| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-05 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-05 |
|
|
View PDF |
The assignment statement sets the value of a variable, field, parameter, or element.
Topics:
Syntax
assignment_statement ::=
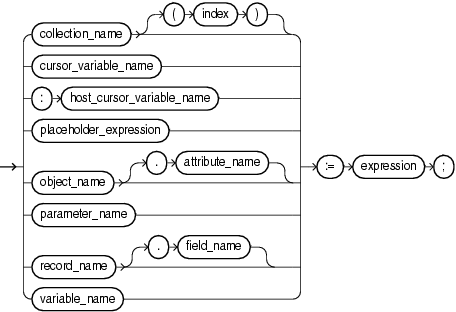
See expression ::=.
placeholder_expression ::=
Semantics
collection_name
The name of a collection. For information about collections, see "Collection".
index
A numeric expression whose value has the data type PLS_INTEGER or a data type that can be implicitly converted to PLS_INTEGER (see Table 3-10, "Possible Implicit PL/SQL Data Type Conversions").
Specify index to assign the value of expression to a specific element of collection_name.
Omit index to assign the value of expression to all elements of collection_name simultaneously; that is, to assign one collection to another. You can assign one collection to another only if the collections have the same data type (not the same element type).
cursor_variable_name
The name of a cursor variable. For information about cursor variables, see "Cursor Variable".
host_cursor_variable_name
The name of a cursor variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind argument. Do not put space between the colon (:) and host_cursor_variable_name.
The data type of a host cursor variable is compatible with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable.
object_name
The name of an instance of an ADT. For general information about ADTs, see "Abstract Data Types".
attribute_name
The name of an attribute of object_name.
parameter_name
The name of a formal OUT or IN OUT parameter of the subprogram in which the assignment statement appears. For information about formal parameters, see "Parameter".
record_name
The name of a record. For information about records, see "Record".
field_name
The name of a field in record_name.
Specify field_name to assign the value of expression to a specific field of record_name.
Omit field_name to assign the value of expression to all fields of record_name simultaneously; that is, to assign one record to another. You can assign one record to another only if their declarations refer to the same table or cursor.
variable_name
The name of a PL/SQL variable. For information about variables, see "Variable".
expression
The expression whose value is to be assigned to the target (the item to the left of the assignment operator) when the assignment statement runs.
The value of expression must have a data type that is compatible with the data type of the target (see "PL/SQL Data Type Conversion").
If the target is a variable defined as NOT NULL, the value of expression cannot be NULL. If the target is a cursor variable, the value of expression must also be a cursor variable.
For general information about expressions, see "Expression".
placeholder_expression
host_variable]
The name of a variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind argument. Do not put space between the colon (:) and host_variable_name.
indicator_variable
The name of an indicator variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind argument. An indicator variable indicates the value or condition of its associated host variable (for example, in the Oracle Precompiler environment, an indicator variable can a detect null or truncated value in an output host variable). Do not put space between host_variable_name and the colon (:) or between the colon and indicator_name. This is correct:
:host_variable_name:indicator_name
Examples
Example 2-25, "Assigning Values to Variables with Assignment Statement"
Example 3-4, "Assigning a Literal Value to a TIMESTAMP Variable"
Example 5-17, "Data Type Compatibility for Collection Assignment"
Related Topics
In this chapter:
In other chapters: