
SQL*Loader is optimized for this case. Whenever SQL*Loader detects that only generated specifications are used, it ignores any specified datafile—no read I/O is performed.
In addition, no memory is required for a bind array. If there are any WHEN clauses in the control file, SQL*Loader assumes that data evaluation is necessary, and input records are read.
This is the simplest form of generated data. It does not vary during the load or between loads.
To set a column to a constant value, use CONSTANT followed by a value:
CONSTANT value
CONSTANT data is interpreted by SQL*Loader as character input. It is converted, as necessary, to the database column type.
You may enclose the value within quotation marks, and you must do so if it contains whitespace or reserved words. Be sure to specify a legal value for the target column. If the value is bad, every record is rejected.
Numeric values larger than 2^32 - 1 (4,294,967,295) must be enclosed in quotation marks.
Use the EXPRESSION parameter after a column name to set that column to the value returned by a SQL operator or specially written PL/SQL function. The operator or function is indicated in a SQL string that follows the EXPRESSION parameter. Any arbitrary expression may be used in this context provided that any parameters required for the operator or function are correctly specified and that the result returned by the operator or function is compatible with the datatype of the column being loaded.
The combination of column name, EXPRESSION parameter, and a SQL string is a complete field specification:
column_name EXPRESSION "SQL string"
In both conventional path mode and direct path mode, the EXPRESSION parameter can be used to load the default value into column_name:
column_name EXPRESSION "DEFAULT"
Use the RECNUM parameter after a column name to set that column to the number of the logical record from which that record was loaded. Records are counted sequentially from the beginning of the first datafile, starting with record 1. RECNUM is incremented as each logical record is assembled. Thus it increments for records that are discarded, skipped, rejected, or loaded. If you use the option SKIP=10, the first record loaded has a RECNUM of 11.
The combination of column name and RECNUM is a complete column specification.
column_name RECNUM
A column specified with SYSDATE gets the current system date, as defined by the SQL language SYSDATE parameter. See the section on the DATE datatype in Oracle Database SQL Language Reference.
The combination of column name and the SYSDATE parameter is a complete column specification.
column_name SYSDATE
The database column must be of type CHAR or DATE. If the column is of type CHAR, then the date is loaded in the form 'dd-mon-yy.' After the load, it can be loaded only in that form. If the system date is loaded into a DATE column, then it can be loaded in a variety of forms that include the time and the date.
A new system date/time is used for each array of records inserted in a conventional path load and for each block of records loaded during a direct path load.
The SEQUENCE parameter ensures a unique value for a particular column. SEQUENCE increments for each record that is loaded or rejected. It does not increment for records that are discarded or skipped.
The combination of column name and the SEQUENCE parameter is a complete column specification.
Table 10-6 describes the parameters used for column specification.
Table 10-6 Parameters Used for Column Specification
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The name of the column in the database to which to assign the sequence. |
|
|
Use the |
|
|
The sequence starts with the number of records already in the table plus the increment. |
|
|
The sequence starts with the current maximum value for the column plus the increment. |
|
|
Specifies the specific sequence number to begin with. |
|
|
The value that the sequence number is to increment after a record is loaded or rejected. This is optional. The default is 1. |
If a record is rejected (that is, it has a format error or causes an Oracle error), the generated sequence numbers are not reshuffled to mask this. If four rows are assigned sequence numbers 10, 12, 14, and 16 in a particular column, and the row with 12 is rejected, the three rows inserted are numbered 10, 14, and 16, not 10, 12, and 14. This allows the sequence of inserts to be preserved despite data errors. When you correct the rejected data and reinsert it, you can manually set the columns to agree with the sequence.
Case study 3, Loading a Delimited Free-Format File, provides an example of using the SEQUENCE parameter. (See SQL*Loader Case Studies for information on how to access case studies.)
Because a unique sequence number is generated for each logical input record, rather than for each table insert, the same sequence number can be used when inserting data into multiple tables. This is frequently useful.
Sometimes, however, you might want to generate different sequence numbers for each INTO TABLE clause. For example, your data format might define three logical records in every input record. In that case, you can use three INTO TABLE clauses, each of which inserts a different part of the record into the same table. When you use SEQUENCE(MAX), SQL*Loader will use the maximum from each table, which can lead to inconsistencies in sequence numbers.
To generate sequence numbers for these records, you must generate unique numbers for each of the three inserts. Use the number of table-inserts per record as the sequence increment, and start the sequence numbers for each insert with successive numbers.
Suppose you want to load the following department names into the dept table. Each input record contains three department names, and you want to generate the department numbers automatically.
Accounting Personnel Manufacturing Shipping Purchasing Maintenance ...
You could use the following control file entries to generate unique department numbers:
INTO TABLE dept (deptno SEQUENCE(1, 3), dname POSITION(1:14) CHAR) INTO TABLE dept (deptno SEQUENCE(2, 3), dname POSITION(16:29) CHAR) INTO TABLE dept (deptno SEQUENCE(3, 3), dname POSITION(31:44) CHAR)
The first INTO TABLE clause generates department number 1, the second number 2, and the third number 3. They all use 3 as the sequence increment (the number of department names in each record). This control file loads Accounting as department number 1, Personnel as 2, and Manufacturing as 3.
The sequence numbers are then incremented for the next record, so Shipping loads as 4, Purchasing as 5, and so on.